Stress and anxiety have become more prevalent issues in recent years with teenagers especially at risk. Recent studies show that experiencing stress while learning can impair brain-cell communication thus negatively impacting learning. Green tea is believed to have the opposite effect, aiding in learning and memory retention. In this study, the authors used Lymnaea stagnalis , a pond snail, to explore the relationship between green tea and a stressor that impairs memory formation to determine the effects of both green tea and stress on the snails’ ability to learn, form, and retain memories. Using a conditioned taste aversion (CTA) assay, where snails are exposed to a sweet substance followed by a bitter taste with the number of biting responses being recorded, the authors found that stress was shown to be harmful to snail learning and memory for short-term, intermediate, and long-term memory.
Read More...Browse Articles
Comparing the reducing sugars in avocados, soybeans, and cinnamon: A Benedict’s test experiment
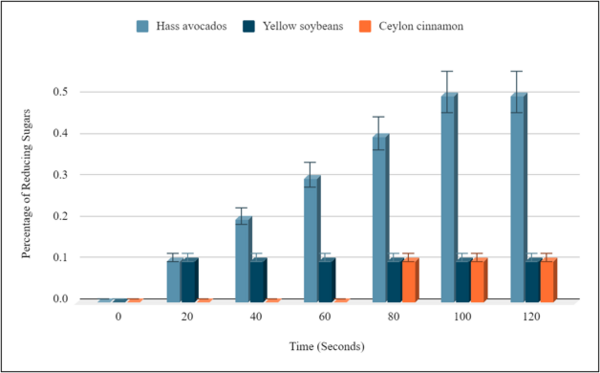
The authors test the levels of reducing sugars in avocados, soybeans, and cinnamon as part of a diet for individuals managing Type II diabetes.
Read More...DyGS: A Dynamic Gene Searching Algorithm for Cancer Detection
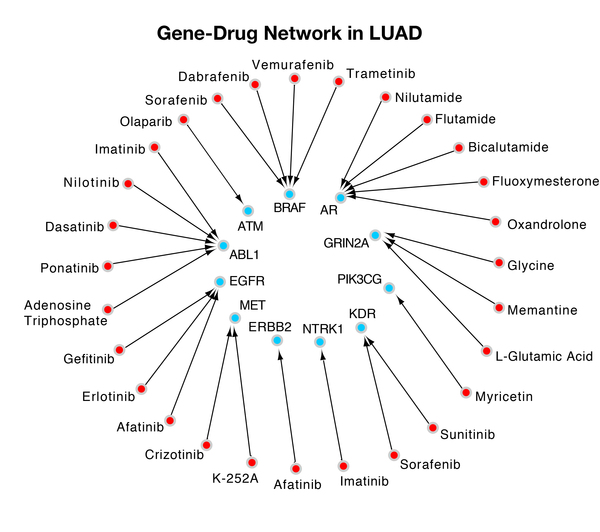
Wang and Gong developed a novel dynamic gene-searching algorithm called Dynamic Gene Search (DyGS) to create a gene panel for each of the 12 cancers with the highest annual incidence and death rate. The 12 gene panels the DyGS algorithm selected used only 3.5% of the original gene mutation pool, while covering every patient sample. About 40% of each gene panel is druggable, which indicates that the DyGS-generated gene panels can be used for early cancer detection as well as therapeutic targets in treatment methods.
Read More...Are alkaline spices the future of antibiotics?
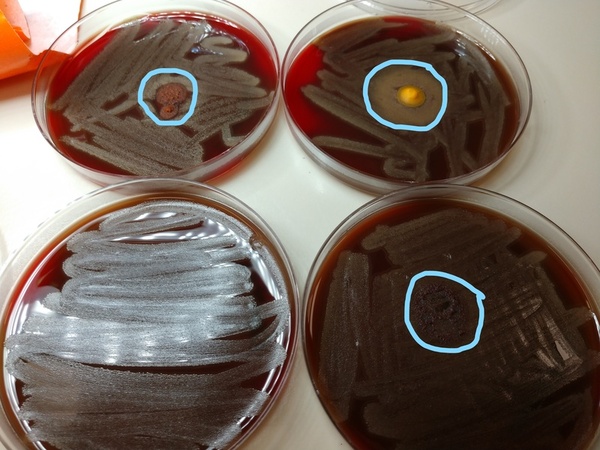
The authors experimented with several commonly available alkaline spices (turmeric, cayenne pepper, and cinnamon) to study their antimicrobial properties, hypothesizing that alkaline spices would have antimicrobial activity. Results showed a zone of inhibition of bacterial growth, with the largest zone of inhibition being around turmeric, followed by cayenne pepper, and the smallest around cinnamon. These results are impactful, as common alkaline spices generally do show antibacterial properties and both bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects correlated with degree of alkalinity.
