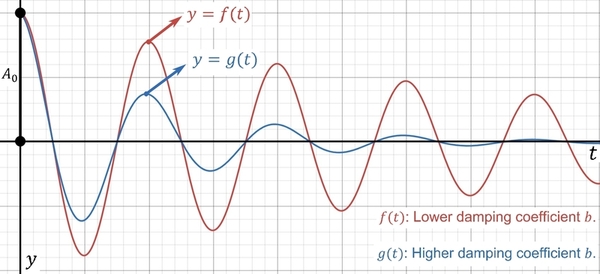
Dynamic viscosity is a quantity that describes the magnitude of a fluid’s internal friction or thickness. Traditionally, scientists measure this quantity by either calculating the terminal velocity of a falling sphere or the time a liquid takes to flow through a capillary tube. However, they have yet to conduct much research on finding this quantity through viscous damped simple harmonic motion. The present study hypothesized that the relationship between the dynamic viscosity and the damping coefficient is positively correlated.
Read More...
_resized.jpg)