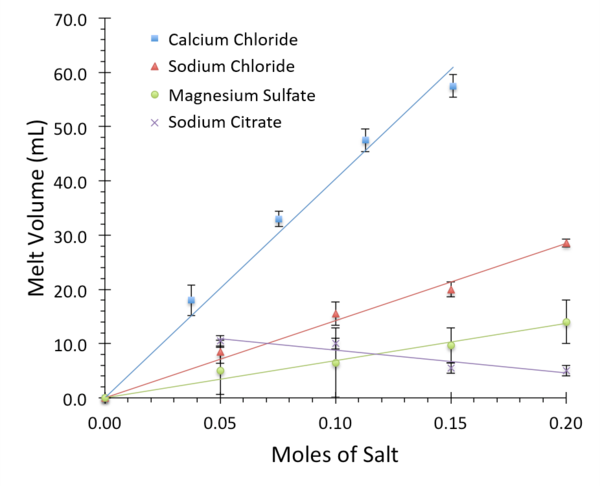
In this study, Imani et al. investigate whether a new proprietary herbal formulation, HF1, can inhibit expression of immune suppressor protein PD-L1. PD-L1 is a transmembrane protein that can be expressed by cancer cells to assist in their ability to avoid attacks from the immune system. Work from this study demonstrates that HF1 treatment can reduce expression of PD-L1 in cultured cancer cells, implicating HF1 as a potential new cancer therapy.
Read More...