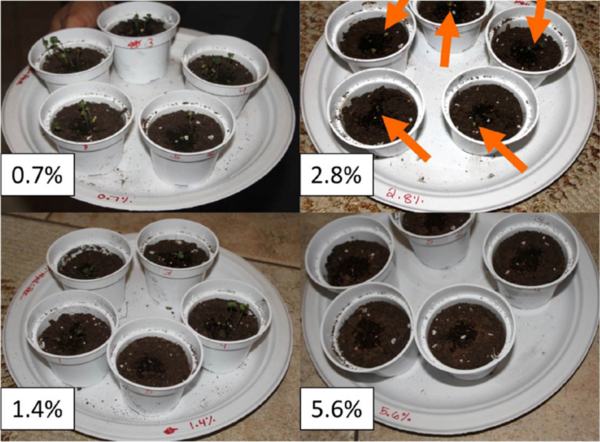

In this study, the authors assess the antioxidant properties of vitamins A, C and E given to mustard plants after oxidative damage. This research shows an interesting comparison of the vitamins' effect on plant recovery and health.
Read More...The Effect of Antioxidant Vitamins on Mustard Plants in a Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Injury Model

In this study, the authors assess the antioxidant properties of vitamins A, C and E given to mustard plants after oxidative damage. This research shows an interesting comparison of the vitamins' effect on plant recovery and health.
Read More...Fabrication of CuSbS2 Solar Cells by Sulfurization of Thermally Evaporated Metal Stacks
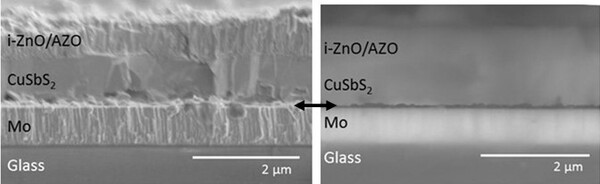
In this article, the authors created CuSbS2 solar cells. They discovered that the cells' efficiency was affected by the formation of MoS2. By incorporating a layer of single-walled carbon nanotubes, however, they were able to prevent MoS2 formation and increase the device's efficiency.
Read More...Biowaste to Biofuel: Using Methane-Producing Microorganisms Found in Soil Samples from Local Wetlands
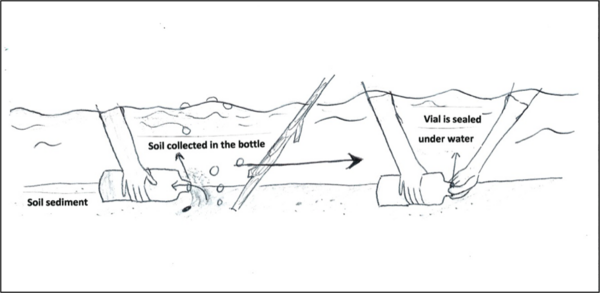
Methane is a naturally-occurring gas that could be utilized as a renewable source of energy. In this study, authors isolated microorganisms from the Puget Sound region that could produce methane biofuel from composted waste.
Read More...Innovative use of recycled textile fibers in building materials: A circular economy approach
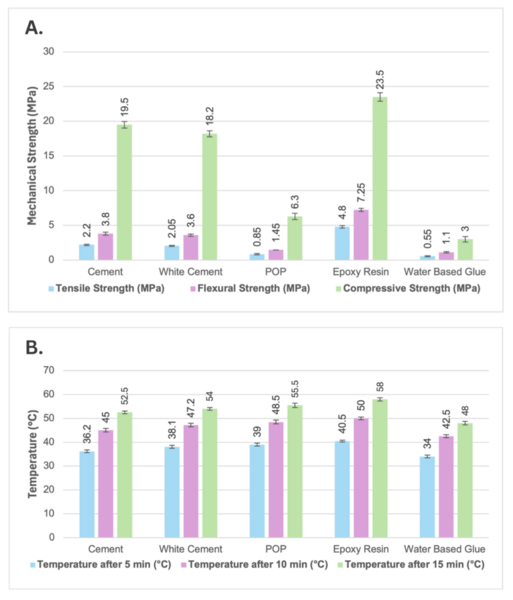
Textile waste from the fashion industry is a major environmental pollutant, but recycling waste into novel building material is a strategy to reduce the negative effects. This manuscript characterized five different binders that can be used to repurpose textile waste into bricks for construction purposes. Water-based glue, cement, white cement, plaster of Paris, and epoxy resin were mixed with shredded textile waste, and the mechanical characteristics and thermal insulation of each brick type were measured. Bricks with increased mechanical strength had the poorest thermal resistance, and the contrasting properties would suit different building purposes. This work provides a first step in generating recycled textile bricks for construction in a circular economy framework.
