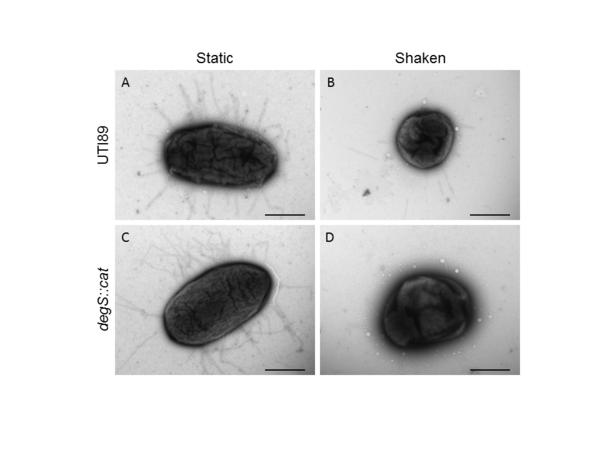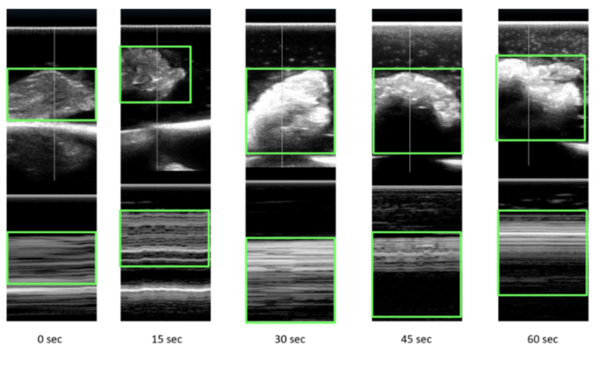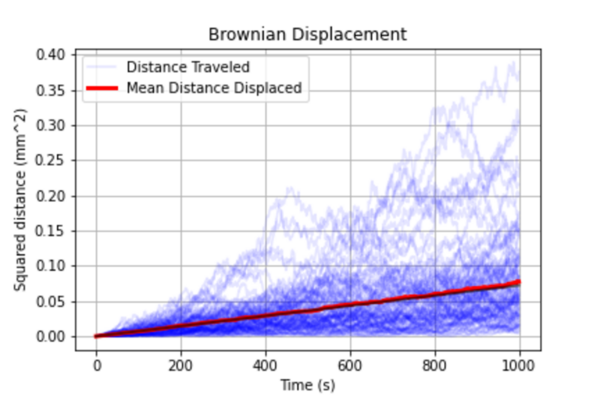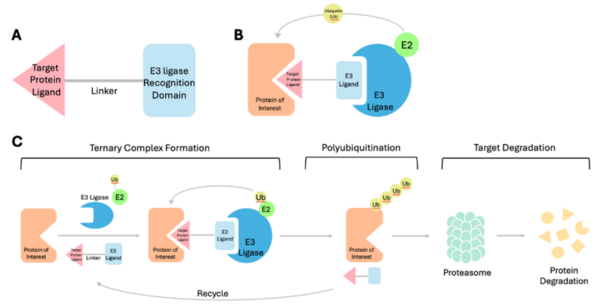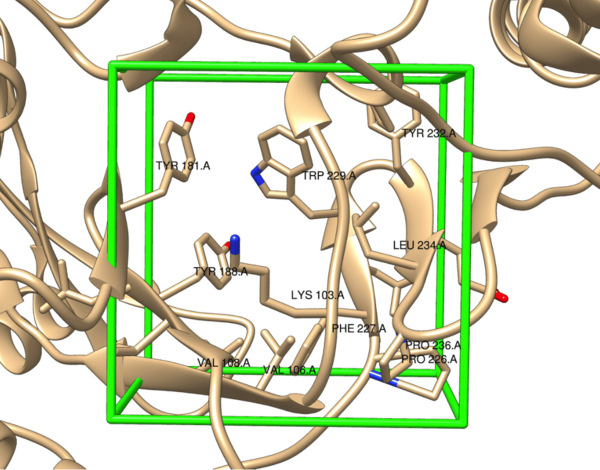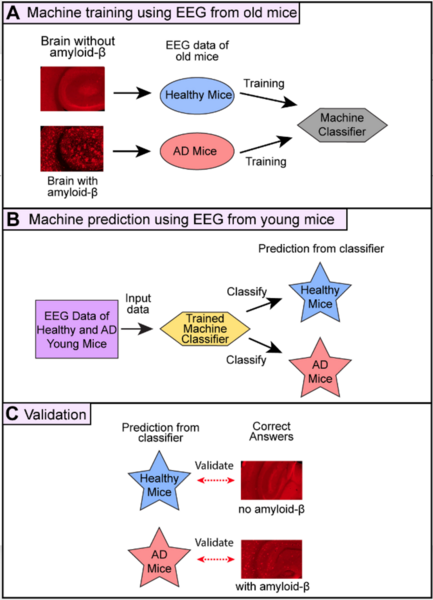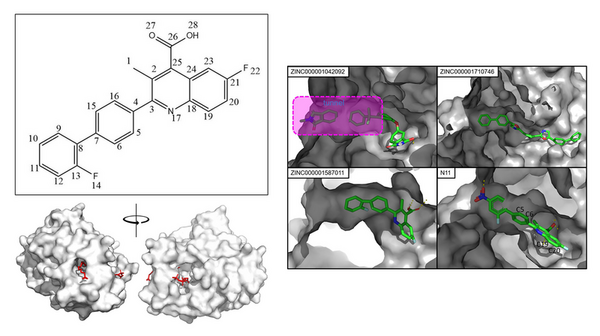
In this study, the authors ask whether a Tau immunotherapy treatment, Hsp70 protein treatment, or dual treatment approach of both the Tau imunotherapy treatment and Hsp70 protein treatment leads to a greater reduction in Tau protein concentration in Alzheimer's disease. Overall, they conclude that the effectiveness of the treatment ultimately relies on the stage of Alzheimer’s.
Read More...