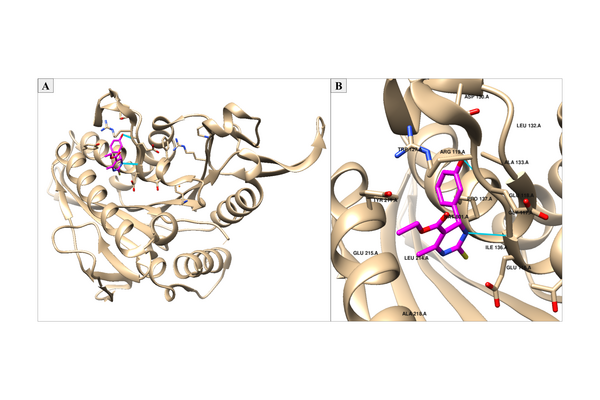
As cancer continues to take millions of lives worldwide, the need to create effective therapeutics for the disease persists. The kinesin Eg5 assembly motor protein is a promising target for cancer therapeutics as inhibition of this protein leads to cell cycle arrest. Monastrol, a small dihydropyrimidine-based molecule capable of inhibiting the kinesin Eg5 function, has attracted the attention of medicinal chemists with its potency, affinity, and specificity to the highly targeted loop5/α2/α3 allosteric binding pocket. In this work, we employed high-throughput virtual screening (HTVS) to identify potential small molecule Eg5 inhibitors from a designed set of novel dihydropyrimidine analogs structurally similar to monastrol.
Read More...