Read More...Effect of Increasing Concentrations of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Hatching, Survival and Development of Artemia salina
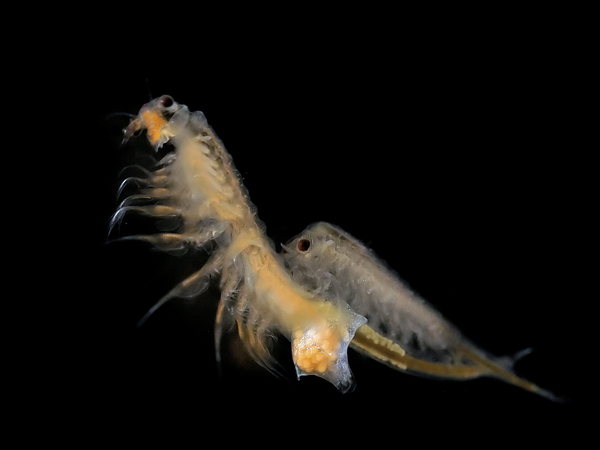

Cannabidiol, or CBD, is a widely available over the counter treatment used for various medical conditions. However, CBD exerts its effects on the endocannabinoid system, which is involved in neural maturation, and could potentially have adverse effects on brain development. Here, the impact of CBD on the development of brine shrimp (Artemia salina) was assessed. Differences in dose responses were observed.
Read More...Diamagnetic Solutions Show a Significant Reduction in Flow Rate When Exposed to a Magnetic Field Greater Than or Equal to 0.7 Tesla
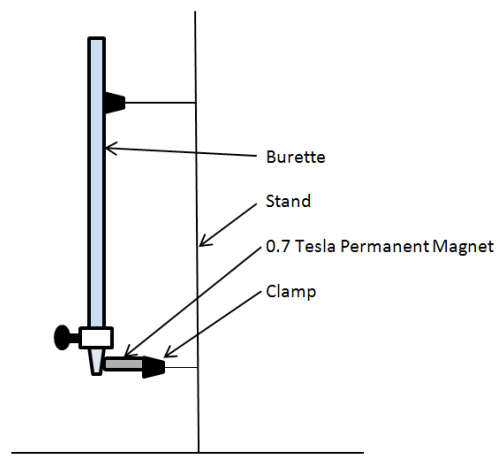
There are complex interactions between water and outside forces such as magnetic fields. This study aims to examine the effects of magnetic forces on the flow rate of water. The alteration of flow rate by magnets could have exciting applications in many fields.
Read More...Correlates of Sugar Consumption Among High School Students and Faculty

The availability, portion sizes, and consumption of highly palatable food has been linked adverse health outcomes. McBurnett and O’Donnell sought to assess the relationship between reward-based eating drive, consumption, cravings, and knowledge of the effects of sugary foods. In this study population, reward-based eating drive was related to both consumption and cravings. Further, for females, the knowledge of sugar’s effects was significantly and inversely associated with its consumption.
Read More...Aberrant response to dexamethasone suppression test associated with inflammatory response in MDD patients
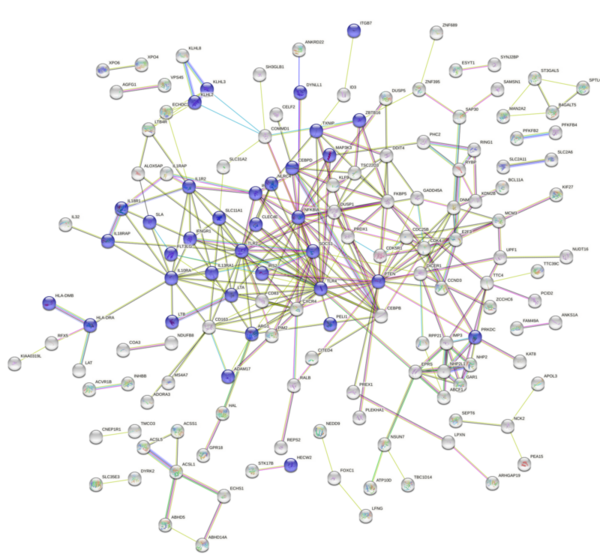
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a prevalent mood disorder. The direct causes and biological mechanisms of depression still elude understanding, though genetic factors have been implicated. This study looked to identify the mechanism behind the aberrant response to the dexamethasone suppression test (DST) displayed by MDD patients, in which they display a lack of cortisol suppression. Analysis revealed several pro-inflammatory genes that were significant and differentially expressed between affected and non-affected groups in response to the DST. Looking at ways to decrease the inflammatory response could have implications for treatment and may explain why some people treated for depression still display symptoms or may lead researchers to different classes of drugs for treatment.
Read More...Durability of the Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Patch Adhesive
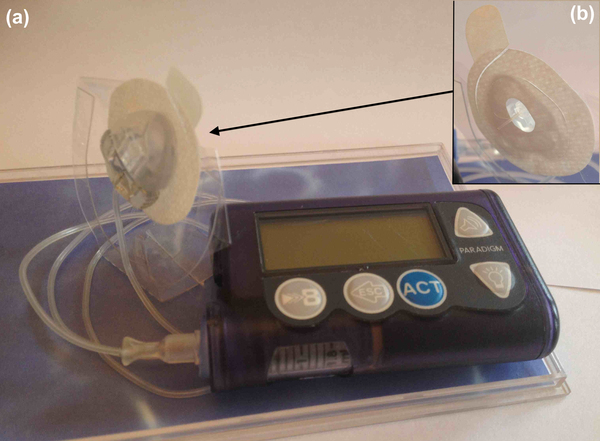
Insulin infusion patches are a common way for diabetics to receive medication. The durability of two different patch adhesives was compared on artificial skin with and without artificial sweat.
Read More...Association of depression and suicidal ideation among adults with the use of H2 antagonists
In this study, the authors investigate associations between use of histamine H2 receptor antagonists and suicidal ideation in different age groups.
Read More...Search Articles
Search articles by title, author name, or tags