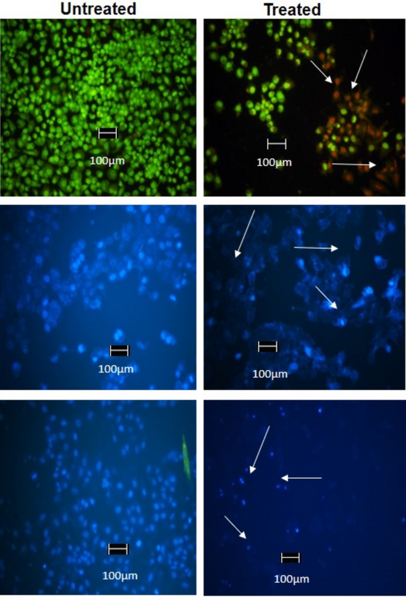
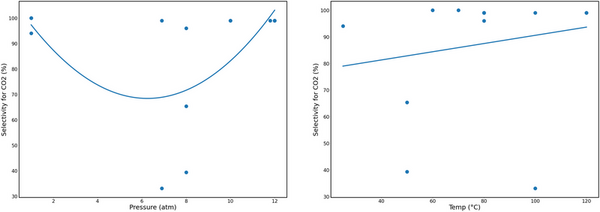
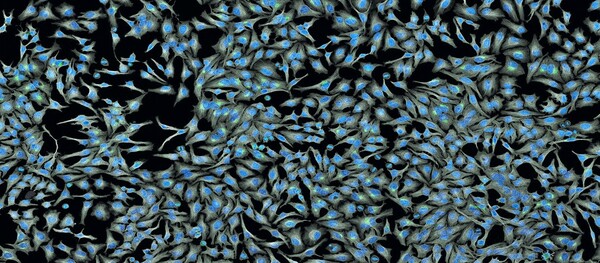
Mainstream cancer treatments, which include radiotherapy and chemotherapeutic drugs, are known to induce oxidative damage to healthy somatic cells due to the liberation of harmful free radicals. In order to avert this, physiological antioxidants must be complemented with external antioxidants. Here the authors performed a preliminary phytochemical screen to identify alkaloids, saponins, flavonoids, polyphenols, and tannins in all parts of the Amaranthus spinosus Linn. plant. This paper describes the preparation of this crude extract and assesses its antioxidant properties for potential use in complementary cancer treatment.
Read More...


.png)