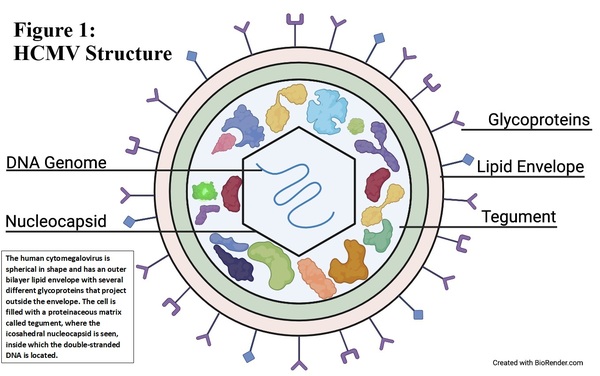
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) causes serious infections in immunocompromised patients and therapies to inhibit latent HCMV are not developed. Using CRISPR/Cas9, the authors were able to delete an important promoter region in HCMV.
Read More...Using CRISPR technology to inhibit the replication of human cytomegalovirus by deletion of a gene promoter

Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) causes serious infections in immunocompromised patients and therapies to inhibit latent HCMV are not developed. Using CRISPR/Cas9, the authors were able to delete an important promoter region in HCMV.
Read More...Effects on Learning and Memory of a Mutation in Dα7: A D. melanogaster Homolog of Alzheimer's Related Gene for nAChR α7

Alzheimer's disease (AD) involves the reduction of cholinergic activity due to a decrease in neuronal levels of nAChR α7. In this work, Sanyal and Cuellar-Ortiz explore the role of the nAChR α7 in learning and memory retention, using Drosophila melanogaster as a model organism. The performance of mutant flies (PΔEY6) was analyzed in locomotive and olfactory-memory retention tests in comparison to wild type (WT) flies and an Alzheimer's disease model Arc-42 (Aβ-42). Their results suggest that the lack of the D. melanogaster-nAChR causes learning, memory, and locomotion impairments, similar to those observed in Alzheimer's models Arc-42.
Read More...Activated NF-κB Pathway in an Irf6-Deficient Mouse Model for Van der Woude Syndrome
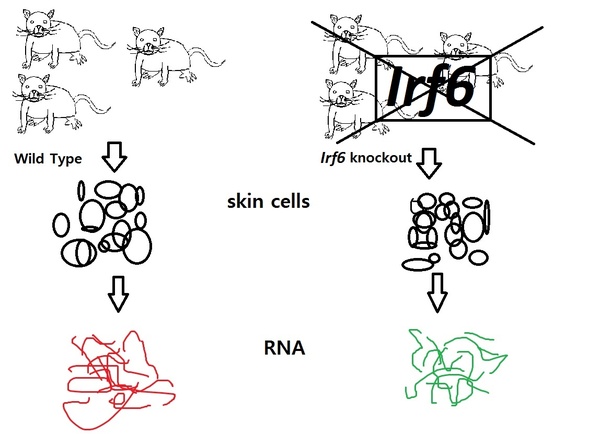
Van der Woude syndrome is a common birth defect caused by mutations in the gene Irf6. In this project, students used microarray expression analysis from wild-type and Irf6-deficient mice in order to identify gene networks or pathways differentially regulated due to the Irf6 mutation. They found NF-κB pathway to be activated in deficient mice.
Read More...Effects of urban traffic noise on the early growth and transcription of Arabidopsis thaliana
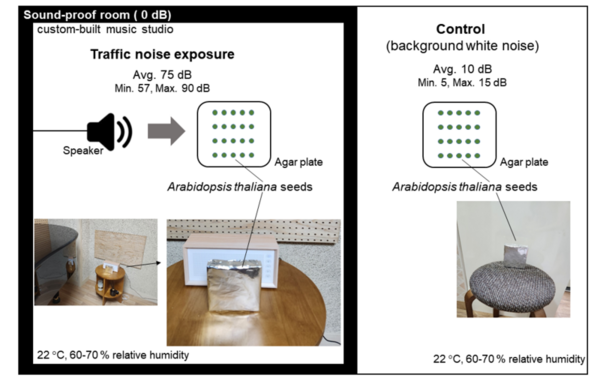
This article explores the largely unstudied impact of noise pollution on plant life. By exposing Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings to urban traffic noise, the study found a significant increase in seedling growth, alongside substantial changes in gene expression. This research reveals critical insights into how noise pollution affects plant physiology and contributes to a broader understanding of its ecological impacts, helping to guide future efforts in ecosystem conservation.
