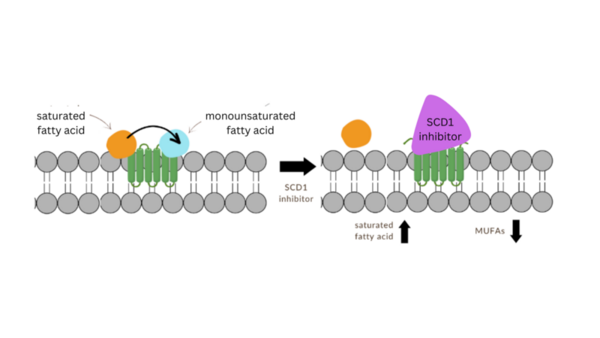
The authors use molecular modeling to test analogs of the stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 (SCD1) inhibitor MF-438 with implications for future development of Parkinson's disease therapeutics.
Read More...Modeling stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 inhibitors to ameliorate α-Syn cytotoxicity in Parkinson's disease

The authors use molecular modeling to test analogs of the stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 (SCD1) inhibitor MF-438 with implications for future development of Parkinson's disease therapeutics.
Read More...Predictions of neural control deficits in elders with subjective memory complaints and Alzheimer’s disease
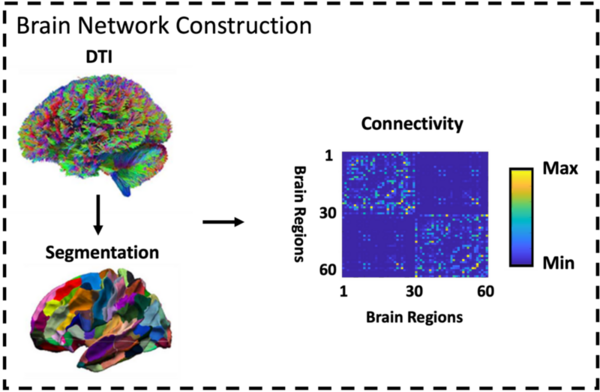
The authors compare neuroimaging datasets to identify potential new biomarkers for earlier detection of Alzheimer's disease.
Read More...A novel approach for predicting Alzheimer’s disease using machine learning on DNA methylation in blood
Here, recognizing the difficulty associated with tracking the progression of dementia, the authors used machine learning models to predict between the presence of cognitive normalcy, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's Disease, based on blood DNA methylation levels, sex, and age. With four machine learning models and two dataset dimensionality reduction methods they achieved an accuracy of 53.33%.
Read More...Prediction of preclinical Aβ deposit in Alzheimer’s disease mice using EEG and machine learning
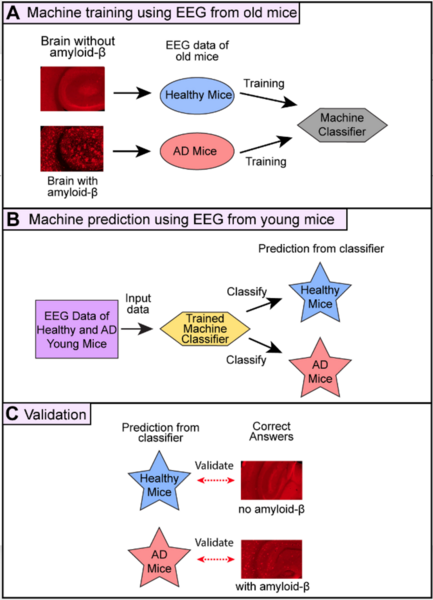
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common disease affecting 6 million people in the U.S., but no cure exists. To create therapy for AD, it is critical to detect amyloid-β protein in the brain at the early stage of AD because the accumulation of amyloid-β over 20 years is believed to cause memory impairment. However, it is difficult to examine amyloid-β in patients’ brains. In this study, we hypothesized that we could accurately predict the presence of amyloid-β using EEG data and machine learning.
