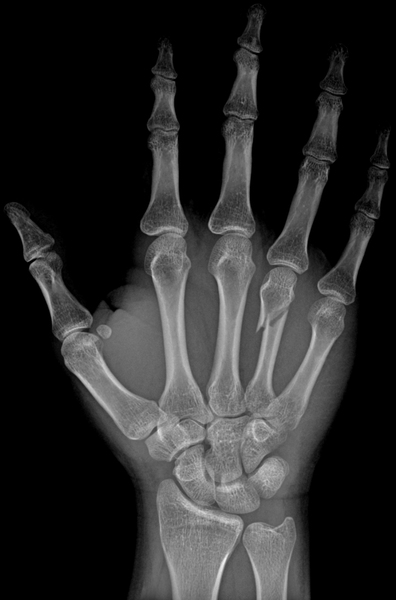
Scientists are always on the quest to improve the body's healing abilities and broken bones are no exception. In this article, the authors investigate properties of 3D-printed biocompatible polymers used to improve bone healing. With such efforts, we can hope to, one day, improve bone scaffolding materials in ways that make the natural healing processes more efficient, reducing the time needed for recovery from bone fractures.
Read More...