
In this study, the authors tested whether the compound bromelain extracted from pineapples could protect skin cells from UV damage.
Read More...Protective effect of bromelain and pineapple extracts on UV-induced damage in human skin cells

In this study, the authors tested whether the compound bromelain extracted from pineapples could protect skin cells from UV damage.
Read More...The Non-Thermal Effect of UV-B Irradiation on Onion Growth
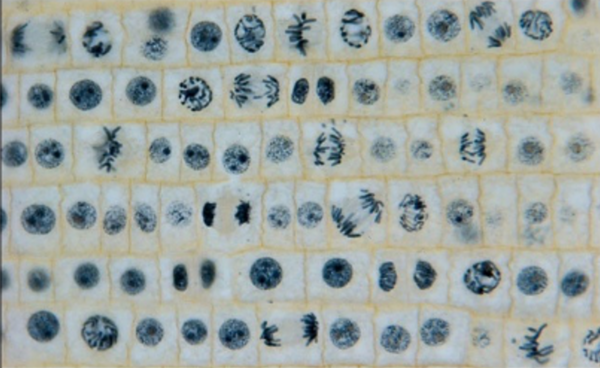
UV-B radiation due to the depletion of ozone threatens plant life, potentially damaging ecosystems and dismantling food webs. Here, the impact of UV-B radiation on the physiology and morphology of Allum cepa, the common onion, was assessed. Mitosis vitality decreased, suggesting UV-B damage can influence the plant’s physiology.
Read More...The role of xpa-1 and him-1 in UV protection of Caenorhabditis elegans
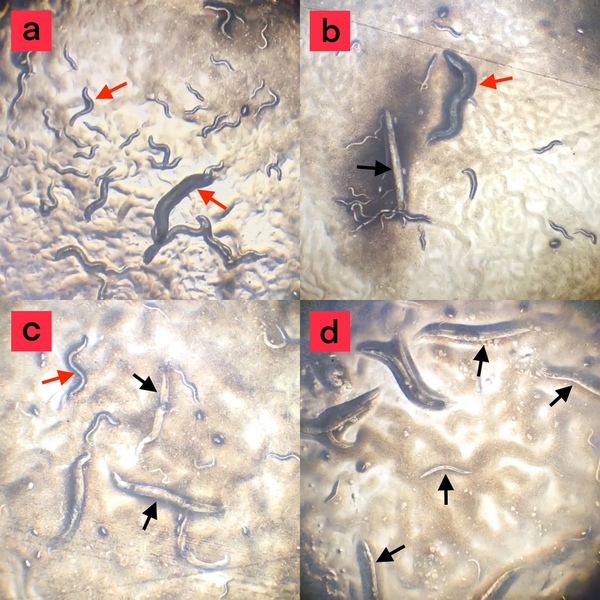
Caenorhabditis elegans xpa-1 and him-1 are orthologs of human XPA and human SMC1A, respectively. Mutations in the XPA are correlated with Xeroderma pigmentosum, a condition that induces hypersensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Alternatively, SMC1A mutations may lead to Cornelia de Lange Syndrome, a multi-organ disorder that makes patients more sensitive to UVinduced DNA damage. Both C. elegans genes have been found to be involved in protection against UV radiation, but their combined effects have not been tested when they are both knocked down. The authors hypothesized that because these genes are involved in separate pathways, the simultaneous knockdown of both of these genes using RNA interference (RNAi) in C. elegans will cause them to become more sensitive to UV radiation than either of them knocked down individually. UV protection was measured via the percent survival of C. elegans post 365 nm and 5.4x10-19 joules of UV radiation. The double xpa-1/him-1 RNAi knockdown showed a significantly reduced percent survival after 15 and 30 minutes of UV radiation relative to wild-type and xpa-1 and him-1 single knockdowns. These measurements were consistent with their hypothesis and demonstrated that xpa-1 and him-1 genes play distinct roles in resistance against UV stress in C. elegans. This result raises the possibility that the xpa-1/him-1 double knockdown could be useful as an animal model for studying the human disease Xeroderma pigmentosum and Cornelia de Lange Syndrome.
Read More...The Effects of Ultraviolet Light on Escherichia coli
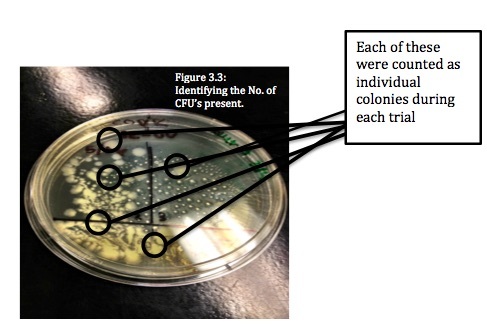
In this study E. coli bacteria was exposed to small UV lights currently used in school laboratories to see the effect on colony growth. This project explores how UV radiation methods could be applied in common households to inhibit bacterial growth.
Read More...The Effect of Ultraviolet Radiation and the Antioxidant Curcumin on the Longevity, Fertility, and Physical Structure of Drosophila melanogaster: Can We Defend Our DNA?
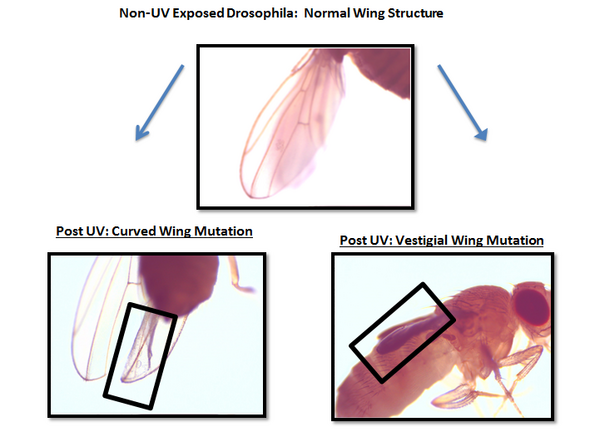
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is known to alter DNA structure and impair cellular function in all living organisms. In this study, Lateef et al examine the effects of UV radiation to determine whether antioxidant-enriched nutrition can combat the potential deleterious effects of UV radiation on Drosophila melanogaster. They found that UVB (320nm) radiation caused a 59% decrease in the Drosophila lifespan and mutagenic effects on flies' physical appearance, but did not significantly affect fertility. Curcumin significantly prolonged lifespan and enhanced fertility for both UV- and non-UV-exposed flies. The research demonstrates the positive potential of natural antioxidants as weapons against radiation-induced diseases including cancer.
Read More...QuitPuff: A Simple Method Using Saliva to Assess the Risk of Oral Pre-Cancerous Lesions and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chronic Smokers
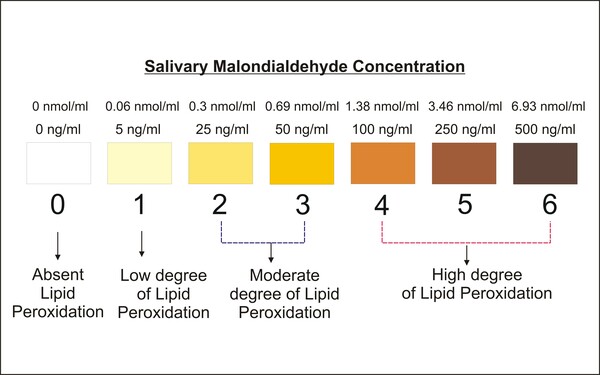
Smoking generates free radicals and reactive oxygen species which induce cell damage and lipid peroxidation. This is linked to the development of oral cancer in chronic smokers. The authors of this study developed Quitpuff, simple colorimetric test to measure the extent of lipid peroxidation in saliva samples. This test detected salivary lipid peroxidation with 96% accuracy in test subjects and could serve as an inexpensive, non-invasive test for smokers to measure degree of salivary lipid peroxidation and potential risk of oral cancer.