Read More...The effects of rocket travel and near-space environment on dried blood and blood plasma
Rethinking the electric vehicle tax policy: prioritizing affordable solutions for environmental impact
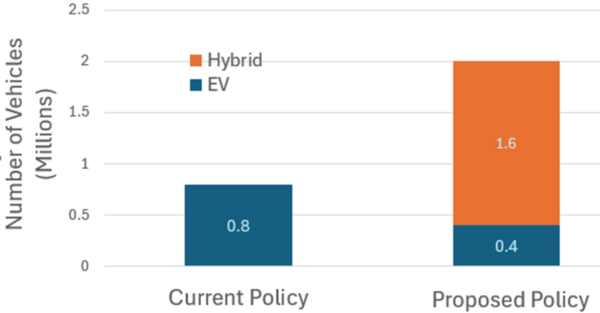
Car emissions harm both the environment and human health, and current U.S. EV tax credits mainly benefit high-income households because EVs are expensive. This study evaluates U.S. vehicle emissions policies by analyzing 2022 national vehicle data to compare the fuel economy and greenhouse gas impacts of the current EV tax credit with a proposed policy that incentivizes hybrid vehicle purchases.
Read More...Student work preferences: Typing or handwriting in the digital era
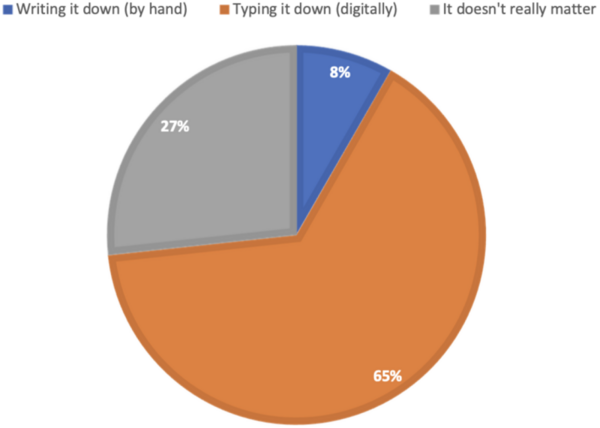
The authors survey high school students regarding preferences for taking notes by hand versus typing.
Read More...A systematic study of cut-resistant socks for hockey players
Quantifying natural recovery of dopamine deficits induced by chronic stress
Here the authors investigated the natural recovery of stress-induced dopamine-related gene deficits in C. elegans by measuring the expression of cat-2 (dopamine biosynthesis) and sod-2 (oxidative stress) following exposure to starvation or hydrocortisone. They found that the reversibility of sod-2 and the expression of cat-2 were highly dependent on the type and severity of the stressor, suggesting that the body's natural ability to recover from dopamine dysfunction has biological limitations.
Read More...Growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Escherichia coli when exposed to anti-acne vitamin A
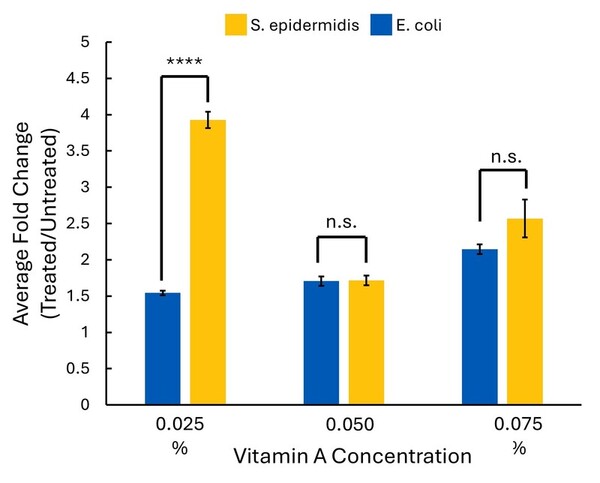
The authors looked at the impact of vitamin A (retinol) on growth of S. epidermidis (most abundant bacterium on the skin) and E. coli (found in the gut microbiome, but not on the skin).
Read More...