In this article, the authors use datasets of professional and youth soccer players' movements to map and statistically compare them. Analysis compared movements that led to goals or no-goals and differences between pros and youth.
Read More...Understanding the movement of professional and high school soccer players

In this article, the authors use datasets of professional and youth soccer players' movements to map and statistically compare them. Analysis compared movements that led to goals or no-goals and differences between pros and youth.
Read More...Wind Resistance and Automobile Shapes

Energy efficiency is becoming more important as we struggle to find better, more sustainable energy sources to power our planet; the car industry is no exception. In this article, the authors examine the effect of shape on automobile aerodynamics By finding the shape that makes cars less resistant to wind, and therefore more energy efficient, can help the automobile industry make better, more eco-friendly cars that are also cheaper to operate.
Read More...Using explainable artificial intelligence to identify patient-specific breast cancer subtypes
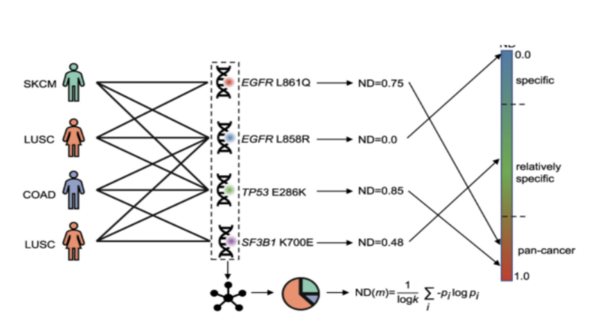
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women, with approximately 300,000 diagnosed with breast cancer in 2023. It ranks second in cancer-related deaths for women, after lung cancer with nearly 50,000 deaths. Scientists have identified important genetic mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 that lead to the development of breast cancer, but previous studies were limited as they focused on specific populations. To overcome limitations, diverse populations and powerful statistical methods like genome-wide association studies and whole-genome sequencing are needed. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) can be used in oncology and breast cancer research to overcome these limitations of specificity as it can analyze datasets of diagnosed patients by providing interpretable explanations for identified patterns and predictions. This project aims to achieve technological and medicinal goals by using advanced algorithms to identify breast cancer subtypes for faster diagnoses. Multiple methods were utilized to develop an efficient algorithm. We hypothesized that an XAI approach would be best as it can assign scores to genes, specifically with a 90% success rate. To test that, we ran multiple trials utilizing XAI methods through the identification of class-specific and patient-specific key genes. We found that the study demonstrated a pipeline that combines multiple XAI techniques to identify potential biomarker genes for breast cancer with a 95% success rate.
Read More...Artificial Intelligence Networks Towards Learning Without Forgetting

In their paper, Kreiman et al. examined what it takes for an artificial neural network to be able to perform well on a new task without forgetting its previous knowledge. By comparing methods that stop task forgetting, they found that longer training times and maintenance of the most important connections in a particular task while training on a new one helped the neural network maintain its performance on both tasks. The authors hope that this proof-of-principle research will someday contribute to artificial intelligence that better mimics natural human intelligence.
Read More...How planarians are affected by mouthwash and cough syrup

Since cough syrup and mouthwash are commonly used items and often end up flushed down the drain or toilet, they can eventually find their way into into freshwater waterways which can be harmful to many marine organisms, such as planarians (aquatic flatworms). To investigate the effects of these substances on planarians, the authors considered different concentrations of Listerine mouthwash and Robitussin syrup along with their active ingredients. By using a behavioral assay, they identified that the active ingredients of cough syrup detrimentally affect planarian behavior. They suggest that these findings could be used to guide disposal methods to lessen detrimental effects on aquatic life.
Read More...A Data-Centric Analysis of “Stop and Frisk” in New York City

The death of George Floyd has shed light on the disproportionate level of policing affecting non-Whites in the United States of America. To explore whether non-Whites were disproportionately targetted by New York City's "Stop and Frisk" policy, the authors analyze publicly available data on the practice between 2003-2019. Their results suggest African Americans were indeed more likely to be stopped by the police until 2012, after which there was some improvement.
Read More...The Effect of Lyrical and Instrumental Music on Reading Comprehension Tasks

Herring and Scott investigated how specific types of background music affected 8th and 9th graders' performance on a reading comprehension task. In the study, their results indicated that music with English lyrics led to lower reading comprehension scores, while foreign language and instrumental music was comparable to no music at all. The authors therefore recommend that teachers avoid playing English language music for students completing reading tasks in order to minimize distractions and improve work efficiency.
Read More...A new therapy against MDR bacteria by in silico virtual screening of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LpxC inhibitors
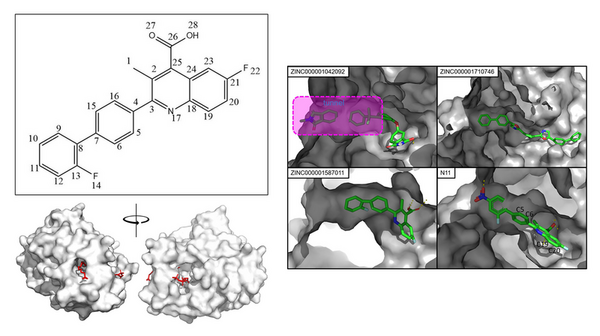
Here, seeking to address the growing threat of multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDR). the authors used in silico virtual screening to target MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa. They considered a key protein in its biosynthesis and virtually screened 20,000 candidates and 30 derivatives of brequinar. In the end, they identified a possible candidate with the highest degree of potential to inhibit the pathogen's lipid A synthesis.
Read More...Examining the Accuracy of DNA Parentage Tests Using Computer Simulations and Known Pedigrees

How accurate are DNA parentage tests? In this study, the authors hypothesized that current parentage tests are reliable if the analysis involves only one or a few families of yellow perch fish Perca flavescens. Their results suggest that DNA parentage tests are reliable as long as the right methods are used, since these tests involve only one family in most cases, and that the results from parentage analyses of large populations can only be used as a reference.
Read More...A Novel Model to Predict a Book's Success in the New York Times Best Sellers List

In this article, the authors identify the characteristics that make a book a best-seller. Knowing what, besides content, predicts the success of a book can help publishers maximize the success of their print products.
Read More...Search articles by title, author name, or tags