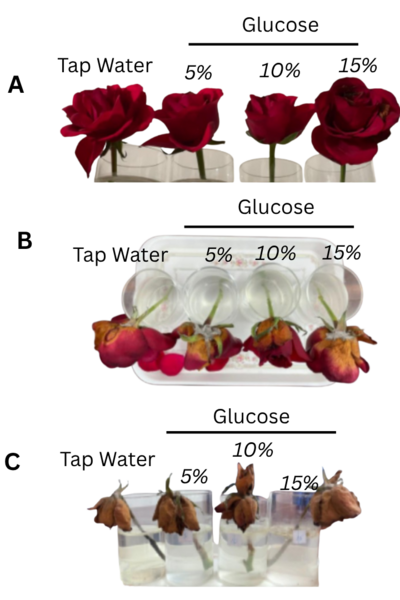
The authors examined the effect of varying glucose concentrations on cut rose longevity.
Read More...Glucose concentration and the longevity of cut roses: sugar-induced senescence

The authors examined the effect of varying glucose concentrations on cut rose longevity.
Read More...Sloan green and red photometry of the Type Ia supernova 2024neh
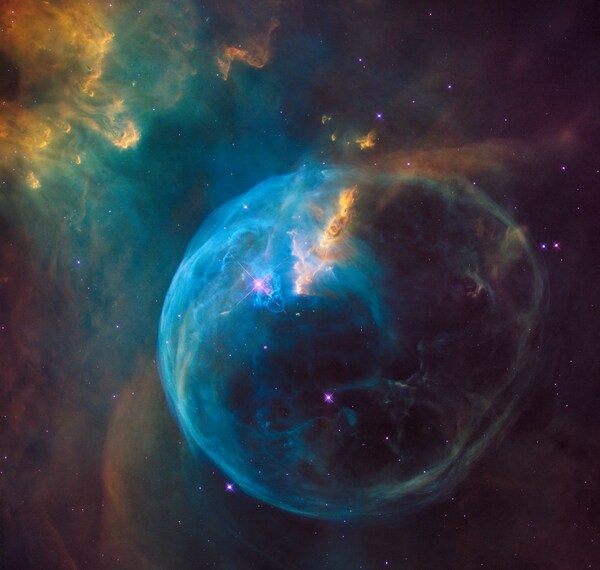

Analysis of the Sloan green and red photometry of the Type Ia supernova 2024neh
Read More...Predicting the spread speed of red imported fire ants under different temperature conditions in China

The authors looked at non-natural factors that influenced the spread rate of fire ants in multiple cities in China.
Read More...Incorporating graphite from pencils as a component of lithium-ion batteries
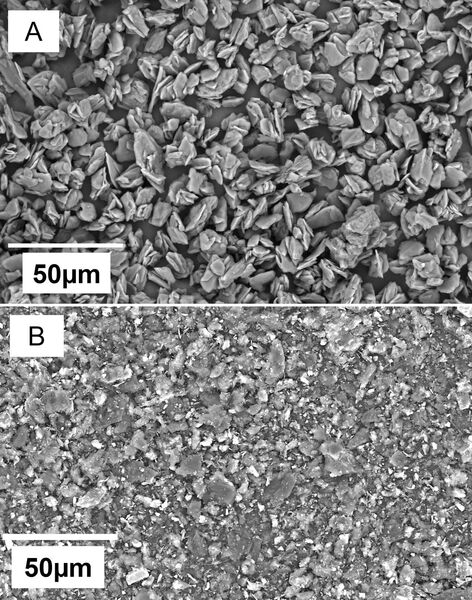
The authors looked at the ability to use graphite from pencils in anodes of lithium-anode batteries.
Read More...Investigating the impact of short-chain fatty acids on myofiber dynamics and insulin sensitivity

