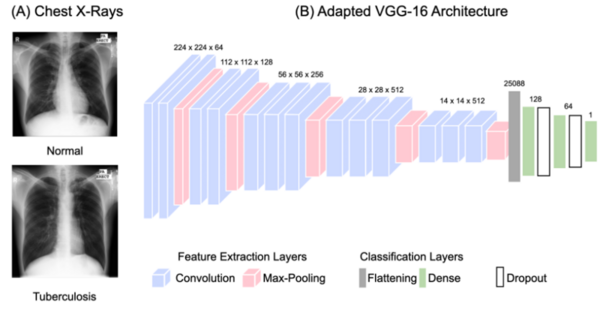
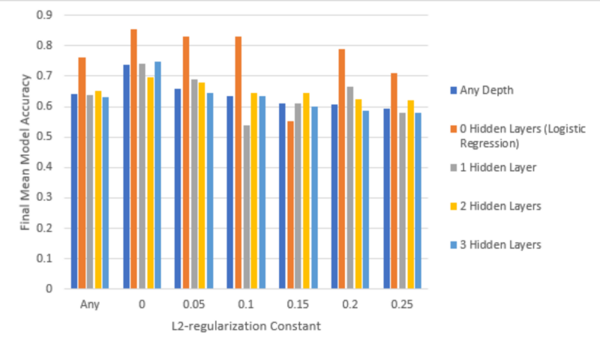
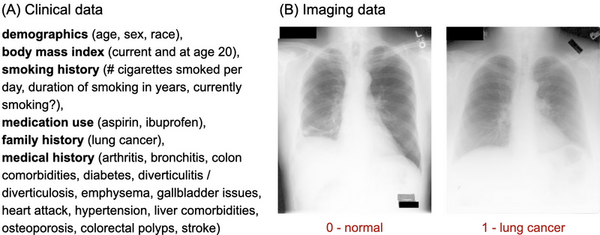
Here, recognizing the recognizing the growing threat of non-biodegradable plastic waste, the authors investigated the ability to use a modified enzyme identified in bacteria to decompose polyethylene terephthalate (PET). They used simulations to screen and identify an optimized enzyme based on machine learning models. Ultimately, they identified a potential mutant PETases capable of decomposing PET with improved thermal stability.
Read More...

.png)
.jpg)