
The authors compare air quality in the presence and absence of a living wall in a high school hallway in Brooklyn, NY.
Read More...School sustainability: The implications of implementing living walls at schools for air purification

The authors compare air quality in the presence and absence of a living wall in a high school hallway in Brooklyn, NY.
Read More...A low-cost method for purification of agricultural wastewater based on S. platensis
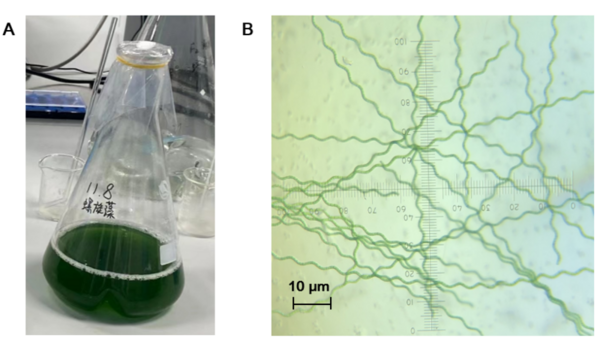
The authors looked at the ability of Spirulina platensis to reduce contaminants in wastewater in order to develop a more accessible treatment option. They found that S platensis did reduce the concentration of pollutants present within simulated agricultural wastewater.
Read More...Correlation between concentration of particulate matter 2.5 and solar energy production in Brooklyn, NY
Impact of Silverado Fire on soil carbon

Soil stores three times more carbon than the atmosphere, making small changes in its storage and release crucial for carbon cycling and climate models. This study examined the impact of the 2020 California Silverado Fire on pyrogenic carbon (PyC) deposits using nitrogen and carbon isotopes as proxies. While the results showed significant variability in δ¹⁵N, δ¹³C, total carbon, and total nitrogen across sites, they did not support the hypothesis that wildfire increases δ¹⁵N while keeping δ¹³C constant, emphasizing the need for location-based controls when using δ¹⁵N to track PyC.
Read More...Forecasting air quality index: A statistical machine learning and deep learning approach

Here the authors investigated air quality forecasting in India, comparing traditional time series models like SARIMA with deep learning models like LSTM. The research found that SARIMA models, which capture seasonal variations, outperform LSTM models in predicting Air Quality Index (AQI) levels across multiple Indian cities, supporting the hypothesis that simpler models can be more effective for this specific task.
Read More...The impact of political ideologies on renewable energy adoption
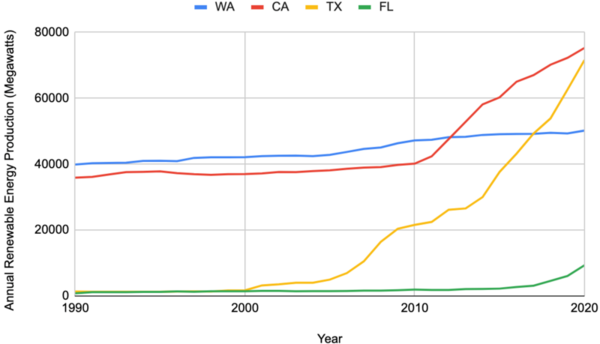
The authors compare rates of renewable energy adoption between states that historically vote for democrats versus republicans in presidential elections.
Read More...The Dependence of CO2 Removal Efficiency on its Injection Speed into Water
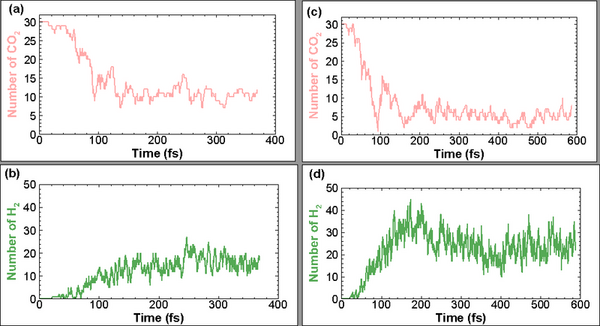
Recent research confirms that climate change, driven by CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels, poses a significant threat to humanity. In response, authors explore methods to remove CO2 from the atmosphere, including breaking its molecular bonds through high-speed collisions.
Read More...Creating a drought prediction model using convolutional neural networks
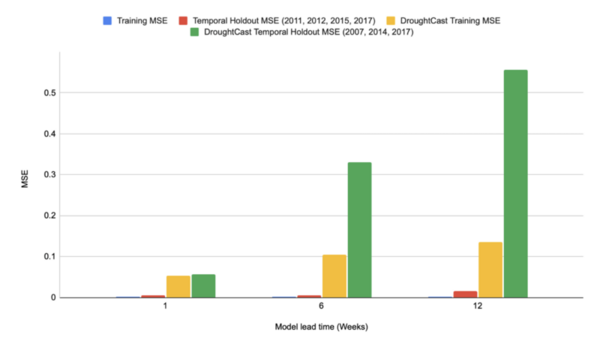
Droughts kill over 45,000 people yearly and affect the livelihoods of 55 million others worldwide, with climate change likely to worsen these effects. However, unlike other natural disasters (hurricanes, etc.), there is no early detection system that can predict droughts far enough in advance to be useful. Bora, Caulkins, and Joycutty tackle this issue by creating a drought prediction model.
Read More...A juxtaposition of the effects of natural and chemical fertilizers on Ocimum basilicum
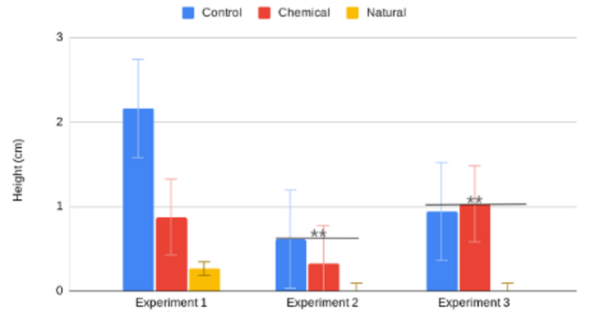
Agricultural fertilizer application is a key innovation in providing enough food to feed the world. Fertilizers come in various types and farmers must choose which fertilizer is the best for their applications. To learn more about the effectiveness of various fertilizers, Wilson and Rasmus studied the effects of natural and chemical fertilizers on growth of basil plants.
Read More...Analysis of electrodialysis as a method of producing potable water
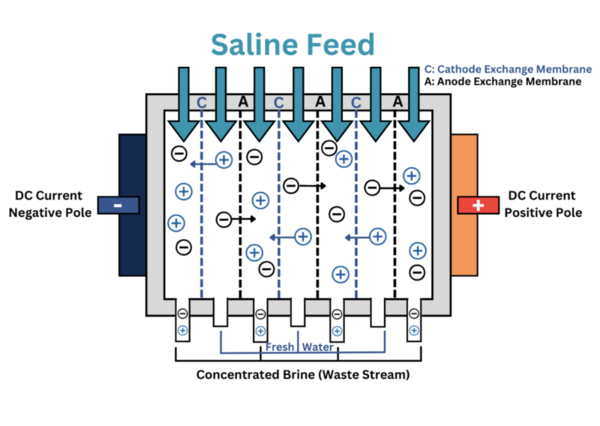
Here, seeking a way to convert the vast quantity of seawater to drinking water, the authors investigated the purification of seawater to drinking water through electrodialysis. Using total dissolved solids (TDS) as their measure, they found that electrodialysis was able to produce deionized water with TDS values under the acceptable range for consumable water.
Read More...