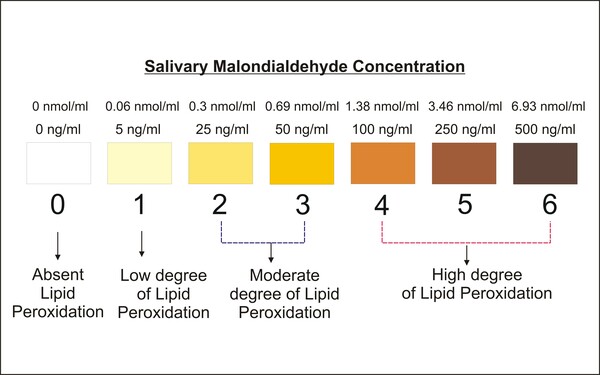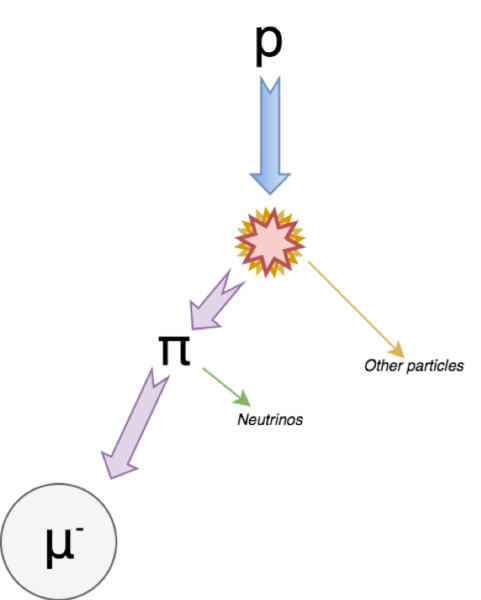
Muons, one of the fundamental elementary particles, originate from the collision of cosmic rays with atmospheric particles and are also generated in particle accelerator collisions. In this study, Samson et al analyze the factors that influence muon flux and lifetime using Cosmic Ray Muon Detectors (CRMDs). Overall, the study suggests that water can be used to decrease muon flux and that scintillator orientation is a potential determinant of the volume of data collected in muon decay studies.
Read More...