Analysis of the catalytic efficiency of spent coffee grounds and titanium dioxide using UV-Vis spectroscopy
(1) Korean Minjok Leadership Academy
https://doi.org/10.59720/25-063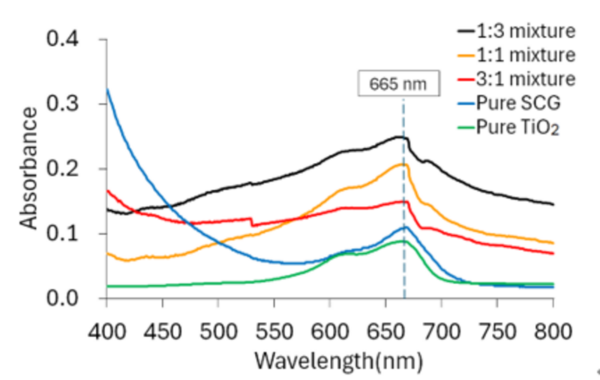
Catalysts serve an essential function in manufacturing consumables such as plastic and fuel. However, some of these are scarce, costly, unsustainable, or some combination of the above. Thus, we decided to examine whether an alternative substance that is more environmentally sustainable and economically viable than a conventional catalyst can serve as an effective catalyst support. We investigated the possibility of using spent coffee grounds, given their catalytic properties of conductivity and structural porosity, as a new eco-friendly alternative to titanium dioxide (TiO2), a catalyst widely used in heterogeneous catalysis. We hypothesized that a mixture of TiO2 and spent coffee grounds would show a level of chemical efficiency comparable to a catalyst comprised of pure TiO2. Toward this, we tested the catalytic performance of five mixtures of TiO2:spent coffee grounds (pure TiO2, spent coffee grounds, 1:3, 1:1, and 3:1) during the photocatalytic decomposition reaction of methylene blue using an Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometer. The TiO2:spent coffee grounds mixture at a 3:1 ratio showed the highest efficiency among the spent coffee grounds mixtures, comparable to that of pure TiO2 catalyst. This finding points to the potential of spent coffee grounds as a sustainable and affordable catalyst support for the costly and unsustainable TiO2.
This article has been tagged with: