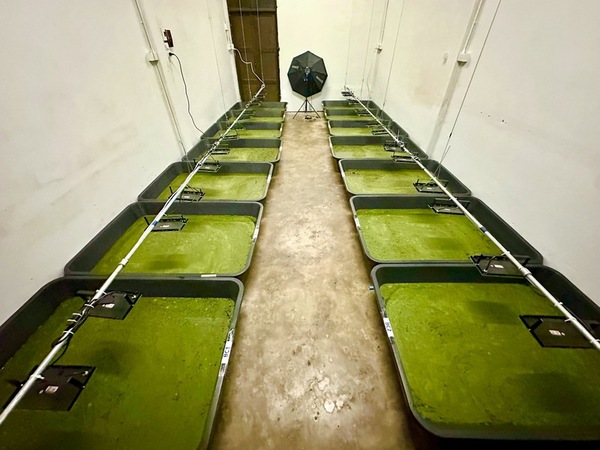
he rapid growth of the human population is driving food crises in Thailand and Southeast Asia, while contributing to global food insecurity and a larger carbon footprint. One potential solution is cultivating duckweed (Wolffia globosa) for consumption, as it grows quickly and can provide an alternative protein source. This research explored two methods to optimize duckweed cultivation: using phosphorus- and nitrogen-rich growing media and plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB).
Read More...