Arsenic contamination in rice, caused by the use of arsenic-laden groundwater for irrigation, is a growing global concern, affecting over 150 million people. To address this, researchers hypothesized that genetically modifying rice plants with arsenic-resistant genes could reduce arsenic uptake and allow the plants to detoxify arsenic, making them safer to consume.
Read More...Browse Articles
Genetic underpinnings of the sex bias in autism spectrum disorder

Here, seeking to identify a possible explanation for the more frequent diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in males than females, they sought to investigate a potential sex bias in the expression of ASD-associated genes. Based on their analysis, they identified 17 ASD-associated candidate genes that showed stronger collective sex-dependent expression.
Read More...Genetic algorithm based features selection for predicting the unemployment rate of India

The authors looked at using genetic algorithms to look at the Indian labor market and what features might best explain any variation seen. They found that features such as economic growth and household consumption, among others, best explained variation.
Read More...Stress-induced genetic memory inheritance and retention in Planarian biological model
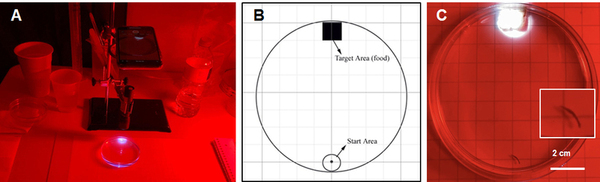
This study explored whether planaria, known for their regenerative abilities, can retain learned memories after regeneration and how stressors like alcohol affect memory.
Read More...The impact of genetic, drug, and procedural factors on cardiac xenograft survival days in non-human primates
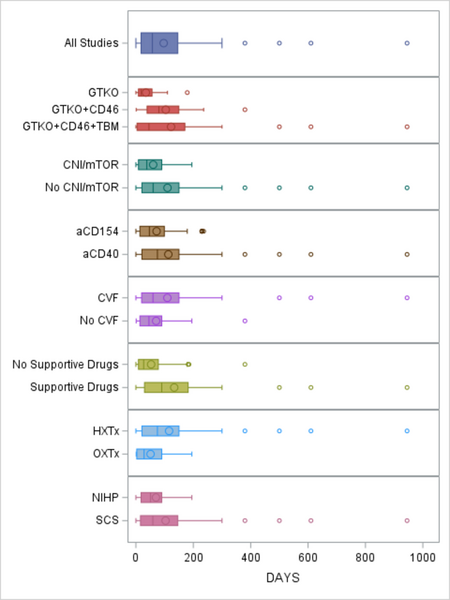
Due to a critical shortage of donor hearts, researchers are exploring cardiac xenotransplantation—transplanting animal hearts into humans—as a potential solution. This study synthesized nearly two decades of preclinical research to evaluate multiple factors affecting xenograft survival.
Read More...Contribution of environmental factors to genetic variation in the Pacific white-sided dolphin

Here the authors sought to understand the effects of different variables that may be tied to pollution and climate change on genetic variation of Pacific white-sided dolphins, a species that is currently threatened by water pollution. Based on environmental data collected alongside a genetic distance matrix, they found that ocean currents had the most significant impact on the genetic diversity of Pacific white-sided dolphins along the Japanese coast.
Read More...Optimizing Interplanetary Travel Using a Genetic Algorithm

In this work, the authors develop an algorithm that solves the problem of efficient space travel between planets. This is a problem that could soon be of relevance as mankind continues to expand its exploration of outer space, and potentially attempt to inhabit it.
Read More...Investigation of unknown causes of uveal melanoma uncovers seven recurrent genetic mutations
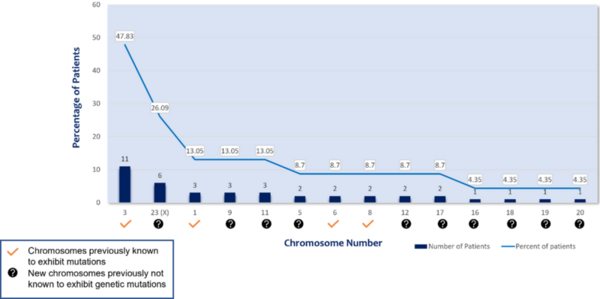
Uveal melanoma (UM) is a rare subtype of melanoma but the most frequent primary cancer of the eye in adults. The goal of this study was to research the genetic causes of UM through a comprehensive frequency analysis of base-pair mismatches in patient genomes. Results showed a total of 130 genetic mutations, including seven recurrent mutations, with most mutations occurring in chromosomes 3 and X. Recurrent mutations varied from 8.7% to 17.39% occurrence in the UM patient sample, with all mutations identified as missense. These findings suggest that UM is a recessive heterogeneous disease with selective homozygous mutations. Notably, this study has potential wider significance because the seven genes targeted by recurrent mutations are also involved in other cancers.
Read More...Simulations of Cheetah Roaming Demonstrate the Effect of Safety Corridors on Genetic Diversity and Human-Cheetah Conflict

Ecological corridors are geographic features designated to allow the movement of wildlife populations between habitats that have been fragmented by human landscapes. Corridors can be a pivotal aspect in wildlife conservation because they preserve a suitable habitat for isolated populations to live and intermingle. Here, two students simulate the effect of introducing a safety corridor for cheetahs, based on real tracking data on cheetahs in Namibia.
Read More...Mapping QTLs for Popping Ability in a Popcorn × Dent Maize Genetic Cross

Have you ever wondered what contributes to the popping ability of popcorn? In this study, the authors use Quantitative Trait Locus (QTL) mapping to identify genes that may contribute to specific popping characteristics including kernel size and popping expansion volume (PEV).
Read More...