
The authors investigate whether Western Bluebirds and other perching birds consume eggshells, as a source of calcium, at a greater rate before reproduction and during nest building when they are unable to store calcium.
Read More...Eggshell consumption in different reproductive stages and broods of the Western Bluebird, Sialia mexicana

The authors investigate whether Western Bluebirds and other perching birds consume eggshells, as a source of calcium, at a greater rate before reproduction and during nest building when they are unable to store calcium.
Read More...Using the COmplex PAthway SImulator, Stage Analysis, and Chemical Kinetics to Develop a Novel Solution to Lower Tau Concentrations in Alzheimer’s Disease
In this study, the authors ask whether a Tau immunotherapy treatment, Hsp70 protein treatment, or dual treatment approach of both the Tau imunotherapy treatment and Hsp70 protein treatment leads to a greater reduction in Tau protein concentration in Alzheimer's disease. Overall, they conclude that the effectiveness of the treatment ultimately relies on the stage of Alzheimer’s.
Read More...Bacterial Load Consistency Among Three Independent Water Distribution Systems
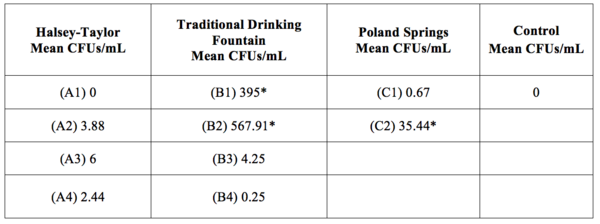
Clean drinking water is an essential component to maintaining public health. The authors of this study tested the bacterial load of water from three different disinfection and filtration systems in order to determine which system might be superior.
Read More...The Effect of Font Type on a School’s Ink Cost

Your choice of font can impact more than style. Here the authors demonstrate that font choice can affect the amount of ink a given print-out requires. The authors estimate that a switch to Garamond font, size 12, by all teachers in his school district would save almost $21,000 annually.
Read More...The impact of genetic, drug, and procedural factors on cardiac xenograft survival days in non-human primates
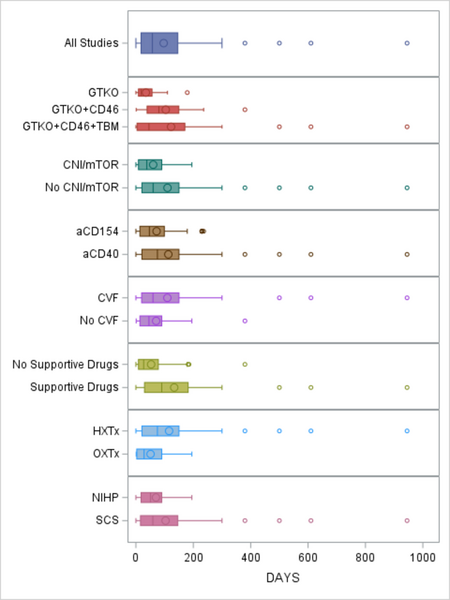
Due to a critical shortage of donor hearts, researchers are exploring cardiac xenotransplantation—transplanting animal hearts into humans—as a potential solution. This study synthesized nearly two decades of preclinical research to evaluate multiple factors affecting xenograft survival.
Read More...Exploring differences in men’s marijuana consumption and cigarette smoking by race and citizenship status
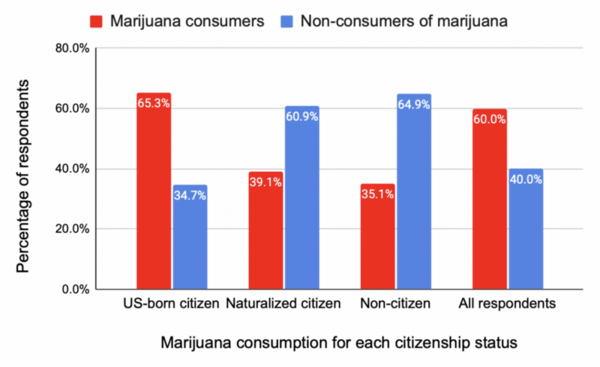
This study examined the relationship between citizenship status, racial background, and the use of marijuana and cigarettes among males in California using data from the 2017–2018 California Health Interview Survey. Findings indicated that non-citizens and naturalized citizens were less likely to use marijuana compared to US-born citizens, while Asian and Latino males were less likely to consume marijuana than White males. Additionally, various racial groups were more likely to smoke cigarettes compared to White males, suggesting that targeted health interventions based on citizenship status and race could be beneficial.