Read More...Predicting smoking status based on RNA sequencing data
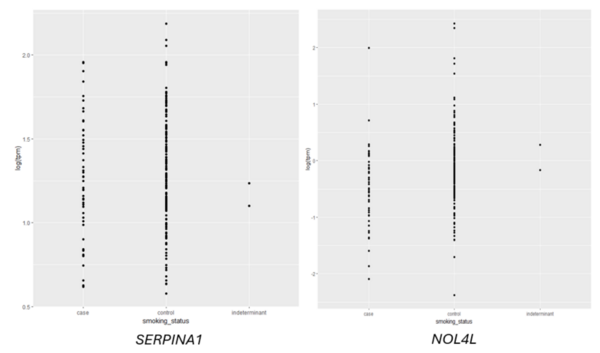
Given an association between nicotine addiction and gene expression, we hypothesized that expression of genes commonly associated with smoking status would have variable expression between smokers and non-smokers. To test whether gene expression varies between smokers and non-smokers, we analyzed two publicly-available datasets that profiled RNA gene expression from brain (nucleus accumbens) and lung tissue taken from patients identified as smokers or non-smokers. We discovered statistically significant differences in expression of dozens of genes between smokers and non-smokers. To test whether gene expression can be used to predict whether a patient is a smoker or non-smoker, we used gene expression as the training data for a logistic regression or random forest classification model. The random forest classifier trained on lung tissue data showed the most robust results, with area under curve (AUC) values consistently between 0.82 and 0.93. Both models trained on nucleus accumbens data had poorer performance, with AUC values consistently between 0.65 and 0.7 when using random forest. These results suggest gene expression can be used to predict smoking status using traditional machine learning models. Additionally, based on our random forest model, we proposed KCNJ3 and TXLNGY as two candidate markers of smoking status. These findings, coupled with other genes identified in this study, present promising avenues for advancing applications related to the genetic foundation of smoking-related characteristics.
Read More...Identification of a core set of model agnostic mRNA associated with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
In this study, the authors analyze gene expression datasets to determine if there is a core set of genes dysregulated during nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Read More...Disruptions in protein-protein interactions between HTT, PRPF40B, and MECP2 are involved in Lopes-Maciel-Rodan syndrome
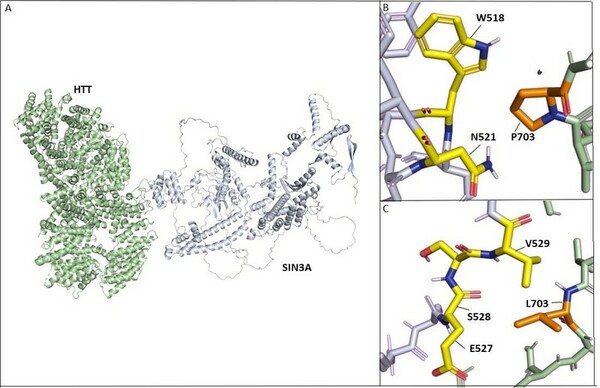
In an extensive study of gene mutations, and their resulting effect on protein-protein interactions, Desai and Stork found that HTT-PRPF40B-MECP2 interactions are weakened with progression of Lopes-Maciel-Rodan syndrome.
