In this paper, Thomas et al. introduce a new, affordable way to study characteristics of rocket motors using small-scale rocket motors.
Read More...Browse Articles
Transfer Learning with Convolutional Neural Network-Based Models for Skin Cancer Classification
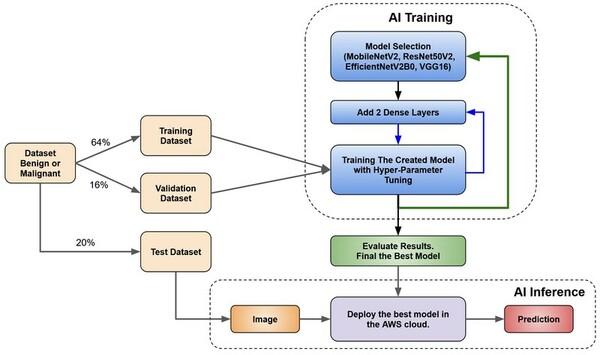
Skin cancer is a common and potentially deadly form of cancer. This study’s purpose was to develop an automated approach for early detection for skin cancer. We hypothesized that convolutional neural network-based models using transfer learning could accurately differentiate between benign and malignant moles using natural images of human skin.
Read More...Quantitative analysis and development of alopecia areata classification frameworks
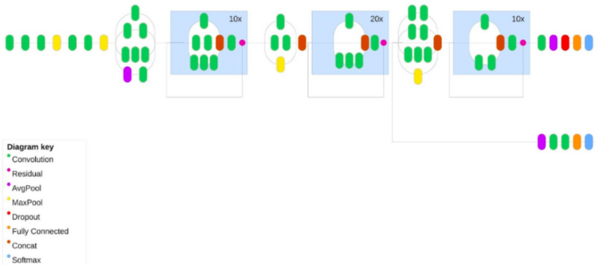
This article discusses Alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder causing sudden hair loss due to the immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles. The article introduces the use of deep learning (DL) techniques, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNN), for classifying images of healthy and alopecia-affected hair. The study presents a comparative analysis of newly optimized CNN models with existing ones, trained on datasets containing images of healthy and alopecia-affected hair. The Inception-Resnet-v2 model emerged as the most effective for classifying Alopecia Areata.
Read More...Testing Simarouba amara’s therapeutic effects against weedicide-induced tumor-like morphology in planarians
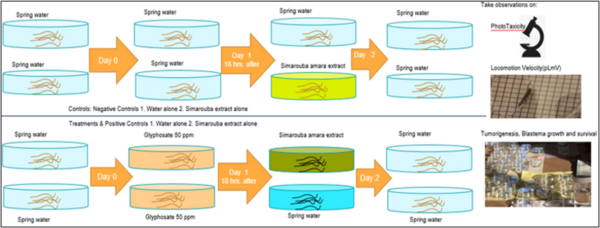
According to the World Health Organization, cancer is a leading cause of death globally. The disease’s prevalence is rapidly increasing in association with factors including the increased use of pesticides and herbicides, such as glyphosate, which is one of the most widely used herbicide ingredients. Natural antioxidants and phytochemicals are being tested as anti-cancer agents due to their antiproliferative, antioxidative, and pro-apoptotic properties. Thus, we aimed to investigate the potential role of S. amara extract as a therapeutic agent against glyphosate-induced toxicity and tumor-like morphologies in regenerating and homeostatic planaria (Dugesia dorotocephala).
Read More...Prediction of diabetes using supervised classification
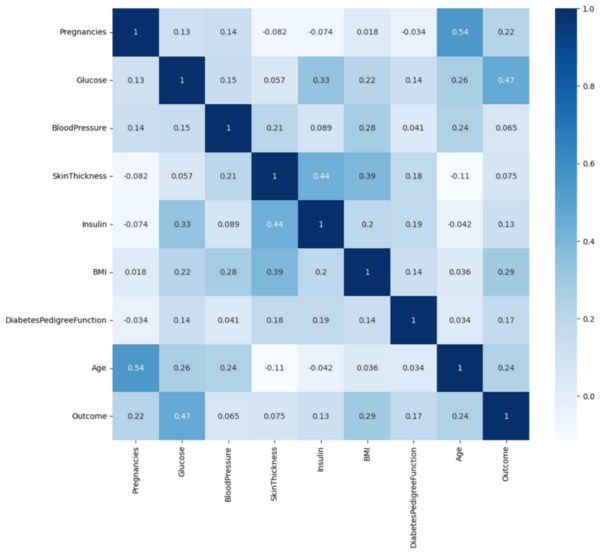
The authors develop and test a machine learning algorithm for predicting diabetes diagnoses.
Read More...Interaction of light with water under clear and algal bloom conditions
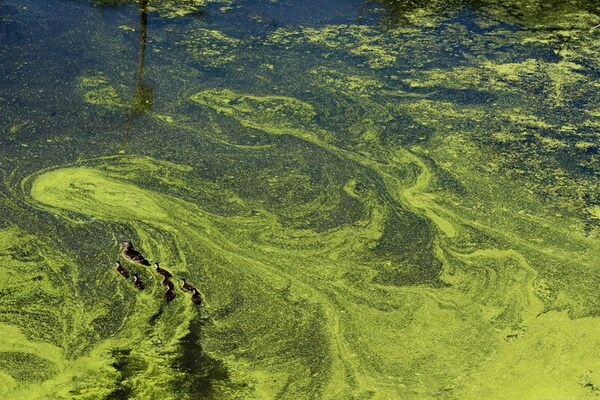

