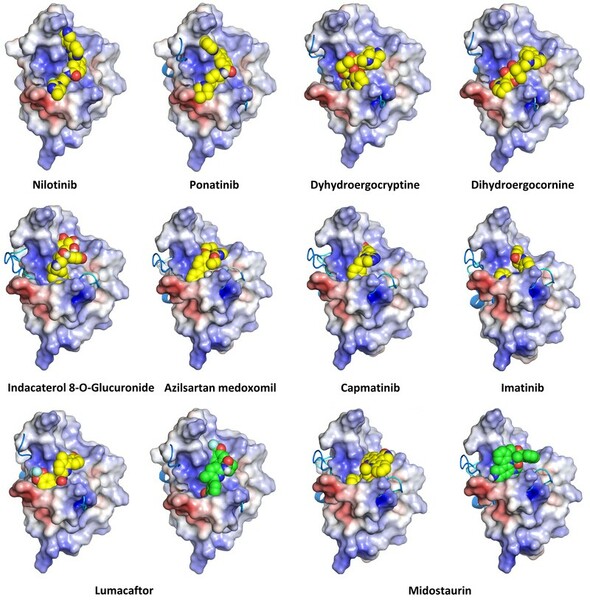
Molecules which bind to proteins that aggregate abnormally in neurodegenerative diseases could be promising drugs for these diseases. In this study, Zhang, Wu, Zhang, and Dang simulate the binding behavior of various molecules to screen for candidates which could be promising candidates for drug development.
Read More...