Examining the prevalence of depression in coronary artery disease patients: a cross-sectional analysis
(1) The City School, E-11 Campus, (2) University of Waterloo
https://doi.org/10.59720/24-059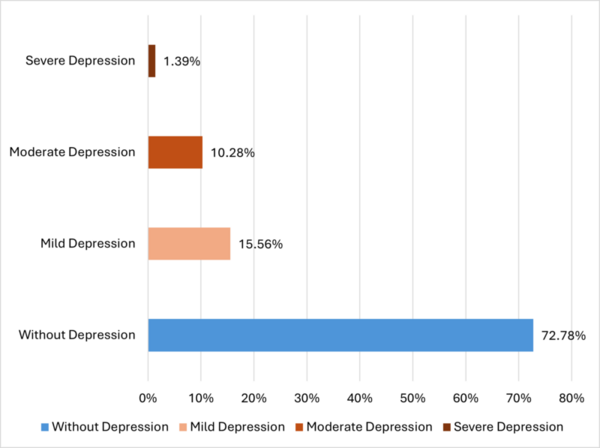
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the narrowing or blockage of heart arteries due to atherosclerosis, an accumulation of fatty materials on the inner linings of arteries. CAD, also called coronary heart disease or heart disease, includes both angina and myocardial infarction. Many research studies have indicated a connection between depression and a heightened risk of chronic diseases, encompassing CAD. Our hypothesis suggests an association between CAD and depression, indicating that CAD patients may be at risk of depressive symptoms. This research aimed to assess depression prevalence and associated risk factors in CAD patients at a tertiary care hospital in Pakistan. A total of 360 patients were included in the study. The analysis, utilizing the Urdu version of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), revealed a point prevalence of depression at 27% in the overall sample. Of those screened positive, 71 were males (25%) and 27 were females (36%). Various factors such as old age, lower literacy levels, unemployment, rural residence, and comorbidities exhibited a positive association with depression. These findings highlight the significant prevalence of depression among CAD patients, emphasizing the need for increased awareness among treating physicians and cardiologists. Recognizing and effectively managing this comorbidity is crucial for comprehensive patient care. This study contributes valuable insights to the understanding of the psychological well-being of CAD patients in the Pakistani healthcare context for further research and targeted interventions.
This article has been tagged with: