Singlet oxygen production analysis of reduced berberine analogs via NMR spectroscopy
(1) Los Altos High School, Los Altos, CA, (2) Amador Valley High School, Pleasanton, CA, (3) American High School, Fremont, CA, (4) Mission San Jose High School, Fremont, CA, (5) Carlmont High School, Belmont, CA, (6) BASIS Independent Silicon Valley, San Jose, CA, (7) Department of Chemistry, Biochemistry, & Physical Science, Aspiring Scholars Directed Research Program, Fremont, CA
https://doi.org/10.59720/22-078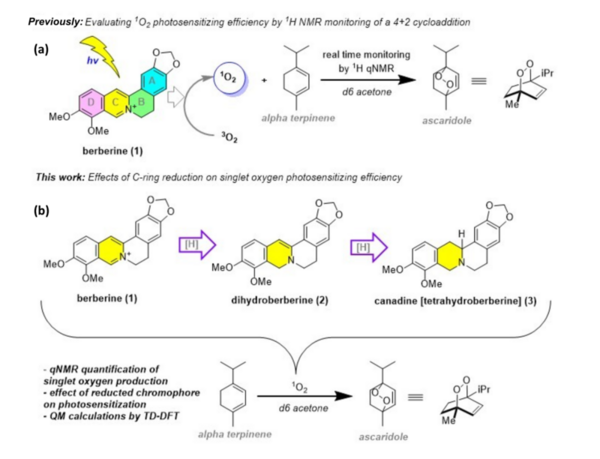
Berberine is a natural product isoquinoline alkaloid derived from plants of the genus Berberis. When exposed to photoirradiation, it produces singlet oxygen through photosensitization of triplet oxygen. The production of singlet oxygen grants Berberine its biological activity, as singlet oxygen forms an activated complex with DNA, oxidizing its guanine residues, halting cell replication and leading to cell death, which can be applied in photodynamic therapy of cancer. Through qNMR analysis of 1H NMR spectra gathered through kinetic experiments, we were able to track the generation of a product between singlet oxygen and alpha terpinene, allowing us to quantitatively measure the photosensitizing properties of our scaffolds. Moreover, we implemented 7,8-dihydroberberine and tetrahydroberberine, the reduced and over-reduced forms of berberine, respectively, in the studies to test the effect of the reduction of a compound on its singlet oxygen production.
This article has been tagged with: