The authors explore how diversity in data sets contributes to bias in artificial intelligence.
Read More...Addressing and Resolving Biases in Artificial Intelligence

The authors explore how diversity in data sets contributes to bias in artificial intelligence.
Read More...Open Source RNN designed for text generation is capable of composing music similar to Baroque composers
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are useful for text generation since they can generate outputs in the context of previous ones. Baroque music and language are similar, as every word or note exists in context with others, and they both follow strict rules. The authors hypothesized that if we represent music in a text format, an RNN designed to generate language could train on it and create music structurally similar to Bach’s. They found that the music generated by our RNN shared a similar structure with Bach’s music in the input dataset, while Bachbot’s outputs are significantly different from this experiment’s outputs and thus are less similar to Bach’s repertoire compared to our algorithm.
Read More...DyGS: A Dynamic Gene Searching Algorithm for Cancer Detection
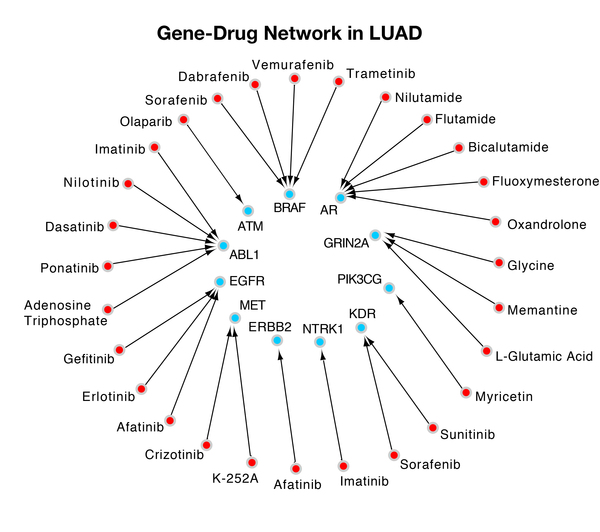
Wang and Gong developed a novel dynamic gene-searching algorithm called Dynamic Gene Search (DyGS) to create a gene panel for each of the 12 cancers with the highest annual incidence and death rate. The 12 gene panels the DyGS algorithm selected used only 3.5% of the original gene mutation pool, while covering every patient sample. About 40% of each gene panel is druggable, which indicates that the DyGS-generated gene panels can be used for early cancer detection as well as therapeutic targets in treatment methods.
Read More...Assessing and Improving Machine Learning Model Predictions of Polymer Glass Transition Temperatures
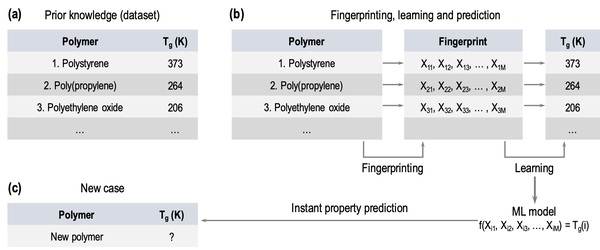
In this study, the authors test whether providing a larger dataset of glass transition temperatures (Tg) to train the machine-learning platform Polymer Genome would improve its accuracy. Polymer Genome is a machine learning based data-driven informatics platform for polymer property prediction and Tg is one property needed to design new polymers in silico. They found that training the model with their larger, curated dataset improved the algorithm's Tg, providing valuable improvements to this useful platform.
Read More...AeroPurify: Autonomous air filtration UAV using real-time 3-D Monte Carlo gradient search

Here the authors present an autonomous drone air filtration system that uses a novel algorithm, the gradient ascent ML particle filter (GA/MLPF), to efficiently locate and mitigate outdoor air pollution. They demonstrate that their GA/MLPF algorithm is significantly more efficient than the conventional gradient ascent algorithm, reducing both the time and number of waypoints needed to find the source of pollution.
Read More...Transfer Learning for Small and Different Datasets: Fine-Tuning A Pre-Trained Model Affects Performance
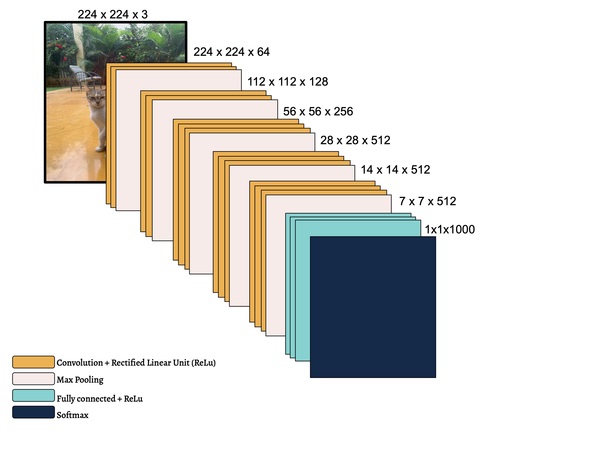
In this study, the authors seek to improve a machine learning algorithm used for image classification: identifying male and female images. In addition to fine-tuning the classification model, they investigate how accuracy is affected by their changes (an important task when developing and updating algorithms). To determine accuracy, a set of images is used to train the model and then a separate set of images is used for validation. They found that the validation accuracy was close to the training accuracy. This study contributes to the expanding areas of machine learning and its applications to image identification.
Read More...Pruning replay buffer for efficient training of deep reinforcement learning

Reinforcement learning (RL) is a form of machine learning that can be harnessed to develop artificial intelligence by exposing the intelligence to multiple generations of data. The study demonstrates how reply buffer reward mechanics can inform the creation of new pruning methods to improve RL efficiency.
Read More...Analyzing carbon dividends’ impact on financial security via ML & metaheuristic search

Impact of carbon tax and dividend on financial security
Read More...Machine learning-based enzyme engineering of PETase for improved efficiency in plastic degradation

Here, recognizing the recognizing the growing threat of non-biodegradable plastic waste, the authors investigated the ability to use a modified enzyme identified in bacteria to decompose polyethylene terephthalate (PET). They used simulations to screen and identify an optimized enzyme based on machine learning models. Ultimately, they identified a potential mutant PETases capable of decomposing PET with improved thermal stability.
Read More...Identifying shark species using an AlexNet CNN model
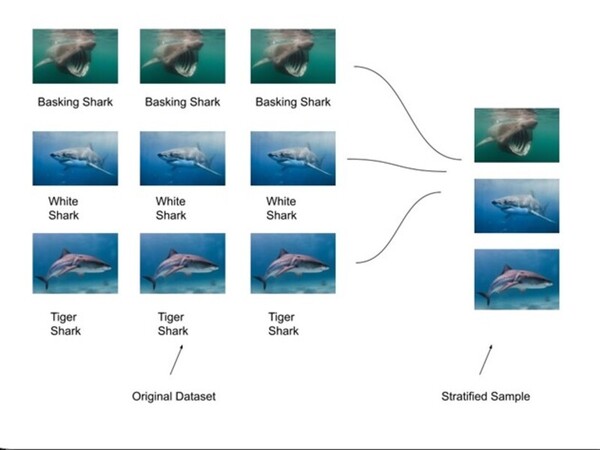
The challenge of accurately identifying shark species is crucial for biodiversity monitoring but is often hindered by time-consuming and labor-intensive manual methods. To address this, SharkNet, a CNN model based on AlexNet, achieved 93% accuracy in classifying shark species using a limited dataset of 1,400 images across 14 species. SharkNet offers a more efficient and reliable solution for marine biologists and conservationists in species identification and environmental monitoring.
Read More...