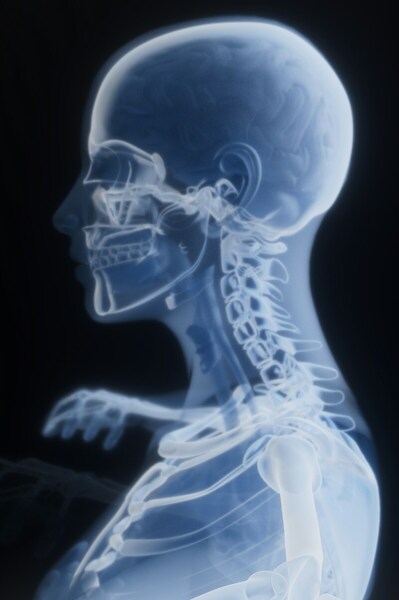
Detecting cervical spondylosis using deep learning
Read More...The effects of image manipulation on classification of cervical spondylosis X-ray images using deep learning
Vineyard vigilance: Harnessing deep learning for grapevine disease detection

Globally, the cultivation of 77.8 million tons of grapes each year underscores their significance in both diets and agriculture. However, grapevines face mounting threats from diseases such as black rot, Esca, and leaf blight. Traditional detection methods often lag, leading to reduced yields and poor fruit quality. To address this, authors used machine learning, specifically deep learning with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), to enhance disease detection.
Read More...Evaluation of in vitro anti-inflammatory effect of PLAY® on UC-MSCs: A COX-2 expression study
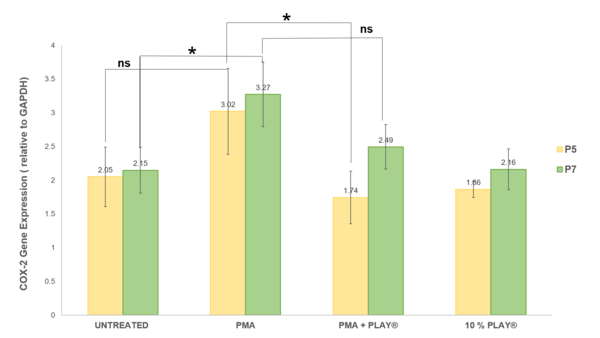
The authors seek to accelerate wound healing by reducing inflammation with a cocktail containing growth factors and bioactive modulators.
Read More...Toxicity of aminomethylphosphonic acid via the Wnt signaling pathway as a novel mechanism

