The authors investigate whether human blood cancers carrying mutations in DNA repair genes possess increased sensitivity to common chemotherapy drugs cisplatin or gemcitabine.
Read More...DNA repair protein mutations alter blood cancer sensitivity to cisplatin or gemcitabine in vitro

The authors investigate whether human blood cancers carrying mutations in DNA repair genes possess increased sensitivity to common chemotherapy drugs cisplatin or gemcitabine.
Read More...Silver nanoparticle-coated orthopedic screws lead to greater calcium precipitation

The authors test whether coating stainless steel orthopedic screws in silver will promote calcium precipitation to improve orthopedic implant integration into bone.
Read More...Diagnosis and treatment delay in patients with OCD in the United States over the past three decades
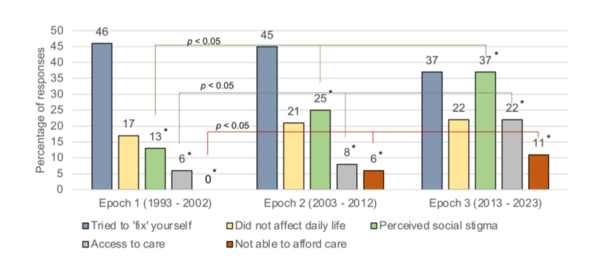
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) can cause significant impairment, and studies indicate that delays in diagnosis and treatment lead to worse outcomes. This study aimed to assess whether these delays have improved over the past three decades and to identify their causes.
Read More...A HOG feature extraction and CNN approach to Parkinson’s spiral drawing diagnosis

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a prevalent neurodegenerative disorder in the U.S., second only to Alzheimer’s disease. Current diagnostic methods are often inefficient and dependent on clinical exams. This study explored using machine and deep learning to enhance PD diagnosis by analyzing spiral drawings affected by hand tremors, a common PD symptom.
Read More...Entropy-based subset selection principal component analysis for diabetes risk factor identification
In this article, the authors looked at developing a strategy that would allow for earlier diagnosis of Diabetes as that improves long-term outcomes. They were able to find that BMI, tricep skin fold thickness, and blood pressure are the risk factors with the highest accuracy in predicting diabetes risk.
Read More...Analysis of the lung microbiome in cystic fibrosis patients using 16S sequencing
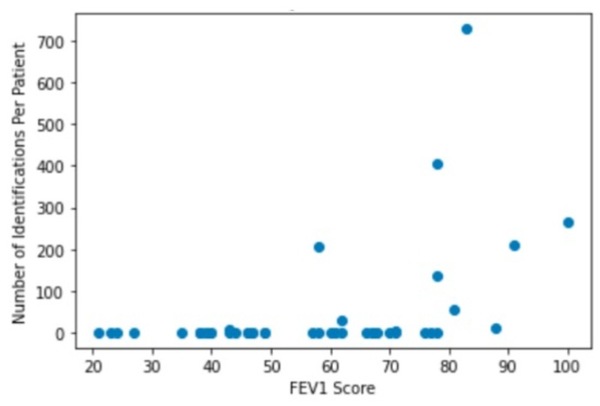
In this article the authors look at the lung microbiome in patients with cystic fibrosis to determine what the major bacterial species present are.
Read More...Upregulation of the Ribosomal Pathway as a Potential Blood-Based Genetic Biomarker for Comorbid Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and PTSD
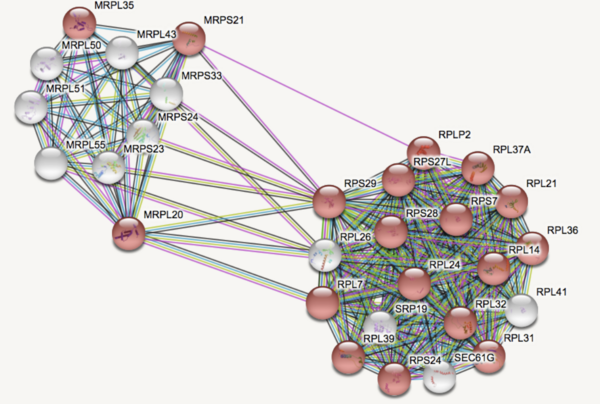
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) are two of the fastest growing comorbid diseases in the world. Using publicly available datasets from the National Institute for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), Ravi and Lee conducted a differential gene expression analysis using 184 blood samples from either control individuals or individuals with comorbid MDD and PTSD. As a result, the authors identified 253 highly differentially-expressed genes, with enrichment for proteins in the gene ontology group 'Ribosomal Pathway'. These genes may be used as blood-based biomarkers for susceptibility to MDD or PTSD, and to tailor treatments within a personalized medicine regime.
Read More...Impact of TCERG1 SNP on gene expression and protein interactome in Huntington’s disease
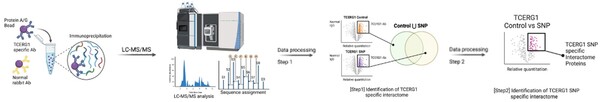
The authors assess a genetic variant within a well-known interaction partner of huntingtin that has been linked to modifying the age of onset of Huntington's disease.
Read More...Using text embedding models as text classifiers with medical data

This article describes the classification of medical text data using vector databases and text embedding. Various large language models were used to generate this medical data for the classification task.
Read More...Survival analysis in cardiovascular epidemiology: nexus between heart disease and mortality
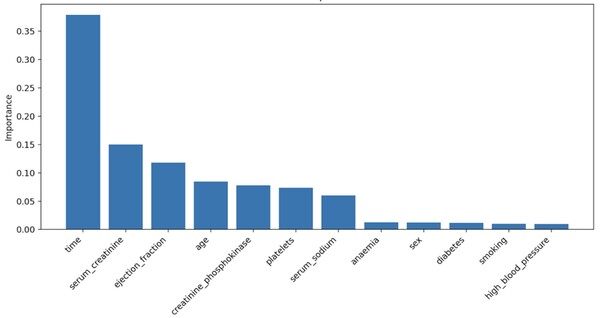
In 2021, over 20 million people died from cardiovascular diseases, highlighting the need for a deeper understanding of factors influencing heart failure outcomes. This study examined multiple variables affecting mortality after heart failure, using random forest models to identify time, serum creatinine, and ejection fraction as key predictors. These findings could contribute to personalized medicine, improving survival rates by tailoring treatment strategies for heart failure patients.
Read More...