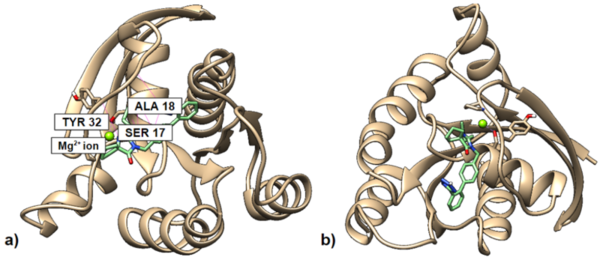
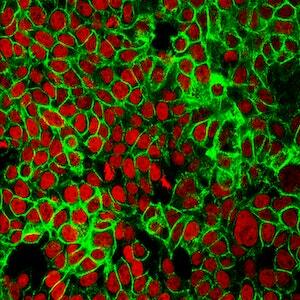
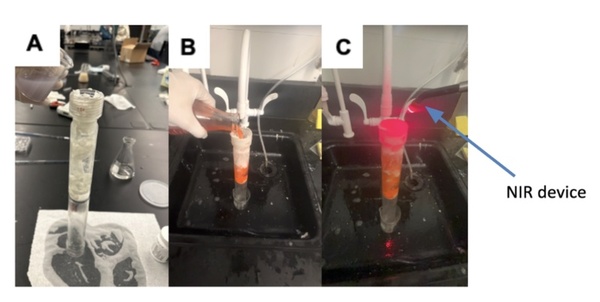
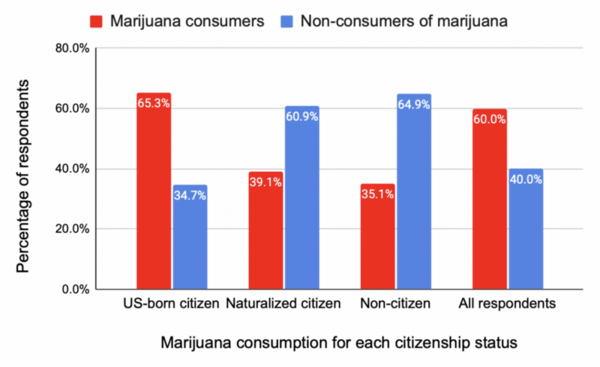
In this work the authors investigate new possible treatment methods for gastric and bladder cancers. They specifically targeted the transient receptor potential cation subfamily M member 7 (TRPM7), an ion channel that plays an important role in the survival of both of these cancers, and extracellular regulated kinases (ERKs),which contributes to the carcinogenesis of many cancers including gastric cancer. As a result, the authors consider the effects of Ginsenoside Rd, NS8593, curcumin, and icariin , known to inhibit TRPM7 and ERK. The authors found that these treatments decrease proliferation and induce apoptosis in studies of gastric and bladder cancer cells.
Read More...