The Wnt signaling pathway, known to coordinate important aspects of cellular homeostasis ranging from differentiation, proliferation, migration, and much more, is dysregulated in many human diseases. This study demonstrates that aminomethylphosphonic acid, which is the main metabolite found in the common herbicide Glyphosate, is toxic to planaria and capable of binding to canonical Wnt proteins.
Read More...Effect of hypervitaminosis A in regenerating planaria: A potential model for teratogenicity testing
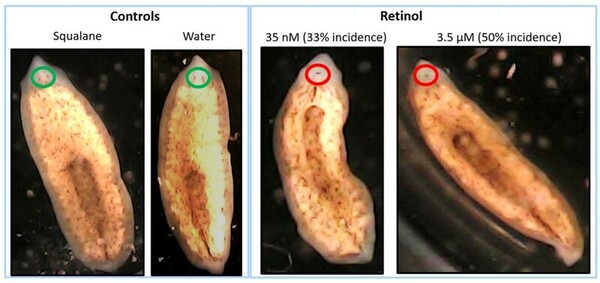
This unique research study evaluated the potential use of the flatworm, brown planaria (Dugesia tigrine), as an alternative model for teratogenicity testing. In this study, we exposed amputated planaria to varying concentrations of a known teratogen, vitamin A (retinol), for approximately 2 weeks, and evaluated multiple parameters including the formation of blastema and eyes. The results from this study demonstrated that high concentrations of retinol caused defects in head and eye formation in regenerating planaria, with similarities to vitamin A related teratogenicity findings in mammals. Based on these results, regenerating brown planaria are a promising alternative model for teratogenicity testing, which can potentially be paradigm shifting as it can reduce cost, time, and pregnant animal use in research.
Read More...Risk assessment modeling for childhood stunting using automated machine learning and demographic analysis
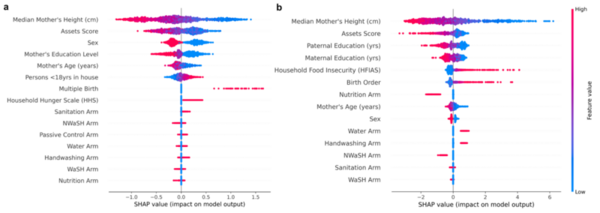
Over the last few decades, childhood stunting has persisted as a major global challenge. This study hypothesized that TPTO (Tree-based Pipeline Optimization Tool), an AutoML (automated machine learning) tool, would outperform all pre-existing machine learning models and reveal the positive impact of economic prosperity, strong familial traits, and resource attainability on reducing stunting risk. Feature correlation plots revealed that maternal height, wealth indicators, and parental education were universally important features for determining stunting outcomes approximately two years after birth. These results help inform future research by highlighting how demographic, familial, and socio-economic conditions influence stunting and providing medical professionals with a deployable risk assessment tool for predicting childhood stunting.
Read More...Obscurity of eyebrows influences recognition of human emotion and impacts older adolescents
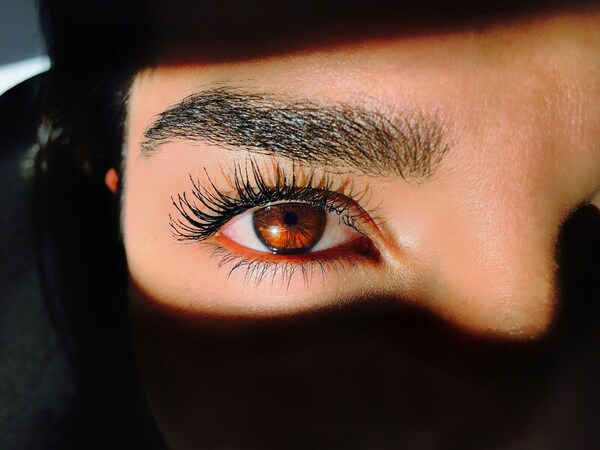

Here, seeking to better understand how facial features provide important visual cues to help convey emotions, the authors evaluated the accuracy and reaction time of participants in regards to experimental photographs where a person's eyebrows were obscured and ones where they were not. Their findings revealed that removing eyebrows resulted in a significant decrease in a participant's ability to recognize anger, with adolescents most likely to misidentify emotions.
Read More...Using the COmplex PAthway SImulator, Stage Analysis, and Chemical Kinetics to Develop a Novel Solution to Lower Tau Concentrations in Alzheimer’s Disease
In this study, the authors ask whether a Tau immunotherapy treatment, Hsp70 protein treatment, or dual treatment approach of both the Tau imunotherapy treatment and Hsp70 protein treatment leads to a greater reduction in Tau protein concentration in Alzheimer's disease. Overall, they conclude that the effectiveness of the treatment ultimately relies on the stage of Alzheimer’s.
Read More...Molecular Alterations in a High-Fat Mouse Model Before the Onset of Diet–Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease

Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most prevalent chronic liver diseases worldwide, but there are few studied warning signs for early detection of the disease. Here, researchers study alterations that occur in a mouse model of NAFLD, which indicate the onset of NAFLD sooner. Earlier detection of diseases can lead to better prevention and treatment.
Read More...The Analysis of the Effects of Smoke and Water Vapor on Insect Pheromone Communication and Physical Condition: An Investigation of the Causes of Colony Collapse Disorder
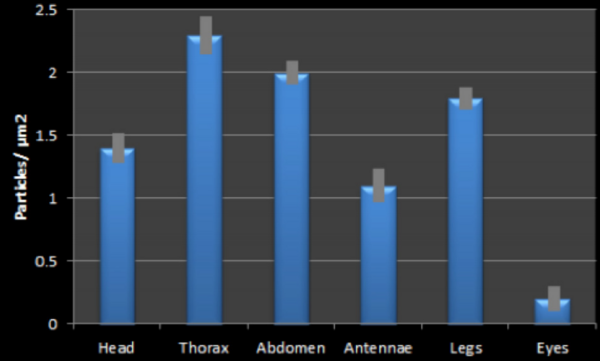
The cause of insect colony collapse disorder (CCD) is still a mystery. In this study, the authors aimed to test the effects of two environmental factors, water vapor and smoke levels, on the social behavior and physical condition of insects. Their findings could help shed light on how changing environmental factors can contribute to CCD.
Read More...