Here, recognizing the potential harmful effects of algal blooms, the authors used satellite images to detect algal blooms in water bodies in Wyoming based on their reflectance of near infrared light. They found that remote monitoring in this way may provide a useful tool in providing early warning and advisories to people who may live in close proximity.
Read More...Determining the impact of caffeine on aggression in Betta splendens
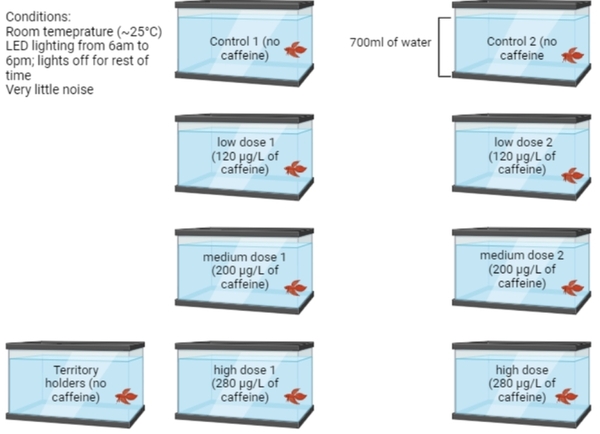
The authors test the effect of caffeine on the behavior of the Siamese fighting fish Betta splendens.
Read More...A comparison of the water quality between Chinatown and Bayside: two demographically different regions
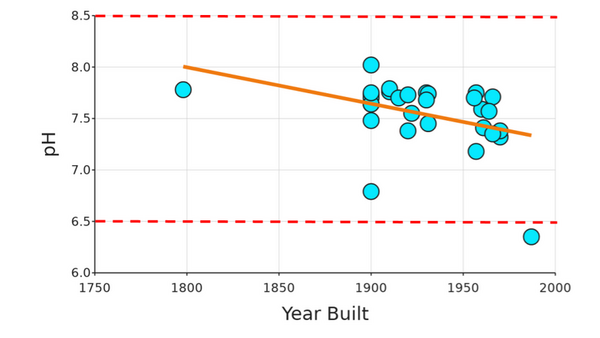
The authors looked at differences in water quality between Chinatown and Bayside. They wanted to look at the racial and economic demographics of each region and how that correlated to access to clean drinking water. Ultimately they did not find any significant differences in water quality, but identified important future directions for this work.
Read More...Heterotrophic culture of Spirulina platensis improved its growth and the study of its nutritional effect
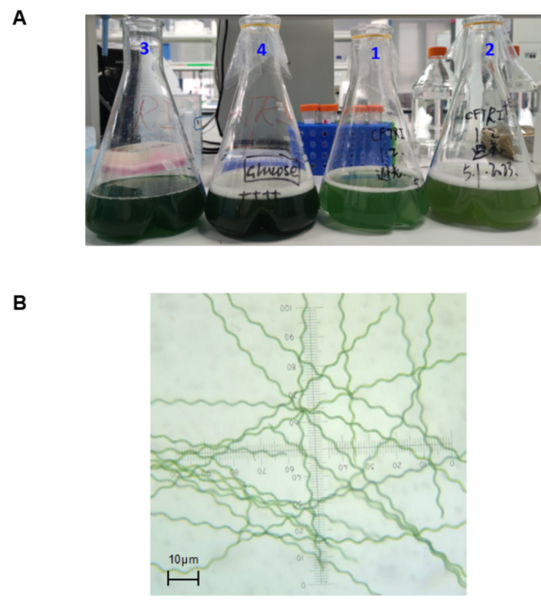

The authors looked at the ability to grow S. platensis on a larger scale with reduced cost given that it is currently quite expensive to grow, but poses as an important food source in the future.
Read More...Alloferon improves the growth performance and developmental time of mealworms (Tenebrio molitor)
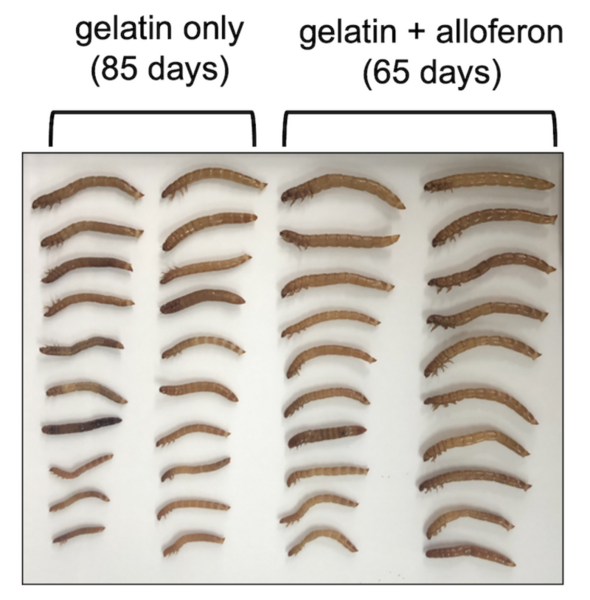

Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) are important food sources for reptiles, birds, and other organisms, as well as for humans. However, the slow growth and low survival rate of mealworms cause problems for mass production. Since alloferon, a synthetic peptide, showed long-term immunological effects on mealworms, we hypothesized that alloferon would function as a growth promoter to maximize mealworm production. We discovered that the overall weight of the alloferon-containing gelatin diet group was 39.5-90% heavier, and the development time of the experimental group was shortened up to 20.6-39.6% than the control group.
Read More...