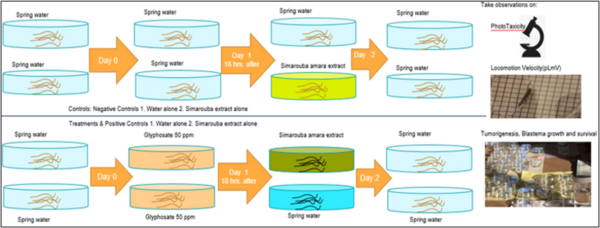
According to the World Health Organization, cancer is a leading cause of death globally. The disease’s prevalence is rapidly increasing in association with factors including the increased use of pesticides and herbicides, such as glyphosate, which is one of the most widely used herbicide ingredients. Natural antioxidants and phytochemicals are being tested as anti-cancer agents due to their antiproliferative, antioxidative, and pro-apoptotic properties. Thus, we aimed to investigate the potential role of S. amara extract as a therapeutic agent against glyphosate-induced toxicity and tumor-like morphologies in regenerating and homeostatic planaria (Dugesia dorotocephala).
Read More...