Read More...Evaluating the clinical applicability of neural networks for meningioma tumor segmentation on 3D MRI
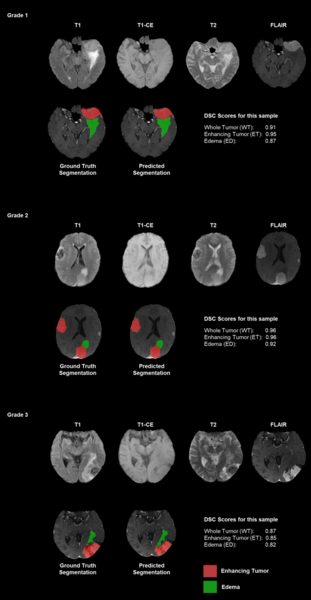
Authors emphasize the challenges of manual tumor segmentation and the potential of deep learning models to enhance accuracy by automatically analyzing MRI scans.
Read More...Statistical models for identifying missing and unclear signs of the Indus script
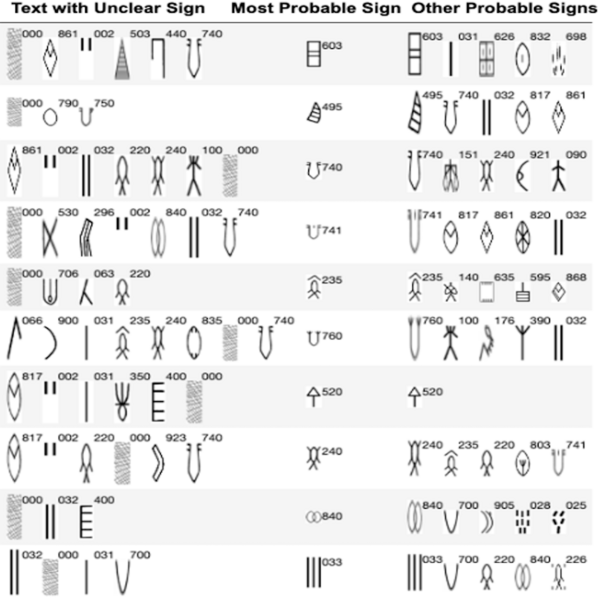
This study utilizes machine learning models to predict missing and unclear signs from the Indus script, a writing system from an ancient civilization in the Indian subcontinent.
Read More...Using CRISPR technology to inhibit the replication of human cytomegalovirus by deletion of a gene promoter
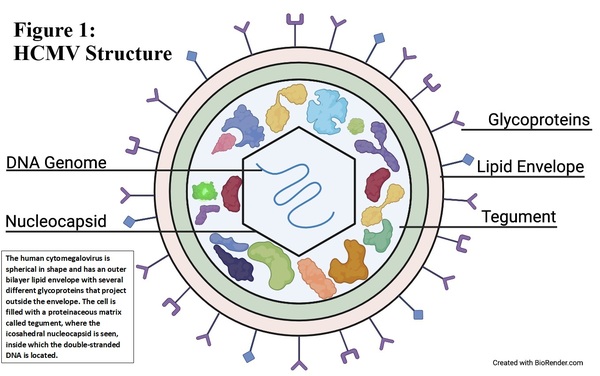
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) causes serious infections in immunocompromised patients and therapies to inhibit latent HCMV are not developed. Using CRISPR/Cas9, the authors were able to delete an important promoter region in HCMV.
Read More...Building a video classifier to improve the accuracy of depth-aware frame interpolation
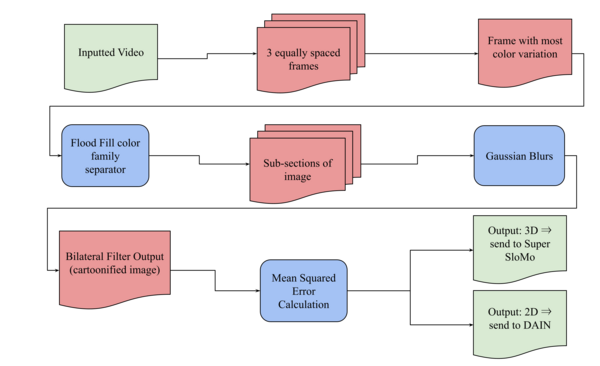
In this study, the authors share their work on improving the frame rate of videos to reduce data sent to users with both 2D and 3D footage. This work helps improve the experience for both types of footage!
Read More...