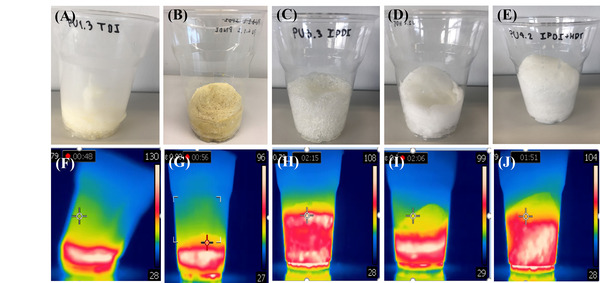
In this study, the authors utilize an infrared camera to visualize and investigate the exothermic reaction of polyurethane foam, which has many everyday uses including automotive seats, bedding, and insulation.
Read More...Monitoring the formation of polyurethane foams with an infrared camera: Classroom activity

In this study, the authors utilize an infrared camera to visualize and investigate the exothermic reaction of polyurethane foam, which has many everyday uses including automotive seats, bedding, and insulation.
Read More...Converting SiO2 wafers to hydrophobic using chlorotrimethylsilane
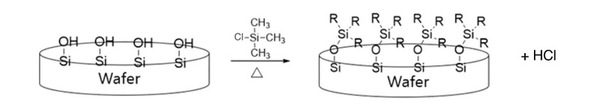
Semiconductors are the center of the fourth industrial revolution as they are key components for all electronics. Exposed wafers made of silicon (Si), which can easily oxidize, convert to silicon dioxide (SiO2). The surface of SiO2 wafers consists of many Si-OH bonds, allowing them to easily bond with water, resulting in a “wet” or hydrophilic condition. We sought to determine a way to modify the surface of SiO2 wafers to become hydrophobic to ensure safe wet cleaning.
Read More...Spectroscopic Kinetic Monitoring and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Biocatalytic Ester Hydrolysis in Non-Aqueous Solvent
Lipases are a common class of enzymes that catalyze the breakdown of lipids. Here the authors characterize the the activity of pancreatic lipase in different organic solvents using a choloremetric assay, as well as using molecular dynamic simulations. They report that the activity of pancreatic lipase in 5% methanol is more than 25% higher than in water, despite enzyme stability being comparable in both solvents. This suggests that, for industrial applications, using pancreatic lipase in 5% methanol solution might increase yield, compared to just water.
Read More...Covalently Entrapping Catalase into Calcium Alginate Worm Pieces Using EDC Carbodiimide as a Crosslinker.
Catalase is a biocatalyst used to break down toxic hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen in industries such as cheese and textiles. Improving the efficiency of catalase would help us to make some industrial products, such as cheese, less expensively. The best way to maintain catalase’s conformation, and thus enhance its activity, is to immobilize it. The primary goal of this study was to find a new way of immobilizing catalase.
Read More...The Development and Maximization of a Novel Photosynthetic Microbial Fuel Cell Using Rhodospirillum rubrum
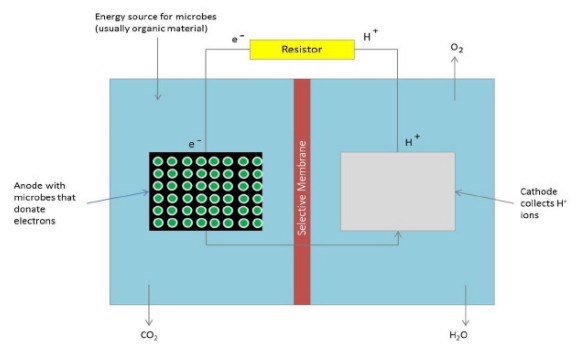
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are bio-electrochemical systems that utilize bacteria and are promising forms of alternative energy. Similar to chemical fuel cells, MFCs employ both an anode (accepts electrons) and a cathode (donates electrons), but in these devices the live bacteria donate the electrons necessary for current. In this study, the authors assess the functionality of a photosynthetic MFC that utilizes a purple non-sulfur bacterium. The MFC prototype they constructed was found to function over a range of environmental conditions, suggesting its potential use in industrial models.
Read More...Efficient synthesis of superabsorbent beads using photopolymerization with a low-cost method
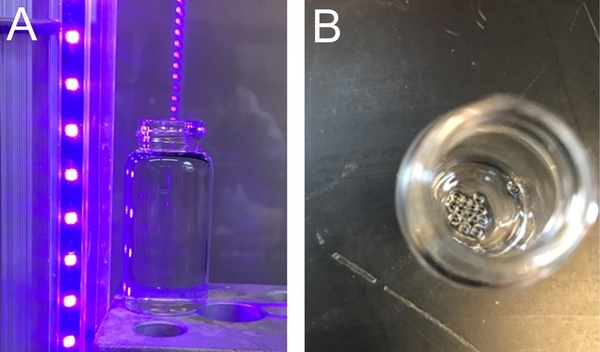
Superabsorbent beads are remarkable, used throughout our daily lives for various practical applications. These beads, as suggested by their name, possess a unique ability to absorb and retain large quantities of liquids. This characteristic of absorbency makes them essential throughout the medical field, agriculture, and other critical industries as well as in everyday products. To create these beads, the process of photopolymerization is fast growing in favor with distinct advantages of cost efficiency, speed, energy efficiency, and mindfulness towards the environment. In this article, researchers explore the pairing of cheap monomers with accessible equipment for creation of superabsorbent beads via the photopolymerization process. This research substantially demonstrates the successful application of photopolymerization in producing highly absorbent beads in a low-cost context, thereby expanding the accessibility of this process for creating superabsorbent beads in both research and practical applications.
Read More...Optimal pH for indirect electrochemical oxidation of isopropyl alcohol with Ru-Ti anode and NaCl electrolyte

