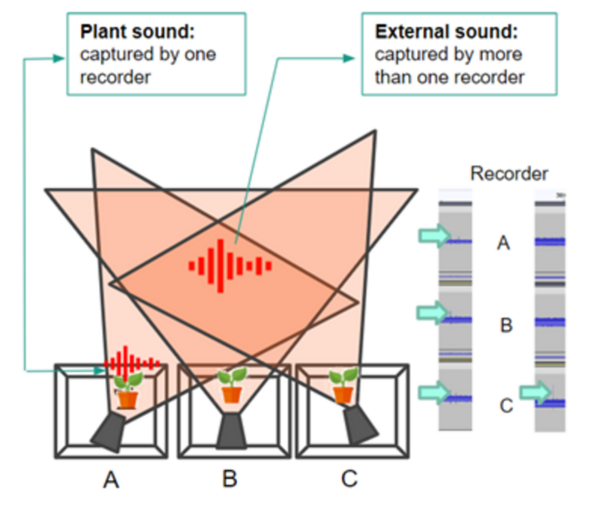
Current horticulture practices often rely on pesticides, causing environmental harm. To address this, authors explore the use of ultrasonic sound emissions to detect plant stress at an individual level.
Read More...Impact of environmental stressors on ultrasonic acoustic emissions in different species of plants

Current horticulture practices often rely on pesticides, causing environmental harm. To address this, authors explore the use of ultrasonic sound emissions to detect plant stress at an individual level.
Read More...The effects of regeneration on memory in planarians
The authors test the ability of planarians to remember conditioned stimuli following regeneration.
Read More...Developing novel plant waste-based hydrogels for skin regeneration and infection detection in diabetic wounds

The purpose of this investigation is to develop a hydrogel to aid skin regeneration by creating an extracellular matrix for fibroblast growth with antibacterial and infection-detection properties. Authors developed two natural hydrogels based on pectin and potato peels and characterized the gels for fibroblast compatibility through rheology, scanning electron microscopy, swelling, degradation, and cell cytotoxicity assays. Overall, this experiment fabricated various hydrogels capable of acting as skin substitutes and counteracting infections to facilitate wound healing. Following further testing and validation, these hydrogels could help alleviate the 13-billion-dollar financial burden of foot ulcer treatment.
Read More...Statistical models for identifying missing and unclear signs of the Indus script
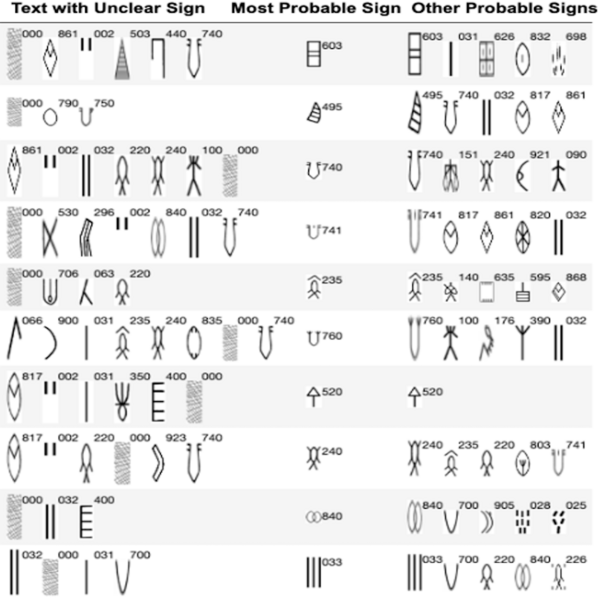
This study utilizes machine learning models to predict missing and unclear signs from the Indus script, a writing system from an ancient civilization in the Indian subcontinent.
Read More...Pressure and temperature influence the efficacy of metal-organic frameworks for carbon capture and conversion
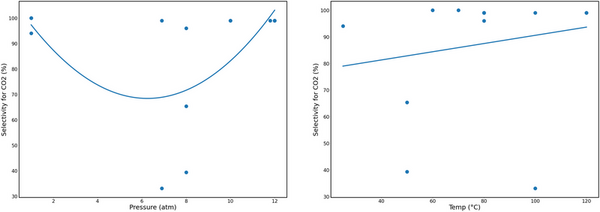
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising new nanomaterials for use in the fight against climate change that can efficiently capture and convert CO2 to other useful carbon products. This research used computational models to determine the reaction conditions under which MOFs can more efficiently capture and convert CO2. In a cost-efficient manner, this analysis tested the hypothesis that pressure and temperature affect the efficacy of carbon capture and conversion, and contribute to understanding the optimal conditions for MOF performance to improve the use of MOFs for controlling greenhouse CO2 emissions.
Read More...Optimal pH for indirect electrochemical oxidation of isopropyl alcohol with Ru-Ti anode and NaCl electrolyte

