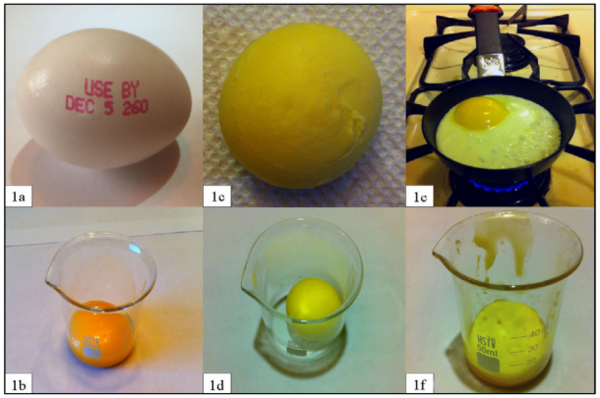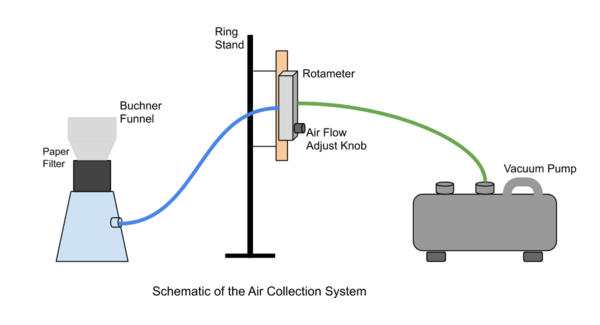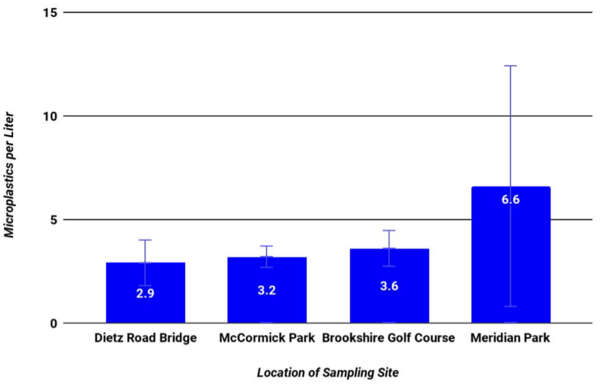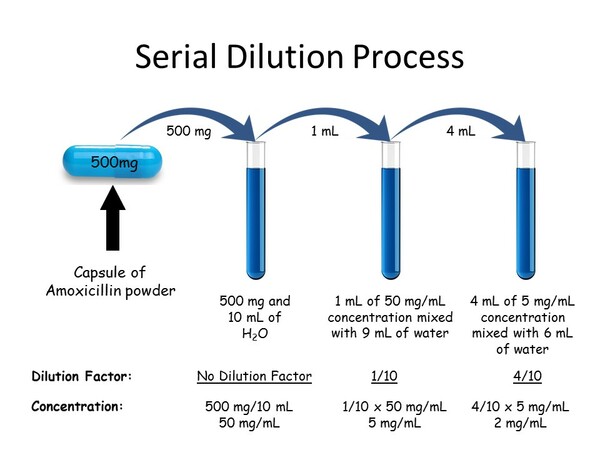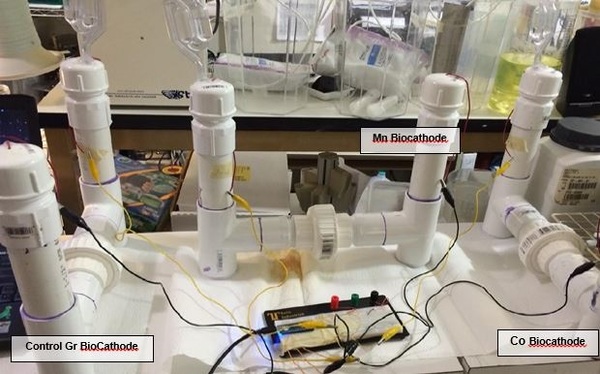
A microbial fuel cell is a system to produce electric current using biochemical products from bacteria. In this project authors operated a microbial fuel cell in which glucose was oxidized by Shewanella oneidensis in the anodic compartment. We compared the power output from biomineralized manganese or cobalt oxides, reduced by Leptothrix cholodnii in the cathodic compartment.
Read More...