Antibacterial effectiveness of turmeric against gram-positive Staphylococcus epidermidis
(1) Williamston High School, Williamston, Michigan
https://doi.org/10.59720/21-121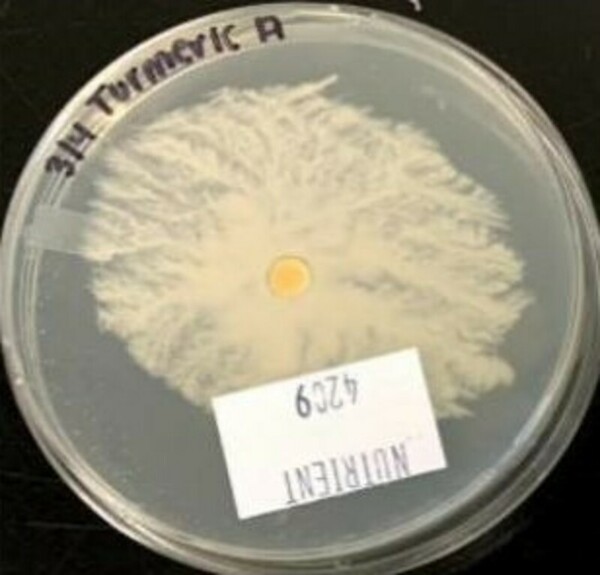
Infections caused by antibiotic resistance are a leading issue faced by the medical field. A potential solution to this involves using common household spices as natural antibacterial agents to reduce infections. One option may be turmeric, as it has high levels of polyphenols that have previously exhibited antibacterial properties. We studied the antibacterial effectiveness of turmeric against gram-positive Staphylococcus epidermidis using antibiotic sensitivity disks. The experiment had a negative control, positive control of Penicillin, and experimental group with turmeric. We infused blank antibiotic sensitivity disks with a 5% concentrated solution of turmeric and placed them on agar plates inoculated with bacteria. The zone of inhibition (ZOI) surrounding each disk was measured to determine antibacterial effectiveness. However, there was no measurable ZOI surrounding the turmeric disk so the measurements for all trials were 0 cm, suggesting that turmeric at a 5% concentration is not an effective antibacterial against S. epidermidis.
This article has been tagged with: