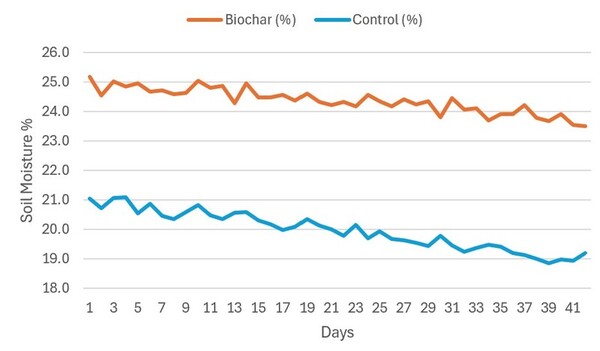
The study explored converting Gracilaria seaweed waste—known for releasing toxic hydrogen sulfide when decomposed—into biochar as a sustainable solution for waste management and soil improvement.
Read More...Enhanced soil fertility through seaweed-derived biochar: A comparative analysis with commercial fertilizers

The study explored converting Gracilaria seaweed waste—known for releasing toxic hydrogen sulfide when decomposed—into biochar as a sustainable solution for waste management and soil improvement.
Read More...A potential enzymatic pathway for polystyrene degradation using saliva of greater wax moth Galleria mellonella
Investigation of the potential of waxworm saliva, the secretion of Galleria mellonella, for plastic degradation.
Read More...Investigating sustainable insulation materials: Analysis of biofoams and petroleum-derived foams
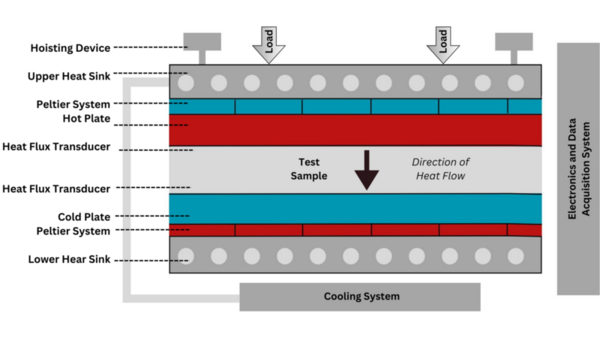
The authors looked into eco-friendly alternatives for insulating material. They ultimately found that a polyurethane derived from eggshells was an effective insulator and further research into it is warranted.
Read More...Development of novel biodegradable bioplastics for packaging film using mango peels

