
The authors explored the effects of the Mount Laurel Doctrine on housing affordability, unemployment rate, and civilian labor force in Burlington County, New Jersey compared to nearby counties.
Read More...The Mount Laurel doctrine: A case study in housing affordability and the labor market in New Jersey

The authors explored the effects of the Mount Laurel Doctrine on housing affordability, unemployment rate, and civilian labor force in Burlington County, New Jersey compared to nearby counties.
Read More...Converting SiO2 wafers to hydrophobic using chlorotrimethylsilane
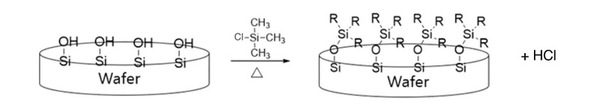
Semiconductors are the center of the fourth industrial revolution as they are key components for all electronics. Exposed wafers made of silicon (Si), which can easily oxidize, convert to silicon dioxide (SiO2). The surface of SiO2 wafers consists of many Si-OH bonds, allowing them to easily bond with water, resulting in a “wet” or hydrophilic condition. We sought to determine a way to modify the surface of SiO2 wafers to become hydrophobic to ensure safe wet cleaning.
Read More...Color photometry and light curve modeling of apparent transient 2023jri
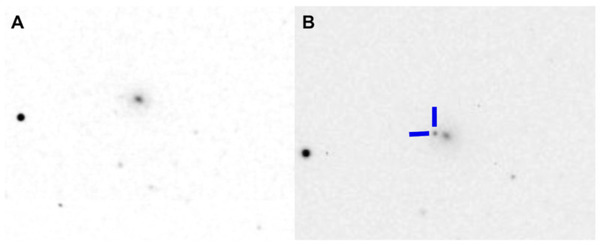
Observing transients like supernovae, which have short-lived brightness variations, helps astronomers understand cosmic phenomena. This study analyzed transient 2023jri, hypothesizing it was a Type IIb supernova. By collecting and analyzing data over four weeks, including light and color curves, they confirmed its classification and provided additional insights into this less-studied supernova type.
Read More...Modeling stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 inhibitors to ameliorate α-Syn cytotoxicity in Parkinson's disease
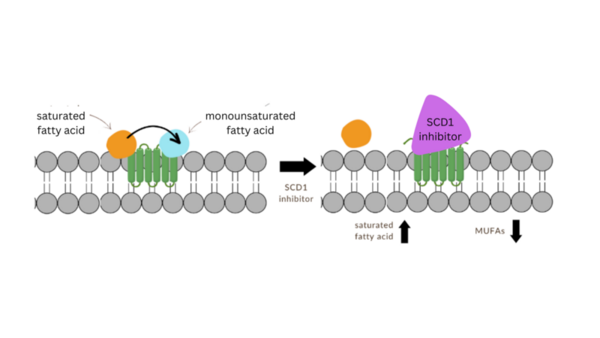
The authors use molecular modeling to test analogs of the stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 (SCD1) inhibitor MF-438 with implications for future development of Parkinson's disease therapeutics.
Read More...The anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects of polyherbal drug AS20 on HeLa cells resistant to 5-Fluorouracil
%20final%202-5-23.jpg)
The authors looked at 5-FU resistant HeLa cells and the ability of an herbal extract to show anti-inflammatory properties.
Read More...Correlation between shutdowns and CO levels across the United States.
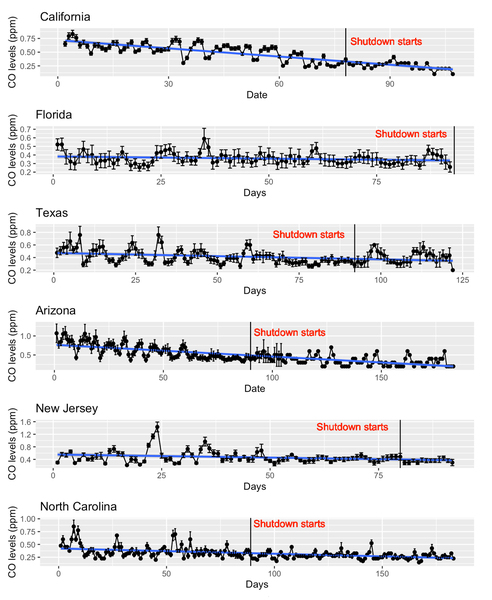
Concerns regarding the rapid spread of Sars-CoV2 in early 2020 led company and local governmental officials in many states to ask people to work from home and avoid leaving their homes; measures commonly referred to as shutdowns. Here, the authors investigate how shutdowns affected carbon monoxide (CO) levels in 15 US states using publicly available data. Their results suggest that CO levels decreased as a result of these measures over the course of 2020, a trend which started to reverse after shutdowns ended.