In this study, the authors determine optimal pH levels for maximizing isopropanol degradation in water. This has important applications for cleaning up polluted wastewater in the environment.
Read More...Role of Environmental Conditions on Drying of Paint
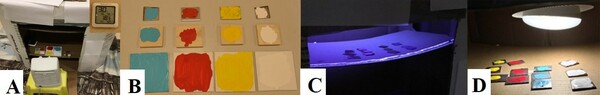
Reducing paint drying time is an important step in improving production efficiency and reducing costs. The authors hypothesized that decreased humidity would lead to faster drying, ultraviolet (UV) light exposure would not affect the paint colors differently, white light exposure would allow for longer wavelength colors to dry at a faster rate than shorter wavelength colors, and substrates with higher roughness would dry slower. Experiments showed that trials under high humidity dried slightly faster than trials under low humidity, contrary to the hypothesis. Overall, the paint drying process is very much dependent on its surrounding environment, and optimizing the drying process requires a thorough understanding of the environmental factors and their interactive effects with the paint constituents.
Read More...Copper nanoparticle synthesis using Picea glauca ‘Conica’
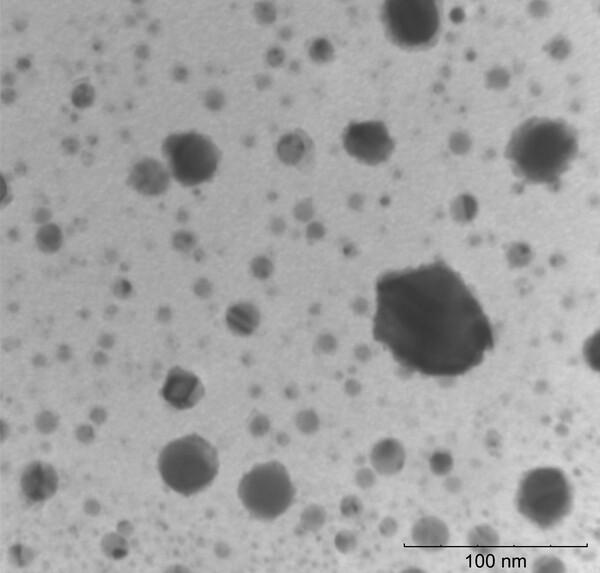
The authors propose a method to recycle Christmas tree needles into a non-toxic reducing agent for synthesizing copper nanoparticles.
Read More...Probiotic biosorption as a way to remove heavy metal in seawater

In this study, the authors address the concerns of heavy metal contamination in industrial and feedlot water waste. They test whether added probiotics are capable of taking up heavy metals in water to attenuate pollution.
Read More...