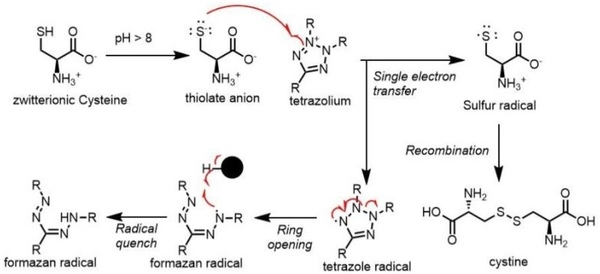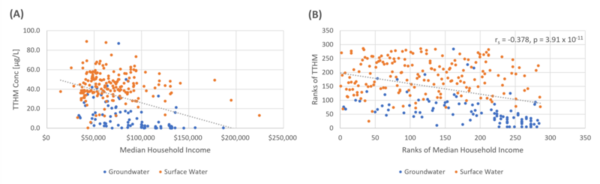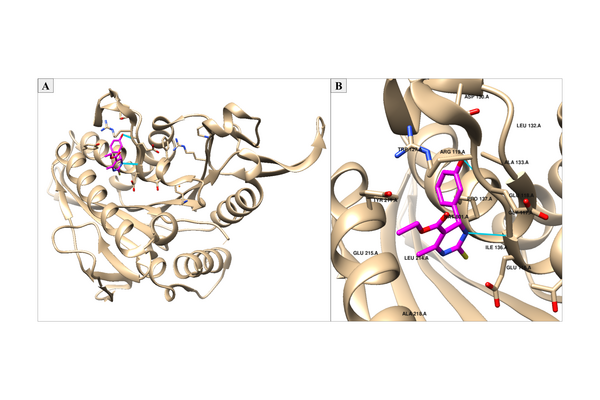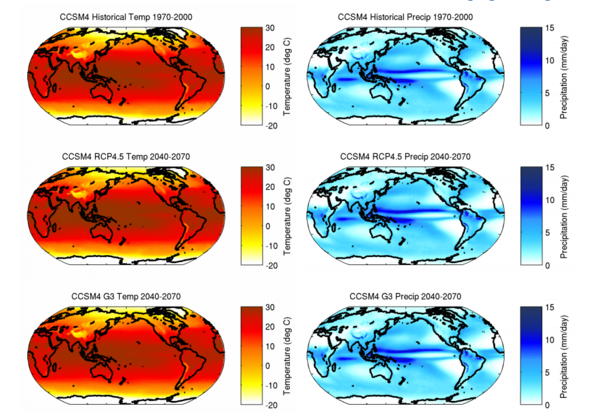
We are changing our environment with steadily increasing carbon dioxide emissions, but we might be able to help. The authors here use a computer program called Community Climate System Model 4 to predict the effects of spraying small particles into the atmosphere to reflect away some of the sun's rays. The software predicts that this could reduce the amount of energy the Earth's atmosphere absorbs and may limit but will not completely counteract our carbon dioxide production.
Read More...