Here the authors explored the development of biodegradable bioplastic films derived from mango peels as a sustainable solution to plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from fruit waste. They optimized the film's mechanical properties and water resistance through adjusting processing conditions and incorporating plasticizers and a hydrophobic coating, ultimately demonstrating its potential as a bacteriostatic and biodegradable alternative to conventional plastic food wrap.
Read More...An exploration of western mosquitofish as the animal component in an aquaponic farming system
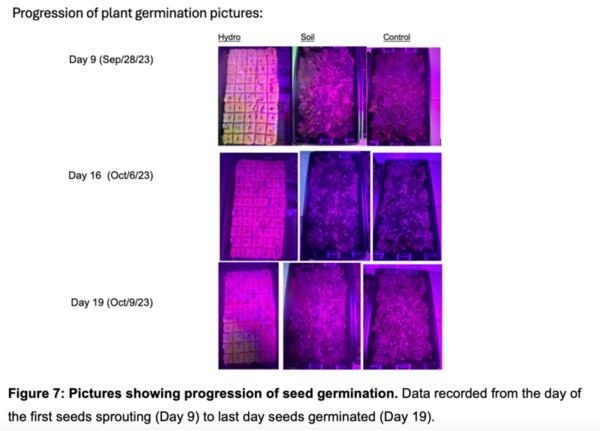
Aquaponics (the combination of aquatic plant farming with fish production) is an innovative farming practice, but the fish that are typically used, like tilapia, are expensive and space-consuming to cultivate. Medina and Alvarez explore other options test if mosquitofish are a viable option in the aquaponic cultivation of herbs and microgreens.
Read More...Lactic acid bacteria protect the growth of Solanum lycopersicum from Sodium dodecyl sulfate
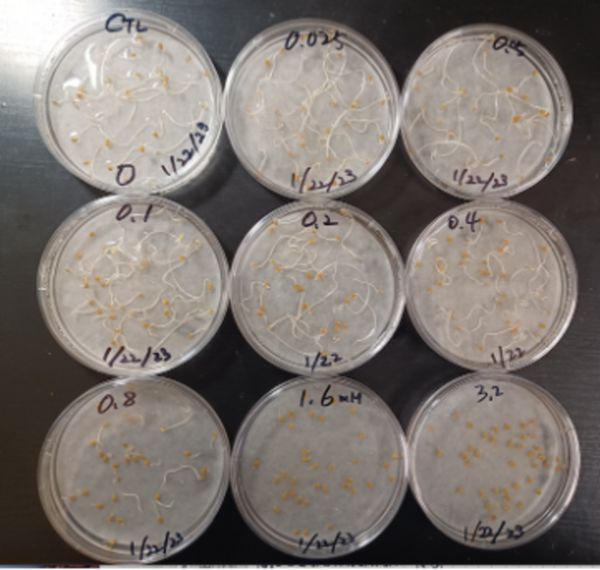
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), a detergent component, can harm plant growth when it contaminates soil and waterways. Authors explored the potential of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) to mitigate SDS-induced stress on plants.
Read More...Slowing ice melting from thermal radiation using sustainable, eco-friendly eggshells
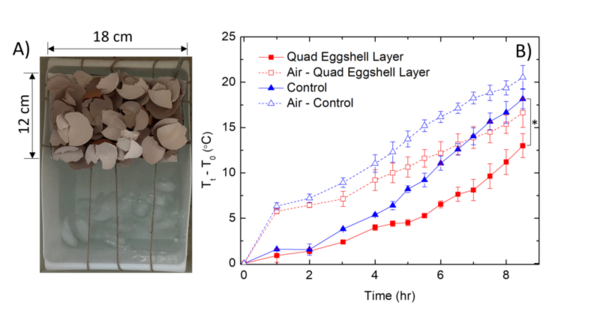
The authors looked at the ability of eggshells to slow ice melting. They found that eggshells were able to increase ice melting time when crushed showing that they were an effective thermal barrier.
Read More...A comparison of the water quality between Chinatown and Bayside: two demographically different regions
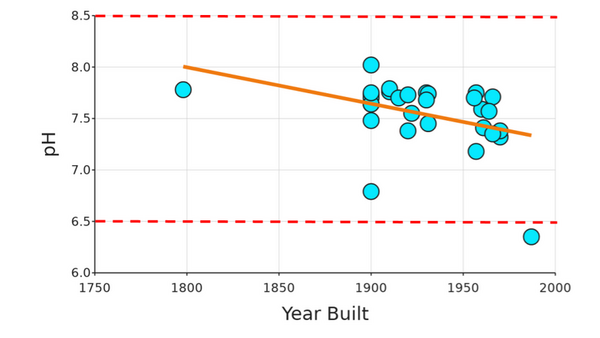
The authors looked at differences in water quality between Chinatown and Bayside. They wanted to look at the racial and economic demographics of each region and how that correlated to access to clean drinking water. Ultimately they did not find any significant differences in water quality, but identified important future directions for this work.
Read More...Polluted water tested from the Potomac River affects invasive species plant growth

Here recognizing the potential for pollution to impact the ecosystems of local waterways, the authors investigated the growth of tiger lilies, which are invasive to the Potomac River, in relation to the level of pollution. The authors report that increasing levels of pollution led to increased growth of the invasive species based on their study.
Read More...From trash to treasure: A sustainable approach to oil spill clean-up
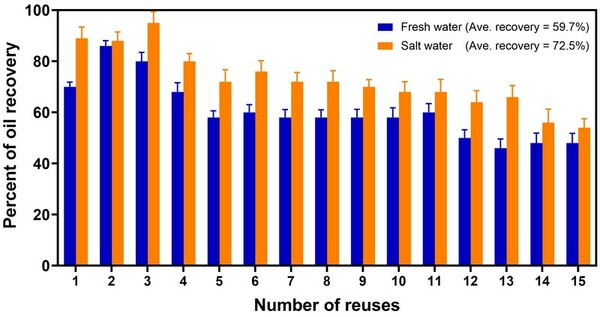
In this study the authors looked at sustainable ways to clean up oil spills that harm marine life. Using water spangle leaves and milk week the authors looked at the ability to recovery oil from both fresh and salt water and the ability to reuse the organic material to clean up spills. Their results show promise to help find a sustainable, eco-friendly way to clean up oil spills and protect marine life and habitats.
Read More...