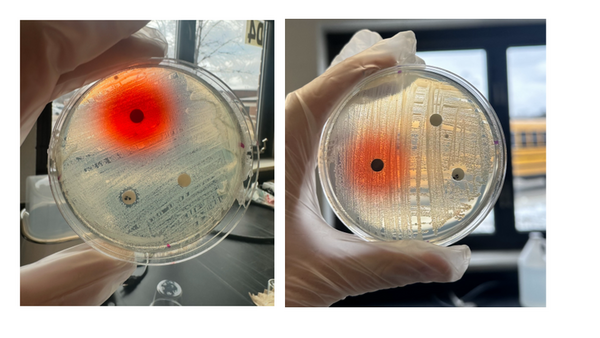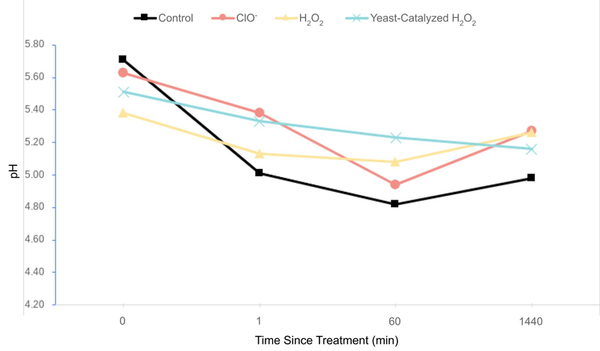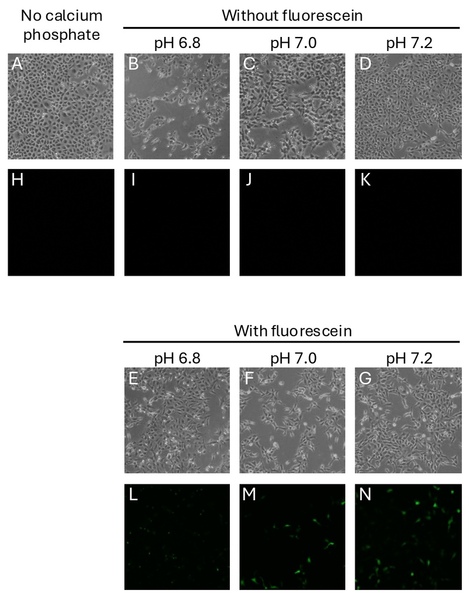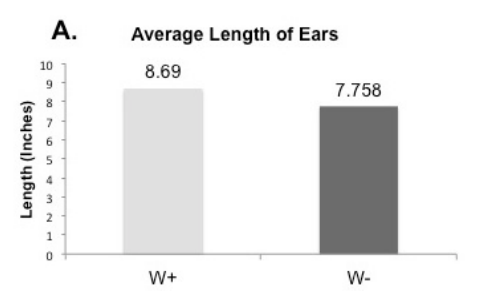
Farmers will need to increase crop yields to feed the world's growing population efficiently. The authors here investigate the effects of growing corn in the presence or absence of ragweed, an invasive weed found in many fields and gardens. Surprisingly, the authors found that corn grown in the presence of weeds grew taller and were more productive than corn that had weeds removed. This may help gardeners rethink the necessity of weeding, and may point a way to improve farm yields in the future.
Read More...