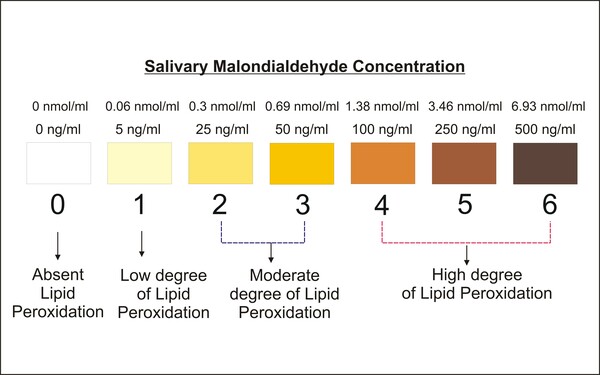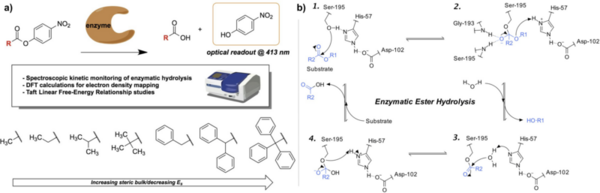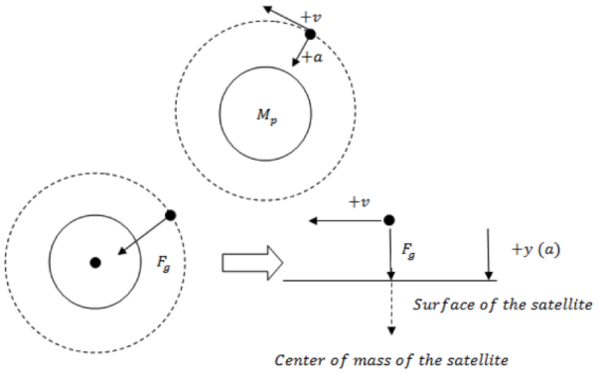
Life requires many things, including a hospitable temperature, elements, and energy. Here the authors utilize Newton's laws of physics and information relating a star's luminosity and temperature to determine the minimum and maximum masses and luminosities of planets and stars that would support life as we know it. This work can be used to determine the likelihood of a planet being able to support life based on attributes we can measure from here on Earth.
Read More...