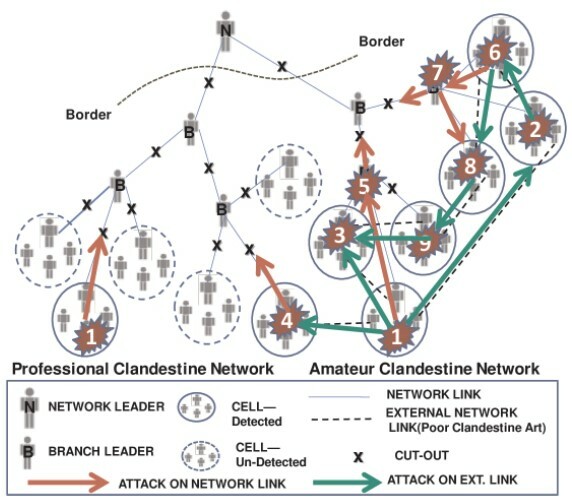
Though current strategies in counterterrorism are somewhat effective, the Simultaneous Attack/Persistent Pursuit (SAPP) Theory may be superior alternative to current methods. The authors simulated five attack strategies (1 SAPP and 4 non-SAPP), and concluded that the SAPP model was significantly more effective in reducing the final number of terrorist attacks. This demonstrates the comparative advantage of utilizing the SAPP model, which may prove to be critical in future efforts in counterterrorism.
Read More...