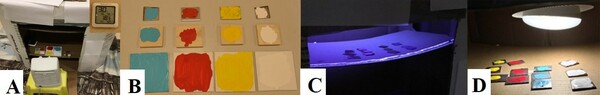
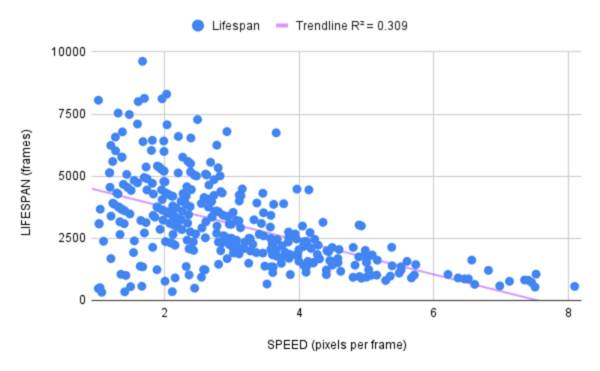
Reducing paint drying time is an important step in improving production efficiency and reducing costs. The authors hypothesized that decreased humidity would lead to faster drying, ultraviolet (UV) light exposure would not affect the paint colors differently, white light exposure would allow for longer wavelength colors to dry at a faster rate than shorter wavelength colors, and substrates with higher roughness would dry slower. Experiments showed that trials under high humidity dried slightly faster than trials under low humidity, contrary to the hypothesis. Overall, the paint drying process is very much dependent on its surrounding environment, and optimizing the drying process requires a thorough understanding of the environmental factors and their interactive effects with the paint constituents.
Read More...

.jpg)