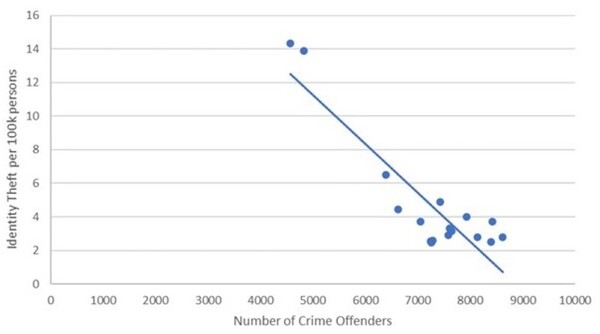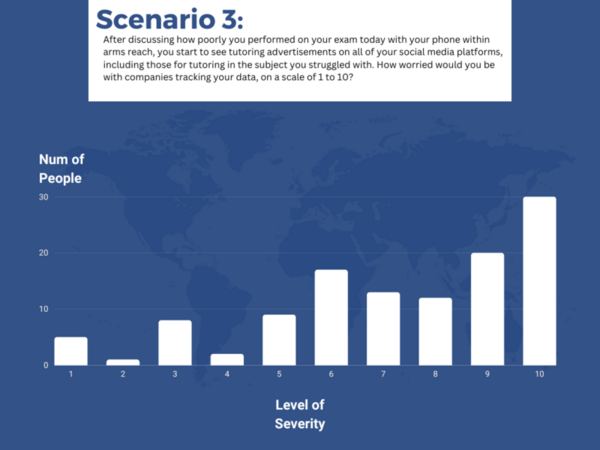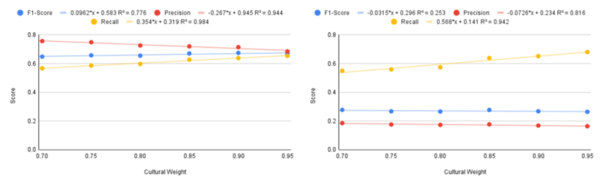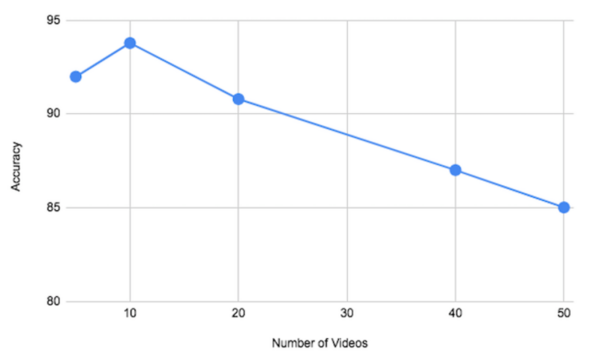
The Tor network allows individuals to secure their online identities by encrypting their traffic, however it is vulnerable to fingerprinting attacks that threaten users' online privacy. In this paper, the authors develop a new video fingerprinting model to explore how well video streaming can be fingerprinted in Tor. They found that their model could distinguish which one of 50 videos a user was hypothetically watching on the Tor network with 85% accuracy, demonstrating that video fingerprinting is a serious threat to the privacy of Tor users.
Read More...