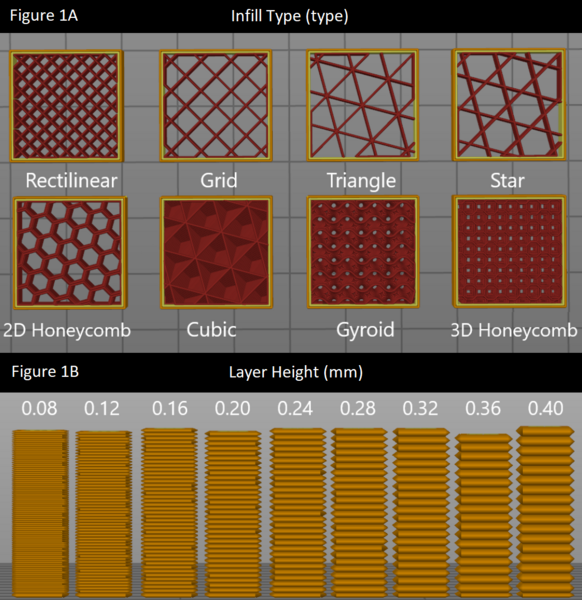
In this study, the authors test different infill patterns to determine which would be the strongest and most durable for 3D printing applications, which have become an integral part of many facets of life.
Read More...Optimizing 3D printing parameters: Evaluating infill type and layer height effects on tensile fracture force

In this study, the authors test different infill patterns to determine which would be the strongest and most durable for 3D printing applications, which have become an integral part of many facets of life.
Read More...Analysis of the effects of positive ions and boundary layer temperature at various hypersonic speeds on boundary layer density
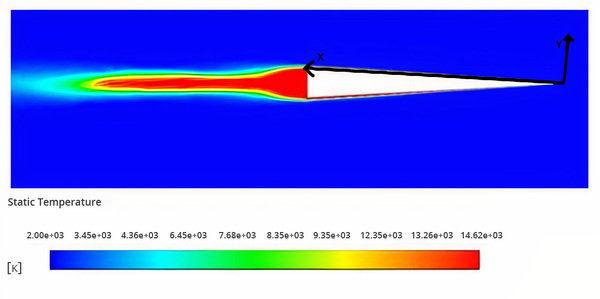
This study's goal was to identify the Mach numbers for which electrostatic drag and heat transfer manipulation would be most applicable inside the stratosphere. The experiments were conducted using computational fluid dynamics software. The study demonstrated that, on average, higher Mach speeds resulted in a considerably higher potential decrease in density. The study highlights that further research on the surface charge method is warranted to explore higher hypersonic speeds within the stratosphere.
Read More...Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Periplasmic Proteins Interacting With the Peptidoglycan Layer of Escherichia coli
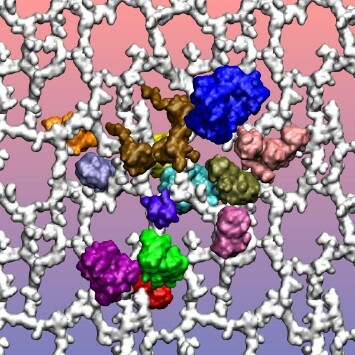
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are a great tool to model and study complex biological systems. In this paper, the authors use MD simulations to construct and simulate a model of the periplasmic space, the peptidoglycan layer and its associated proteins, in an Escherichia coli cell.
Read More...Specialized chicken toys are effective in relieving stagnant egg production for stressed layer hens

The authors looked at egg laying rates in chickens at two different small farms. They found when the chickens were provided homemade, colorful toys in their environment that their egg production rates increased.
Read More...Fabrication of CuSbS2 Solar Cells by Sulfurization of Thermally Evaporated Metal Stacks
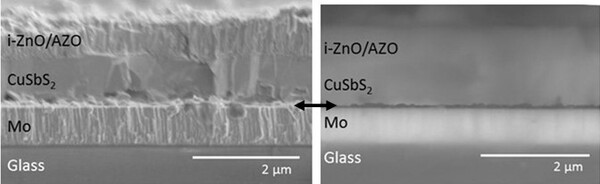
In this article, the authors created CuSbS2 solar cells. They discovered that the cells' efficiency was affected by the formation of MoS2. By incorporating a layer of single-walled carbon nanotubes, however, they were able to prevent MoS2 formation and increase the device's efficiency.
Read More...The Non-Thermal Effect of UV-B Irradiation on Onion Growth
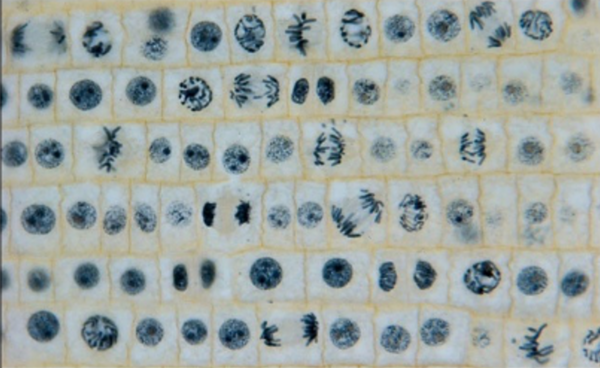
UV-B radiation due to the depletion of ozone threatens plant life, potentially damaging ecosystems and dismantling food webs. Here, the impact of UV-B radiation on the physiology and morphology of Allum cepa, the common onion, was assessed. Mitosis vitality decreased, suggesting UV-B damage can influence the plant’s physiology.
Read More...Inhibiting the ERK pathway and the TRPM7 ion channel in gastric and bladder cancer cells
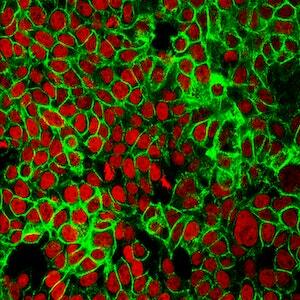
In this work the authors investigate new possible treatment methods for gastric and bladder cancers. They specifically targeted the transient receptor potential cation subfamily M member 7 (TRPM7), an ion channel that plays an important role in the survival of both of these cancers, and extracellular regulated kinases (ERKs),which contributes to the carcinogenesis of many cancers including gastric cancer. As a result, the authors consider the effects of Ginsenoside Rd, NS8593, curcumin, and icariin , known to inhibit TRPM7 and ERK. The authors found that these treatments decrease proliferation and induce apoptosis in studies of gastric and bladder cancer cells.
Read More...Optimized biochemical depolymerization of plastics from surgical face masks

The authors combine chemical, enzymatic, and microbial-based methods to optimize degradation of plastics within a surgical facemask.
Read More...Quantum-inspired neural networks enhance stock prediction accuracy

The authors developed a quantum inspired model for stock market fluctuations.
Read More...Lung cancer AI-based diagnosis through multi-modal integration of clinical and imaging data
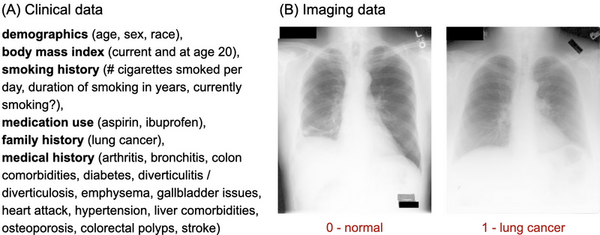
Lung cancer is highly fatal, largely due to late diagnoses, but early detection can greatly improve survival. This study developed three models to enhance early diagnosis: an MLP for clinical data, a CNN for imaging data, and a hybrid model combining both.
Read More...