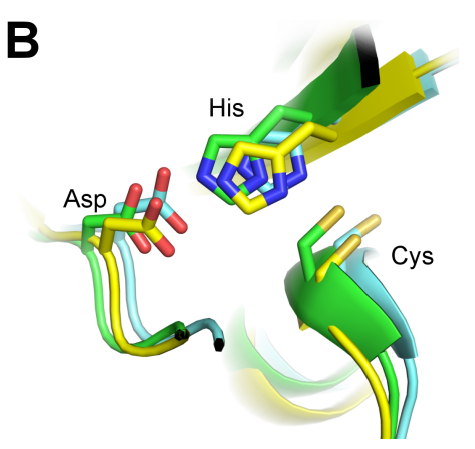
Malaria is a major public health issue, especially in developing countries, and vector control is a major facet of malaria eradication efforts. Recently, sterile insect technique (SIT), or the release of sterile mosquitoes into the wild, has shown significant promise as a method of keeping vector populations under control. In this study, the authors investigate the Anopheles gambiae transglutaminase 3 protein (AgT3), which is essential to the mating of the Anopheles mosquito. They show that an active site mutation is able to abolish the activity of the AgT3 enzyme and propose it as a potential target for chemosterilant inhibitors.
Read More...