Read More...The effects of stress on the bacterial community associated with the sea anemone Diadumene lineata

In healthy ecosystems, organisms interact in a relationship that helps maintain one another's existence. Stress can disrupt this interaction, compromising the survival of some of the members of such relationships. Here, the authors investigate the effect of stress on the interaction between anemones and their microbiome. Their study suggests that stress changes the composition of the surface microbiome of the anemone D. lineata, which is accompanied by an increase in mucus secretion. Future research into the composition of this stress-induced mucus might reveal useful antimicrobial properties.
Read More...Analysis of the effects of positive ions and boundary layer temperature at various hypersonic speeds on boundary layer density
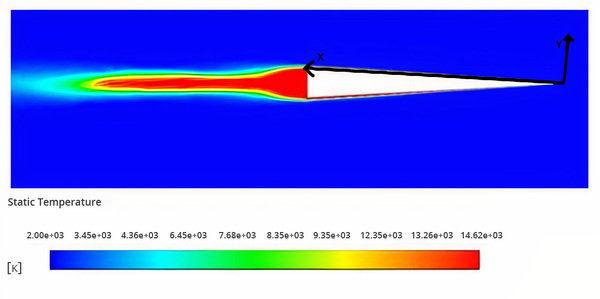
This study's goal was to identify the Mach numbers for which electrostatic drag and heat transfer manipulation would be most applicable inside the stratosphere. The experiments were conducted using computational fluid dynamics software. The study demonstrated that, on average, higher Mach speeds resulted in a considerably higher potential decrease in density. The study highlights that further research on the surface charge method is warranted to explore higher hypersonic speeds within the stratosphere.
Read More...The Development and Maximization of a Novel Photosynthetic Microbial Fuel Cell Using Rhodospirillum rubrum
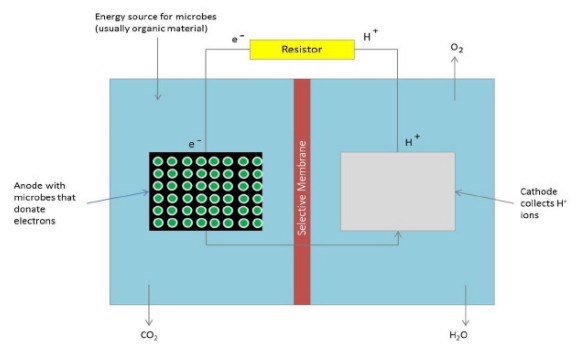
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are bio-electrochemical systems that utilize bacteria and are promising forms of alternative energy. Similar to chemical fuel cells, MFCs employ both an anode (accepts electrons) and a cathode (donates electrons), but in these devices the live bacteria donate the electrons necessary for current. In this study, the authors assess the functionality of a photosynthetic MFC that utilizes a purple non-sulfur bacterium. The MFC prototype they constructed was found to function over a range of environmental conditions, suggesting its potential use in industrial models.
Read More...Investigating the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the cognitive dissonance of adolescents
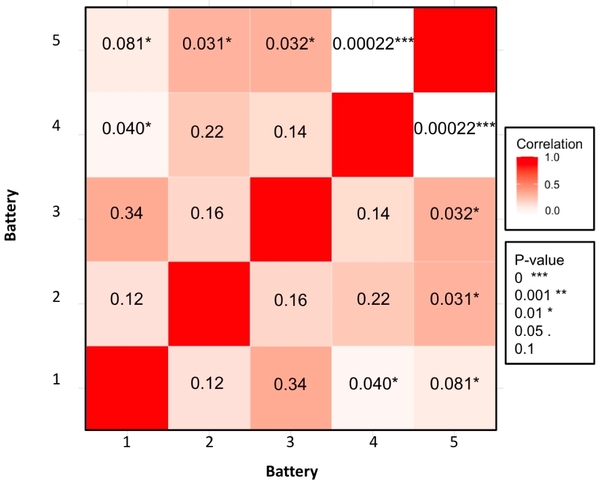
The authors survey adolescents about aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic to explore perspectives that may give rise to cognitive dissonance.
Read More...