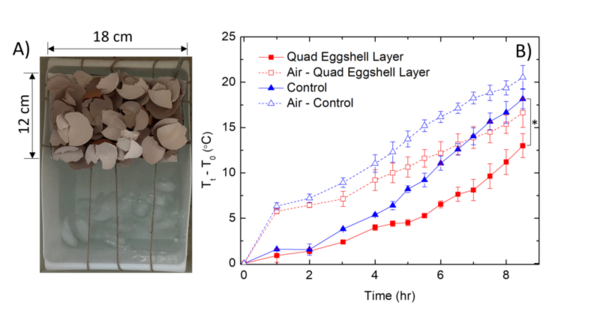
With low-temperature transportation being critical for the progress of research and medical services by preserving biological samples and vaccines, the optimization of cold storage materials is more critical now than ever. The exclusive use of dry ice has its limitations. Notably, it proves insufficient for cold storage during long-range transportation necessary for the delivery of specimens to rural areas. In this article, the authors have proposed a new means of cold storage through the combination of dry ice and ethanol. Upon thorough analysis, the authors have determined their new method as considerably better than the use of pure dry ice across many characteristics, including cold storage capacity, longevity of material, and financial and environmental feasibility.
Read More...