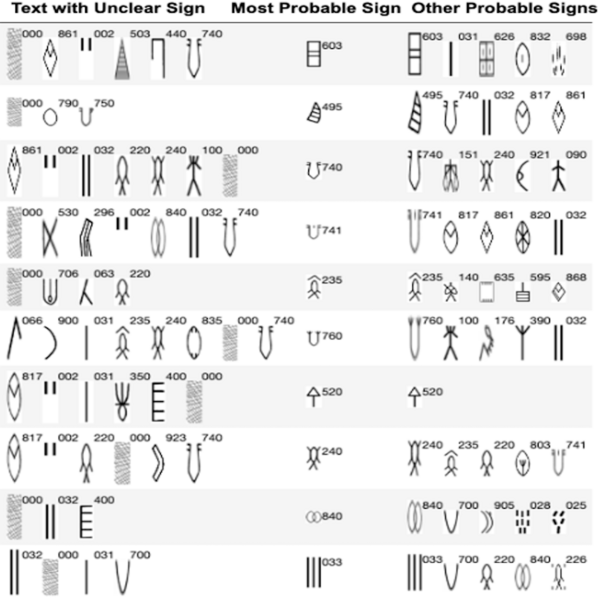
This study utilizes machine learning models to predict missing and unclear signs from the Indus script, a writing system from an ancient civilization in the Indian subcontinent.
Read More...Statistical models for identifying missing and unclear signs of the Indus script

This study utilizes machine learning models to predict missing and unclear signs from the Indus script, a writing system from an ancient civilization in the Indian subcontinent.
Read More...Utilizing meteorological data and machine learning to predict and reduce the spread of California wildfires

This study hypothesized that a machine learning model could accurately predict the severity of California wildfires and determine the most influential meteorological factors. It utilized a custom dataset with information from the World Weather Online API and a Kaggle dataset of wildfires in California from 2013-2020. The developed algorithms classified fires into seven categories with promising accuracy (around 55 percent). They found that higher temperatures, lower humidity, lower dew point, higher wind gusts, and higher wind speeds are the most significant contributors to the spread of a wildfire. This tool could vastly improve the efficiency and preparedness of firefighters as they deal with wildfires.
Read More...Reddit v. Wall Street: Why Redditors beat Wall Street at its own game
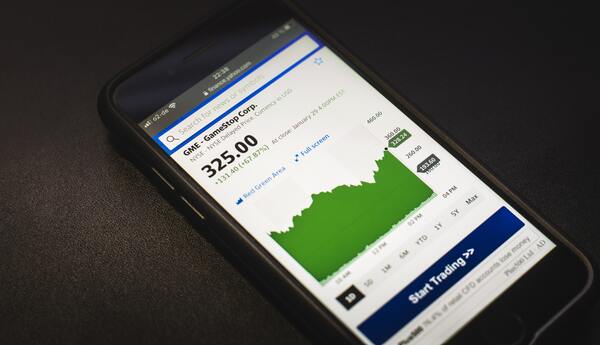
Here the authors investigated the motivation of a short squeeze of GameStop stock where users of the internet forum Reddit drove a sudden increase in GameStop stock price during the start of 2021. They relied on both qualitative and quantitative analyses where they tracked activity on the r/WallStreetBets subreddit in relation to mentions of GameStop. With these methods they found that while initially the short squeeze was driven by financial motivations, later on emotional motivations became more important. They suggest that social phenomena can be dynamic and evolve necessitating mixed method approaches to study them.
Read More...An explainable model for content moderation
The authors looked at the ability of machine learning algorithms to interpret language given their increasing use in moderating content on social media. Using an explainable model they were able to achieve 81% accuracy in detecting fake vs. real news based on language of posts alone.
Read More...The efficacy of spent green tea leaves and coffee grounds on the growth of Ocimum basilicum
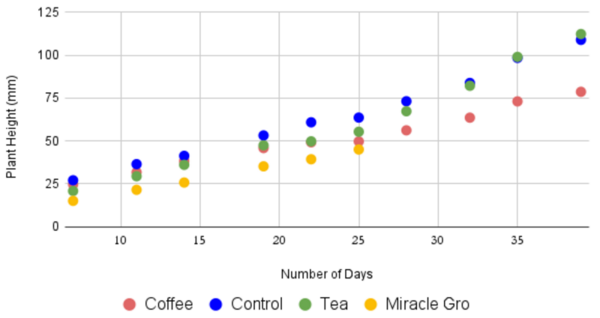
The authors looked at fertilizer derived from coffee ground tea leaves, measuring the effectiveness by measuring the height, weight, and number of leaves on basil plants.
Read More...Can essential oils be allelopathic to Lolium multiforum without harming Solanum lycopersicum?

Seeking to investigate eco-friendly biological methods to control weeds and enhance food crop yields, here the authors considered the effects of three essential oils on seed germination and radicle length of both a weed and a common crop. They found that treatment with turmeric oil had phytotoxic potential, leading to a reduction in both seed germination and radicle length of the weed. In contrast, ginger oil possessed allelopathic properties towards both. The authors suggest that essential oils could be used as eco-friendly bio-herbicides.
Read More...Effect of pH on the antibacterial properties of turmeric
Some spices have antimicrobial or antibacterial properties that people have already tested. Turmeric has a wide variety of uses and has even been implemented in alternative medicine as a treatment for cancer, inflammation, osteoarthritis, and other diseases. We tested the antimicrobial effects of turmeric under two different pHs to characterize this effect in vitro. Decreasing the pH of a solution of turmeric may increase antibacterial properties.
Read More...Household spices and minerals as alternative disinfectants for mobile phones

In this study, the authors investigate the disinfectant potential of many household spices and minerals. More specifically, they test whether these compounds can be used to disinfect mobile phones after daily use with the hope of identifying environmentally-friendly cleaning options.
Read More...Characterization of antibacterial properties of common spices
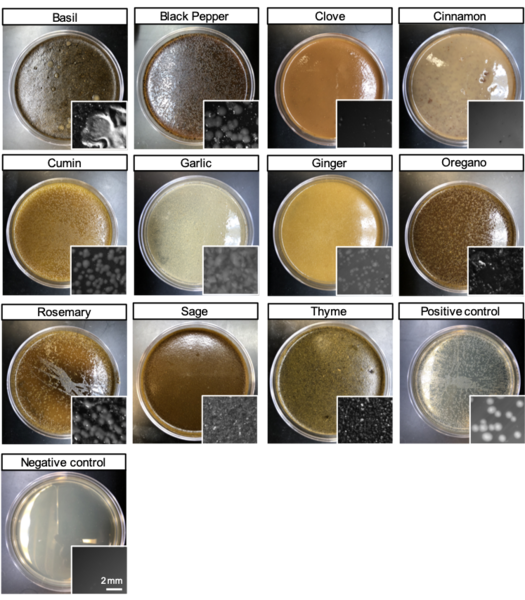

Bacterial infection is resurging as one of the most dangerous challenges facing the medical establishment. Americans spend about 55 to 70 billion dollars per year on antibiotics, yet these antibiotics are becoming increasingly ineffective as illness-causing bacteria gain resistance to the prescribed drugs. We tested if 11 commonly-used spices could inhibit growth of the gram-negative bacteria, E. coli, the main takeaway from these experiments is that certain spices and herbs have antibacterial effects that inhibit growth of E.coli , and these spices could show similarly promising activity towards other bacteria.
Read More...