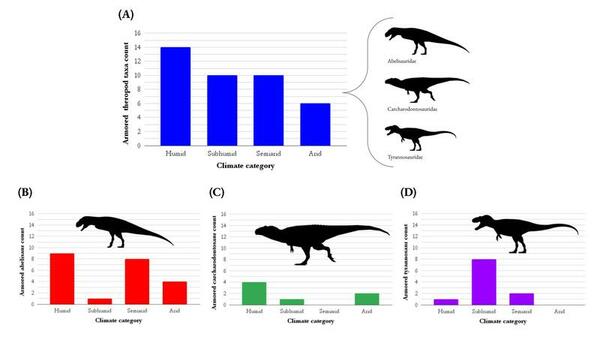
The facial integument, or external skin tissues, were assessed on set of dinosaurs from the Allosauroidea clade to test whether dermal patterns served specific functions.
Read More...Preliminary investigation of Allosauroidea facial integument and the evolution of theropod facial armor

The facial integument, or external skin tissues, were assessed on set of dinosaurs from the Allosauroidea clade to test whether dermal patterns served specific functions.
Read More...Evaluating cinnamaldehyde as an antibacterial agent in a produce wash for leafy greens

Recognizing a growing demand for organic produce, the authors sought to investigate plant-based antibiotic solutions to meet growing consumer demand for safe produce and also meet microbial standards of the USDA. The authors investigated the use of cinnamaldehyde as an antibacterial again E. coli, finding that lettuce treated with cinnamaldehyde displayed significantly lower colony-forming units of E. coli when compared to lettuce treated with chlorine bleach.
Read More...Can the Growth Mindset Encourage Girls to Pursue “Male” Careers?

Despite major advances in gender equality, men still far outnumber women in science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) professions. The purpose of this project was to determine whether mindset could affect a student’s future career choices and whether this effect differed based on gender. When looking within the gender groups, 86% of females who had a growth mindset were likely to consider a “male” career, whereas only 16% of females with fixed mindset would likely to consider a “male” career. Especially for girls, cultivating a growth mindset may be a great strategy to address the problem of fewer girls picking STEM careers.
Read More...Probiotic biosorption as a way to remove heavy metal in seawater

In this study, the authors address the concerns of heavy metal contamination in industrial and feedlot water waste. They test whether added probiotics are capable of taking up heavy metals in water to attenuate pollution.
Read More...Genomic Signature Analysis for the Strategic Bioremediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Mangrove Ecosystems in the Gulf of Tonkin

Engineered bacteria that degrade oil are currently being considered as a safe option for the treatment of oil spills. For this approach to be successful, the bacteria must effectively express oil-degrading genes they uptake as part of an external genoming vehicle called a "plasmid". Using a computational approach, the authors investigate plasmid-bacterium compatibility to find pairs that ensure high levels of gene expression.
Read More...The role of CYP46A1 and its metabolic product, 24S-hydroxycholesterol, in Neuro 2A cell death
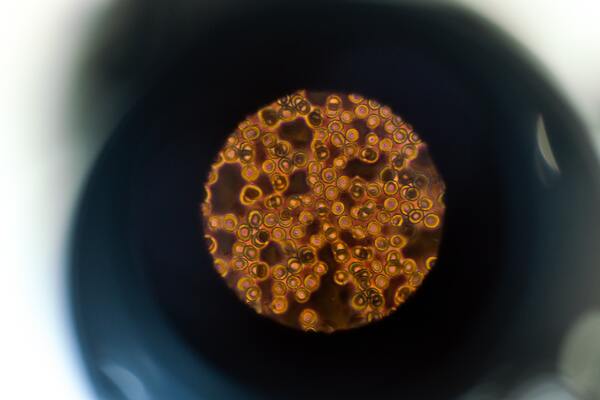
Cholesterol is a major component of neuronal cell membrane and myelin sheath. In this study, the authors either transfected Neuro 2A cells with CYP46A1 cDNA or treated the cells with 24SHC. Cells expressing CYP46A1 had significantly less viability compared to the negative control. Up to 55% reduction in cell viability was also observed in 24S-HC-treated cells. This work supports that CYP46A1 and 24S-HC could directly trigger cell death. The direct involvement of 24S-HC in cell death provides further evidence that 24S-HC can be a promising biomarker for diagnosing brain damage severity.
Read More...Comparative screening of dose-dependent and strain-specific antimicrobial efficacy of berberine against a representative library of broad-spectrum antibiotics

We hypothesize that berberine has broad-spectrum antibacterial properties, along with potency that is comparable to current broad-spectrum antibiotics that are commercially available. Here, we screened berberine against four strains of bacteria and evaluated its antimicrobial activity against five broad-spectrum antibiotics from different classes to better quantify berberine’s antibacterial activity and compare its efficacy as an antibacterial agent to the broad-spectrum antibiotics. Our results indicated that berberine had strain-selective cytotoxic effects and was significantly less potent than most of the broad-spectrum antibiotics
Read More...Effect of mass and center of gravity on vehicle speed and braking performance

In this study, the authors test whether a gravity vehicle, which is a vehicle powered by its own gravity on a ramp, could be designed to move faster when mathematical calculations for optimal mass and center of gravity were applied in the design.
Read More...Long Range Radio Communication for Urban Sensor Networks
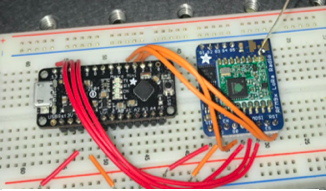
This study investigates the feasibility of using long-range radio communication in a busy city environment in order to begin better understanding how the Internet of Things might be implemented into smart cities.
Read More...Effect of Increasing Concentrations of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Hatching, Survival and Development of Artemia salina

Cannabidiol, or CBD, is a widely available over the counter treatment used for various medical conditions. However, CBD exerts its effects on the endocannabinoid system, which is involved in neural maturation, and could potentially have adverse effects on brain development. Here, the impact of CBD on the development of brine shrimp (Artemia salina) was assessed. Differences in dose responses were observed.
Read More...