Read More...Expressional correlations between SERPINA6 and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma-linked genes
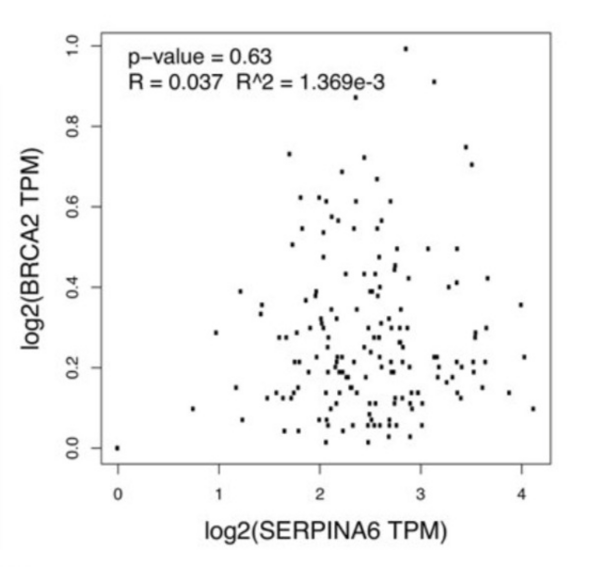
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common form of pancreatic cancer, with early diagnosis and treatment challenges. When any of the genes KRAS, SMAD4, TP53, and BRCA2 are heavily mutated, they correlate with PDAC progression. Cellular stress, partly regulated by the gene SERPINA6, also correlates with PDAC progression. When SERPINA6 is highly expressed, corticosteroid-binding globulin inhibits the effect of the stress hormone cortisol. In this study, the authors explored whether there is an inverse correlation between the expression of SERPINA6 and PDAC-linked genes.
Read More...Transcriptional Regulators are Upregulated in the Substantia Nigra of Parkinson’s Disease Patients
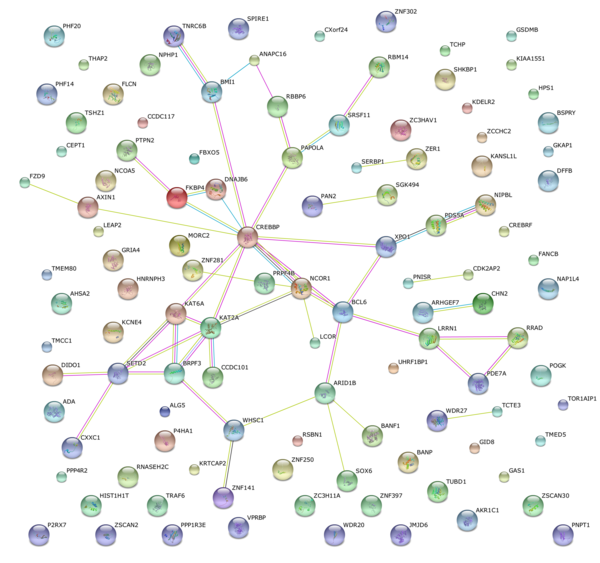
This article investigates differences in gene expression in the brains of patients with and without Parkinson's disease. The authors identify a crucial transcriptional regulator may be a relevant target for future therapeutic treatment for Parkinson's disease.
Read More...Combinatorial treatment by siNOTCH and retinoic acid decreases A172 brain cancer cell growth
Treatments inhibiting Notch signaling pathways have been explored by researchers as a new approach for the treatment of glioblastoma tumors, which is a fast-growing and aggressive brain tumor. Recently, retinoic acid (RA) therapy, which inhibits Notch signaling, has shown a promising effect on inhibiting glioblastoma progression. RA, which is a metabolite of vitamin A, is very important in embryonic cellular development, which includes the regulation of multiple developmental processes, such as brain neurogenesis. However, high doses of RA treatment caused many side effects such as headaches, nausea, redness around the injection site, or allergic reactions. Therefore, we hypothesized that a combination treatment of RA and siRNA targeting NOTCH1 (siNOTCH1), the essential gene that activates Notch signaling, would effectively inhibit brain cancer cell proliferation. The aim of the study was to determine whether inhibiting NOTCH1 would inhibit the growth of brain cancer cells by cell viability assay. We found that the combination treatment of siNOTCH1 and RA in low concentration effectively decreased the NOTCH1 expression level compared to the individual treatments. However, the combination treatment condition significantly decreased the number of live brain cancer cells only at a low concentration of RA. We anticipate that this novel combination treatment can provide a solution to the side effects of chemotherapy.
Read More...