Read More...A Novel Alzheimer's Disease Therapeutic Model: Attenuating Hyperphosphorylated Tau and Amyloid β (Aβ) Aggregates by Characterizing Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Neuroprotective Properties of Natural Extracts
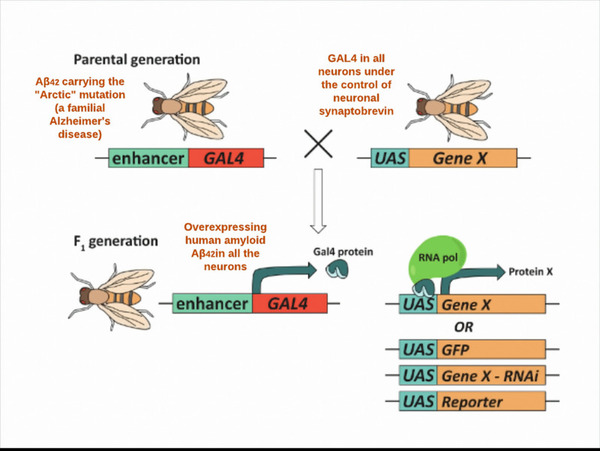
Oxidative damage and neuro-inflammation were the key pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. In this study, 30 natural extracts from plant roots and leaves with extensive anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties were consumed by Drosophila melanogaster. Several assays were performed to evaluate the efficacy of these combinational extracts on delaying the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. The experimental group showed increased motor activity, improved associative memory, and decreased lifespan decline relative to the control group.
Read More...Effects of Withania Somnifera on Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 1A in the model organism Eisenia Fetida
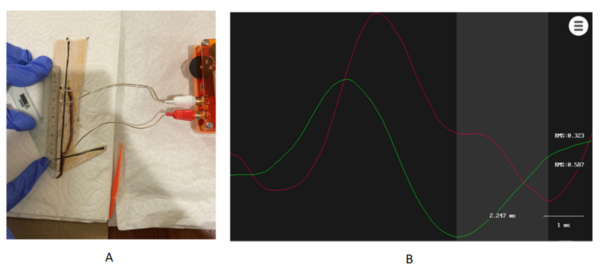
In this study, the authors investigate whether Eisenia Fetida nerve signal speed correlates with Withania somnifera ingestion, a possible way to protect against demyelination.
Read More...A novel approach for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease using deep neural networks with magnetic resonance imaging
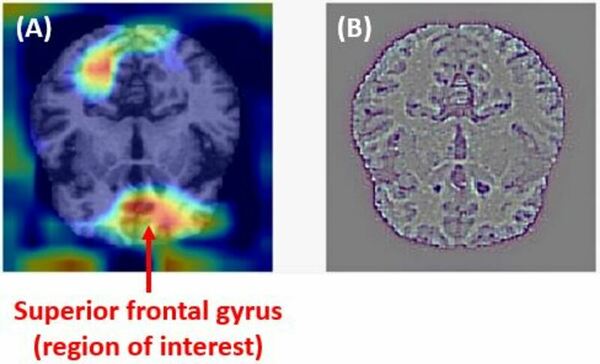
In the battle against Alzheimer's disease, early detection is critical to mitigating symptoms in patients. Here, the authors use a collection of MRI scans, layering with deep learning computer modeling, to investigate early stages of AD which can be hard to catch by human eye. Their model is successful, able to outperform previous models, and detected regions of interest in the brain for further consideration.
Read More...Misconceptions regarding heart disease are prevalent among american adults and minors
In this study, the authors created a survey to assess misconceptions and knowledge deficits regarding cardiovascular diseases exist among US adults and minors.
Read More...Using the COmplex PAthway SImulator, Stage Analysis, and Chemical Kinetics to Develop a Novel Solution to Lower Tau Concentrations in Alzheimer’s Disease
In this study, the authors ask whether a Tau immunotherapy treatment, Hsp70 protein treatment, or dual treatment approach of both the Tau imunotherapy treatment and Hsp70 protein treatment leads to a greater reduction in Tau protein concentration in Alzheimer's disease. Overall, they conclude that the effectiveness of the treatment ultimately relies on the stage of Alzheimer’s.
Read More...The Effects of Ezetimibe on Triglyceride and Alanine Transaminase Reduction in Drosophila Melanogaster Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)

Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a condition where a surplus of triglycerides or fat are present in the liver. In this study, ezetimibe, a cholesterol lowering drug, was used to treat flies modeling NAFLD. Compared to the coconut oil fed flies that were transferred to the control medium, the flies transferred to the control medium treated with ezetimibe showed a decrease in their triglyceride and alanine transaminase level.
Read More...