In this study, the authors determine optimal pH levels for maximizing isopropanol degradation in water. This has important applications for cleaning up polluted wastewater in the environment.
Read More...Developing “Off the Shelf” Pancreases for Diabetic Patients Using Bacterial and Kombucha Tea Waste
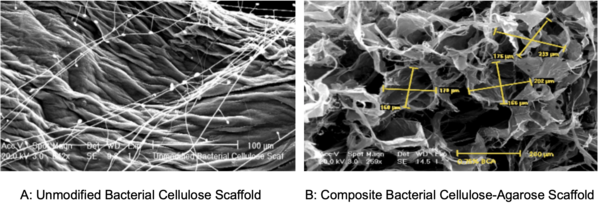
In this study, the authors investigate the suitability of using bacterial cellulose as a scaffold for cell transplants. Interestingly, this cellulose is a can be found in the discard from a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) used to make kombucha.
Read More...Kinetic Monitoring and Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy of the Green Oxidation of (-)-Menthol to (-)-Menthone
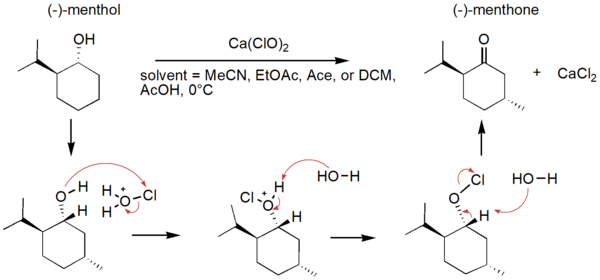
In an effort to reduce the production of hazardous substances, green chemistry aims to make chemical processes more sustainable. One way to do so is changing solvents in chemical reactions. Here, authors assessed different “green” solvents on the oxidation of (-)-menthol to (-)-menthone using Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, optimizing the solvent system for this reaction.
Read More...The Effect of Ultraviolet Radiation and the Antioxidant Curcumin on the Longevity, Fertility, and Physical Structure of Drosophila melanogaster: Can We Defend Our DNA?
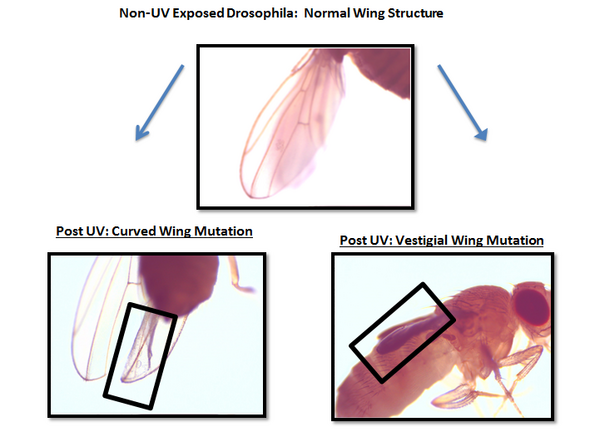
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is known to alter DNA structure and impair cellular function in all living organisms. In this study, Lateef et al examine the effects of UV radiation to determine whether antioxidant-enriched nutrition can combat the potential deleterious effects of UV radiation on Drosophila melanogaster. They found that UVB (320nm) radiation caused a 59% decrease in the Drosophila lifespan and mutagenic effects on flies' physical appearance, but did not significantly affect fertility. Curcumin significantly prolonged lifespan and enhanced fertility for both UV- and non-UV-exposed flies. The research demonstrates the positive potential of natural antioxidants as weapons against radiation-induced diseases including cancer.
Read More...The Effects of Antioxidants on the Climbing Abilities of Drosophila melanogaster Exposed to Dental Resin
Dental resins can be a source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which in unruly amounts can be toxic to cellular and overall health. In this report, the authors test whether the consumption of antioxidant rich foods like avocado and asparagus can protect against the effect of dental resin-derived ROS. However, rather than testing humans, they use fruit flies and their climbing abilities as an experimental readout.
Read More...