The authors looked at the impacts of short-chain fatty acids on muscle fiber formation as well as insulin sensitivity using a model of mouse myoblasts.
Read More...Levering machine learning to distinguish between optimal and suboptimal basketball shooting forms
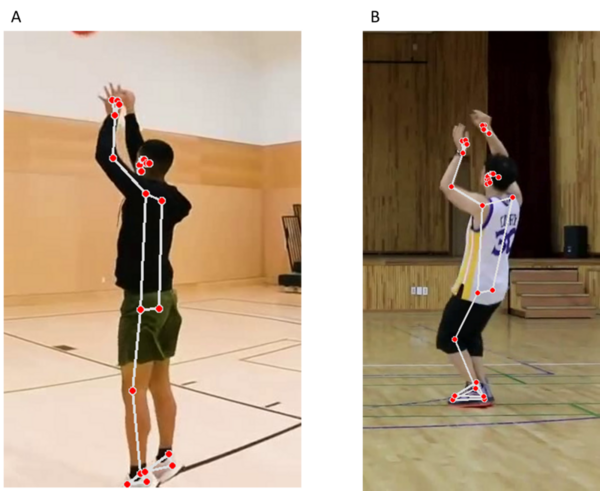

The authors looked at different ways to build computational resources that would analyze shooting form for basketball players.
Read More...The impact of political ideologies on renewable energy adoption
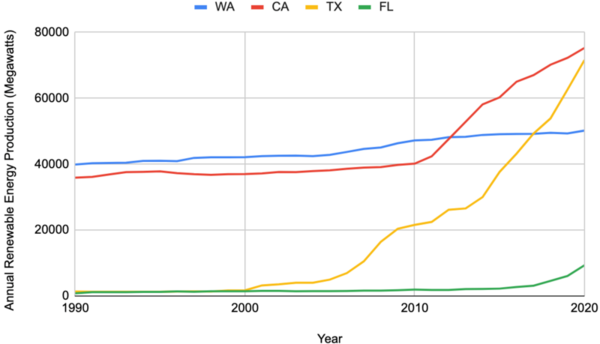
The authors compare rates of renewable energy adoption between states that historically vote for democrats versus republicans in presidential elections.
Read More...Genetic Bioaugmentation of Oryza sativa to Facilitate Self-Detoxification of Arsenic In-Situ
Arsenic contamination in rice, caused by the use of arsenic-laden groundwater for irrigation, is a growing global concern, affecting over 150 million people. To address this, researchers hypothesized that genetically modifying rice plants with arsenic-resistant genes could reduce arsenic uptake and allow the plants to detoxify arsenic, making them safer to consume.
Read More...Using text embedding models as text classifiers with medical data

This article describes the classification of medical text data using vector databases and text embedding. Various large language models were used to generate this medical data for the classification task.
Read More...Evaluating the antimicrobial activity of maitake mushroom extract against Staphylococcus epidermidis
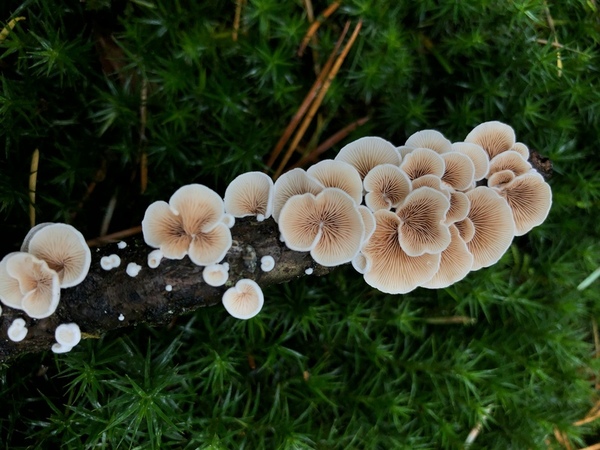

Here, seeking to explore new antimicrobial therapies, the authors investigated the antimicrobial activity of Maitake mushroom extract against Staphylococcus epidermidis, a common cause of antibiotic resistant hospital-acquired infections. They found that Maitake extract showed potent antimicrobial activity, with higher concentrations showing inhibition comparable to tetracycline.
Read More...