Read More...The effects of UV-C and ionizing radiation on the functions of Escherichia Coli

In this study, the authors send E. coli cultures to space via the Cubes in SpaceTM program to determine if ultraviolet C and ionizing radiation negatively affect bacterial growth.
Read More...The Effect of UV Treatment on the Degradation of Compostable Polylactic Acid
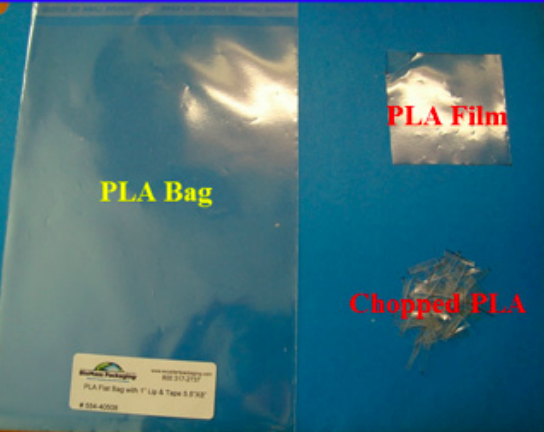

Polylactic acid (PLA) is a bio-based, compostable plastic that is comparable in cost to petroleum-based plastics. This study aims to evaluate the effects of UV treatment and mechanical chopping on the degradation of PLA. Based on their findings, the authors propose an alternative PLA degradation process that may be more time and energy efficient than current processes.
Read More...Analysis of the catalytic efficiency of spent coffee grounds and titanium dioxide using UV-Vis spectroscopy
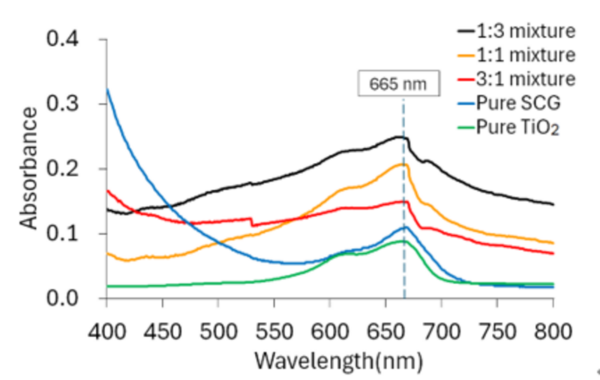
This paper looks at using spent coffee grounds as a partial substitute for titanium dioxide (TiO2) as a catalyst for chemical reactions. Using UV-Vis spectrophotometry, they found that adding the coffee grounds to TiO2 in a 3:1 ratio, there is still meaningful catalytic activity. This offers a cheaper solution than just using pure TiO2.
Read More...Ultraviolet exposure and thermal mass variation on surface temperature responses in building materials
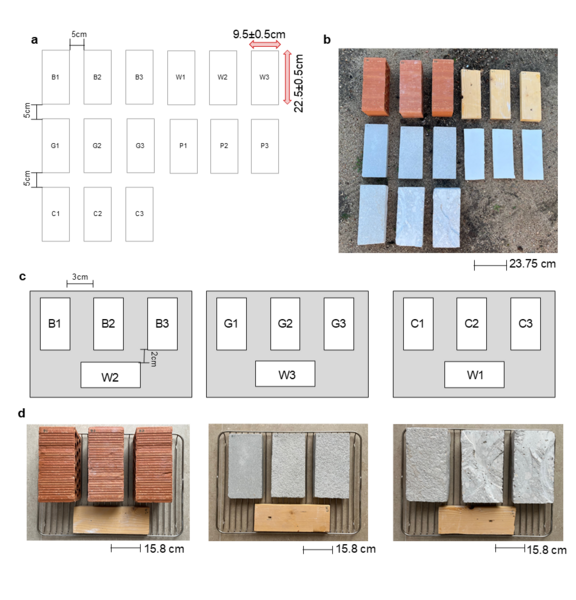
The authors studied the response of various construction materials to UV solar radiation and heat.
Read More...