How Ethanol Concentration Affects Catalase Catalysis of Hydrogen Peroxide
(1) Milton Academy, Milton, Massachussetts
https://doi.org/10.59720/21-127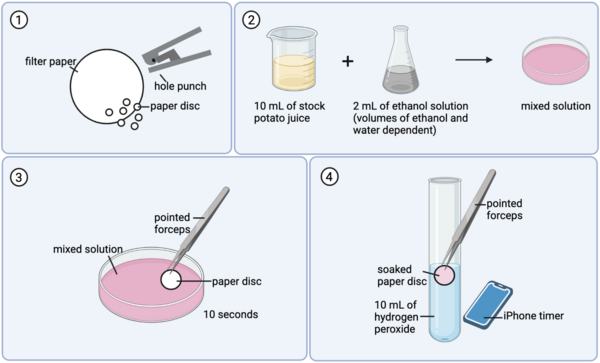
Catalase is a critical enzyme in the human body because it is capable of converting potentially dangerous hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. We sought to determine whether ethanol affects its activity as alcohol consumption has been often linked to hepatitis occurring in the liver, where catalase level is especially high, and ethanol is known to be capable of denaturing proteins. We tested different concentrations of ethanol and found that higher concentrations reduced the activity of catalase. We infer that this is due to ethanol’s ability to replace intramolecular hydrogen bonds within catalase with intermolecular hydrogen bonds between its hydroxyl group and catalase. We also conjecture that catalase catalyzes ethanol oxidation, which consumes hydrogen peroxide and thus decreases the amount of remaining hydrogen peroxide that undergoes conversion by catalase. This work has important implications on the negative effects of ethanol on metabolism, in which catalase plays an important role, and protein function more broadly.
This article has been tagged with: