Cutibacterium acnes sequence space topology implicates recA and guaA as potential virulence factors
(1) IB World School 0971, (2) Biology Department, IB World School 0971
https://doi.org/10.59720/24-015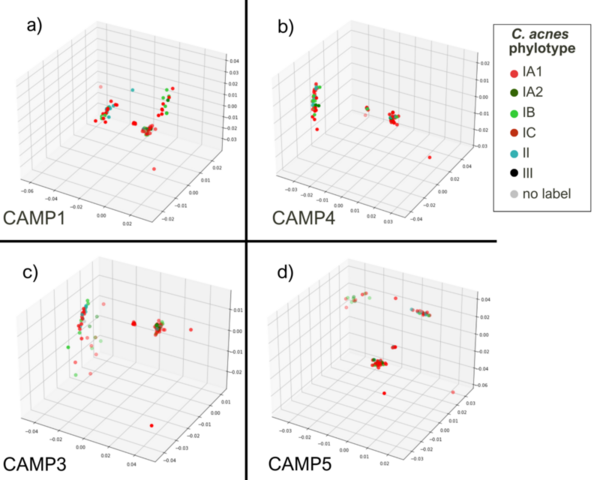
Cutibacterium acnes is a bacterium believed to play an important role in the pathogenesis of common skin diseases such as acne vulgaris. Currently, acne is known to be associated with strains from the type IA1 and IC clades of C. acnes, while those from the type IA2, IB, II, and III phylogroups are associated with skin health. This is the first study to explore the sequence space of individual gene products of different C. acnes phylogroups. Our analysis compared the sequence space topology of virulence factors to proteins with unknown functions and housekeeping proteins. We hypothesized that sequence space features of virulence factors are different from housekeeping protein features, which potentially provides an avenue to deduce unknown proteins’ functions. This proposition should be confirmed based on further experimental outcomes. A notable similarity in the sequence spaces’ topological features of previously known as housekeeping proteins encoded by recA and guaA genes to ‘putative virulence’ genes camp2 and tly was observed. Our research suggests further investigation of recA and guaA’s potential virulence properties to better understand acne pathogenesis and develop more targeted acne treatments.
This article has been tagged with: