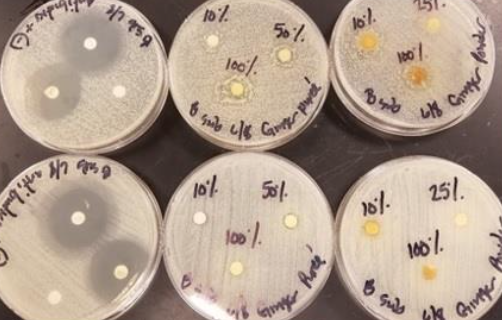
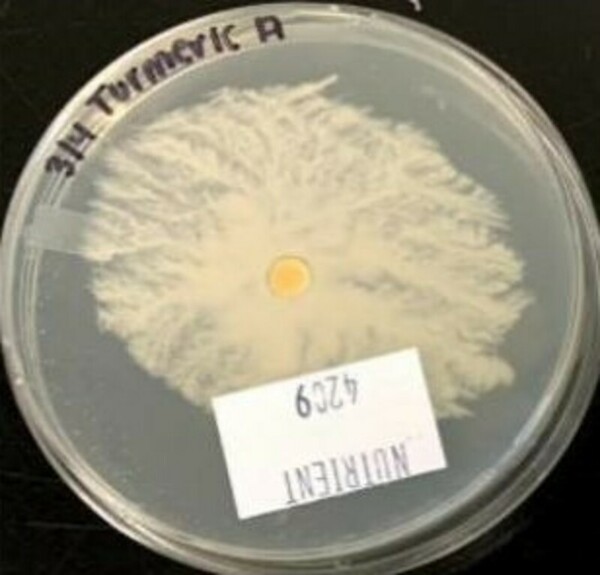
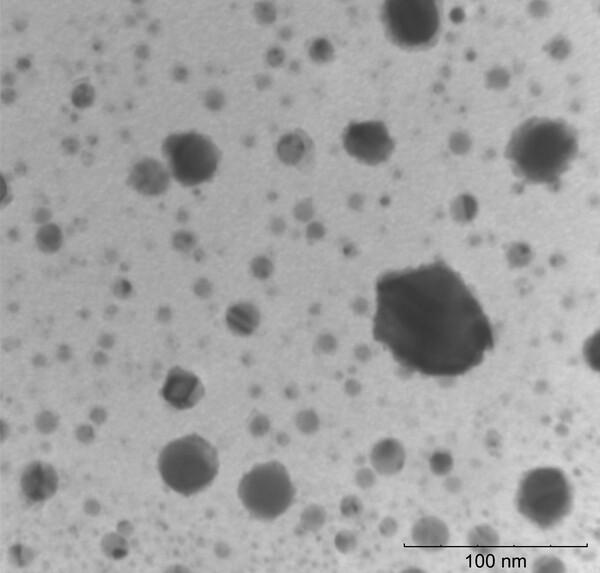
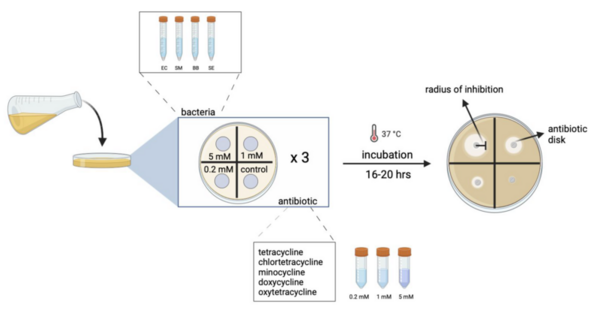
Plant pathogens can cause significant crop loss each year, but controlling them with bactericides or antibiotics can be costly and may be harmful to the environment. Green tea naturally contains polyphenols, which have been shown to have some antimicrobial properties. In this study, the authors show that green tea extract can inhibit growth of the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato and may be useful as an alternative bactericide for crops.
Read More...