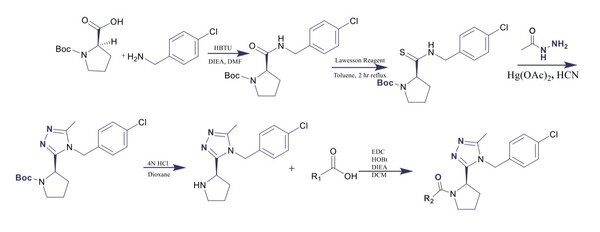
Treatments inhibiting Notch signaling pathways have been explored by researchers as a new approach for the treatment of glioblastoma tumors, which is a fast-growing and aggressive brain tumor. Recently, retinoic acid (RA) therapy, which inhibits Notch signaling, has shown a promising effect on inhibiting glioblastoma progression. RA, which is a metabolite of vitamin A, is very important in embryonic cellular development, which includes the regulation of multiple developmental processes, such as brain neurogenesis. However, high doses of RA treatment caused many side effects such as headaches, nausea, redness around the injection site, or allergic reactions. Therefore, we hypothesized that a combination treatment of RA and siRNA targeting NOTCH1 (siNOTCH1), the essential gene that activates Notch signaling, would effectively inhibit brain cancer cell proliferation. The aim of the study was to determine whether inhibiting NOTCH1 would inhibit the growth of brain cancer cells by cell viability assay. We found that the combination treatment of siNOTCH1 and RA in low concentration effectively decreased the NOTCH1 expression level compared to the individual treatments. However, the combination treatment condition significantly decreased the number of live brain cancer cells only at a low concentration of RA. We anticipate that this novel combination treatment can provide a solution to the side effects of chemotherapy.
Read More...